Abstract
1.The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product, p105Rb (RB), is an important regulator in the control of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Several cellular factors that complex with RB and exert their cellular regulatory functions have been identified, such as the RB:cyclophilin A (CypA) complex.
2.CypA is a cytoplasmic immunophilin and known for its involvement in T-cell differentiation and proliferation. Although CypA has a pivotal role in the immune response, its function in other signaling pathways is largely unknown.
3.In this study, we used a model of neuronal differentiation to demonstrate that the nuclear translocation of CypA, the appearance of hypophosphorylated RB and the enhancement of RB: CypA complex formation correlates with retinoic acid induced neuronal differentiation.
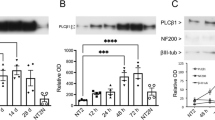
4.Inhibition of CypA expression results in repression of both the hypophosphorylated RB and the neuron-specific differentiation marker, class III β tubulin.
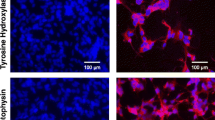
5.The evidence of enriched CypA and colocalization of RB with CypA in the nucleus of primary adult sensory neurons substantiated the important event of RB-mediated neuronal differentiation of p19 EC cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernards, R., Schackleford, G. M., Gerber, M. R., Horowitz, J. M., Friend, S. H., Schartl, M., Bogenmann, E., Rapaport, J. M., McGee, T., Dryja, T. P., and Weinberg, R. A. (1989). Structure and expression of the murine retinoblastoma gene and characterization of its encoded protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86:6474–6478.
Brehm, A., Miska, E. A., McCance, D. J., Reid, J. L., Bannister, A. J., and Kouzarides, T. (1998). Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription [see comments]. Nature 391:597–601.
Capano, M., Virji, S., and Crompton, M. (2002). Cyclophilin-A is involved in excitotoxin-induced caspase activation in rat neuronal B50 cells. Biochem J. 363:29–36.
Chen, L. I., Nishinaka, T., Kwan, K., Kitabayashi, I., Yokoyama, K., Fu, Y. H., Grünwald, S., and Chiu, R. (1994). The retinoblastoma gene product RB stimulates Sp1-mediated transcription by liberating Sp1 from a negative regulator. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:4380–4389.
Chen, P. L., Riley, D. J., Chen, Y., and Lee, W. H. (1996). Retinoblastoma protein positively regulates terminal adipocyte differentiation through direct interaction with C/EBPs. Genes Dev. 10:2794–2804.
Chen, P. L., Scully, P., Shew, J. Y., Wang, J. Y., and Lee, W. H. (1989). Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell 58:1193–1198.
Chen, T.-T., and Wang, J. Y. J. (2000). Establishment of irreversible growth arrest in myogenic differentiation requires the RB LXCXE-binding function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:5571–5580.
Colgan, J., Asmal, M., and Luban, J. (2000). Isolation, characterization and targeted disruption of mouse ppia: Cyclophilin A is not essential for mammalian cell viability. Genomics 68:167–178.
Cui, Y., Mirkia, K., Fu, Y.-H. F., Zhu, L., Yokoyama, K. K., and Chiu, R. (2002). Interaction of the retinoblastoma gene product, RB, with cyclophilin A negatively affects cyclosporin-inhibited NFAT signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 86:630–641.
Doyle, V., Virji, S., and Crompton, M. (1999). Evidence that cyclophilin-A protects cells against oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 341:127–132.
Flemington, E. K., Speck, S. H., and Kaelin, W. G., Jr. (1993). E2F-1-mediated transactivation is inhibited by complex formation with the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90:6914–6918.
Goldner, F. M., and Patrick, J. W. (1996). Neuronal localization of the cyclophilin A protein in the adult rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 372:283–293.
Gu, W., Schneider, J. W., Condorelli, G., Kaushal, S., Mahdavi, V., and Nadal-Ginard, B. (1993). Interaction of myogenic factors and the retinoblastoma protein mediates muscle cell commitment and differentiation. Cell 72:309–324.
Handschumacher, R. E., Harding, M. W., Rice, J., Drugge, R. J., and Speicher, D. W. (1984). Cyclophilin: A specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science 226:544–547.
Helin, K., Harlow, E., and Fattaey, A. (1993). Inhibition of E2F-1 transactivation by direct binding of the retinoblastoma protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13:6501–6508.
Hovland, A. R., La Rosa, F. G., Hovland, P. G., Cole, W. C., Kumar, A., Prasad, J. E., and Prasad, K. N. (1999). Cyclosporin A regulates the levels of cyclophilin A in neuroblastoma cells in culture. Neurochem. Intl. 35:229–235.
Jin, Z. G., Melaragno, M. G., Liao, D. F., Yan, C., Haendeler, J., Suh, Y. A., Lambeth, J. D., Berk, B. C. (2000). Cyclophilin A is a secreted growth factor induced by oxidative stress. Circ Res. 87:789–796.
Kim, S. J., Lee, H. D., Robbins, P. D., Busam, K., Sporn, M. B., and Roberts, A. B. (1991). Regulation of transforming growth factor beta 1 gene expression by the product of the retinoblastoma-susceptibility gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:3052–3056.
Kim, S. J., Onwuta, U. S., Lee, Y. I., Li, R., Botchan, M. R., and Robbins, P. D. (1992). The retinoblastoma gene product regulates Sp1-mediated transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:2455–2463.
Kim, J. S., Pirnia, F., Choi, Y. H., Nguyen, P. M., Knepper, B., Tsokos, M., Schulte, T. W., Birrer, M. J., Blagosklonny, M. V., Schaefer, O., Mushinski, J. F., and Trepel, J. B. (2000). Lovastatin induces apoptosis in a primitive neuroectodermal tumor cell line in association with RB down-regulation and loss of the G1 checkpoint. Oncogene 19:6082–6090.
Lee, E. Y., Hu, N., Yuan, S. S., Cox, L. A., Bradley, A., Lee, W. H., and Herrup, K. (1994). Dual roles of the retinoblastoma protein in cell cycle regulation and neuron differentiation. Genes Dev. 8:2008–2021.
Lee, M. K., Tuttle, J. B., Rebhun, L. I., Cleveland, D. W., and Frankfurter, A. (1990). The expression and posttranslational modification of a neuron-specific beta-tubulin isotype during chick embryogenesis. Cell Motil. Cytoskelton 17:118–132.
Lipinski, M. M., and Jacks, T. (1999). The retinoblastoma gene family in differentiation and development. Oncogene 18:7873–7882.
Liu, J., Farmer, J. D., Jr., Lane, W. S., Friedman, J., Weissman, I., and Schreiber, S. L. (1991). Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell 66:807–815.
MacLellan, W. R., Xiao, G., Abdellatif, M., and Schneider, M. D. (2000). A novel Rb-and p300-binding protein inhibits transactivation by MyoD. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:8903–8915.
Magnaghi-Jaulin, L., Groisman, R., Naguibneva, I., Robin, P., Lorain, S., Le Villain, J. P., Troalen, F., Trouche, D., and Harel-Bellan, A. (1998). Retinoblastoma protein represses transcription by recruiting a histone deacetylase [see comments]. Nature 391:601–605.
Matsuda, S., Moriguchi, T., Koyasu, S., and Nishida, E. (1998). T lymphocytes activation signals for Il-2 production involve activation of MKK6-p38 and MKK7-SAPK/JNK signaling pathways sensitive to cyclosporin A. J. Biol. Chem. 273:12378–12382.
Mattaj, I. W., and Englmeier, L. (1998). Nucleocytoplasmic transport: The soluble phase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67:265–306.
Nishinaka, T., Fu, Y. H., Chen, L. I., Yokoyama, K., and Chiu, R. (1997). A unique cathepsin-like protease isolated from CV-1 cells is involved in rapid degradation of retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product, RB, and transcription factor SP1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1351:274–286.
Nishitani, J., Nishinaka, T., Cheng, C. H., Rong, W., Yokoyama, K. K., and Chiu, R. (1999). Recruitment of the retinoblastoma protein to c-Jun enhances transcription activity mediated through the AP-1 binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 274:5454–5461.
Novitch, B. G., Mulligan, G. J., Jacks, T., and Lassar, A. B. (1996). Skeletal muscle cells lacking the retinoblastoma protein display defects in muscle gene expression and accumulate in S and G2 phases of the cell cycle. J. Cell Biol. 135:441–456.
Rey, O., Young, S., Cantrell, D., and Rozengurt, E. (2001). Rapid protein kinase D translocation in response to G protein-coupled receptor activation:dependence on protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 276:32616–32626.
Robertson, K. D., Ait-si-Ali, S., Yokochi, T., Wade, P. A., Jones, P. L., and Wolffe, A. P. (2000). DNMT1 forms a complex with Rb, E2F1 and HDAC1 and represses transcription from E2F-responsive promoters. Nat. Genet. 25:338–342.
Siegert, J. L., and Robbins, P. D. (1999). Rb inhibits the intrinsic kinase activity of TATA-binding protein-associated factor TAFII250. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:846–854.
Siegert, J. L., Rushton, J. J., Sellers, W. R., Kaelin, W. G., Jr., Robbins, P. D. (2000). Cyclin D1 suppresses retinoblastoma protein-mediated inhibition of TAFII250 kinase activity. Oncogene 19:5703–5711.
Slack, R. S., Hamel, P. A., Bladon, T. S., Gill, R. M., and McBurney, M. W. (1993). Regulated expression of the retinoblastoma gene in differentiating embryonal carcinoma cells. Oncogen 8:1585–1591.
Smith, D. S., and Skene, J. H. (1997). A transcription-dependent switch controls competence of adult neurons for distinct modes of axon growth. J. Neurosci. 17:646–658.
Stein, G. H., Beeson, M., and Gordon, L. (1990). Failure to phosphorylate the retinoblastoma gene product in senescent human fibroblasts. Science 249:666–669.
Szekely, L., Jiang, W. Q., Bulic-Jakus, F., Rosen, A., Ringertz, N., Klein, G., and Wiman, K. G. (1992). Cell type and differentiation dependent heterogeneity in retinoblastoma protein expression in SCID mouse fetuses. Cell Growth Differ. 3:149–156.
Tam, S. K. C., Gu, W., Mahdavi, V., and Nadal-Ginard, B. (1995). Cardiac myocyte terminal differentiation. Potential for cardiac regeneration. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 752:72–79.
Teruel, M. N., and Meyer, T. (2000). Translocation and reversible localization of signaling proteins: A dynamic future for signal transduction. Cell 103:181–184.
Twiss, J. L., Smith, D. S., Chang, B., and Shooter, E. M. (2000). Translational control of ribosomal protein L4 mRNA is required for rapid neurite regeneration. Neurobio. Disease 7:416–428.
Udvadia, A. J., Roger, K. T., Higgins, P. D., Murata, Y., Martin, K. H., Humphrey, P. A., and Horowitz, J. M. (1993). Sp-1 binds promoter elements regulated by the RB protein and Sp-1-mediated transcription is stimulated by RB coexpression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90:3265–3269.
Watanabe, Y., Watanabe, T., Kitagawa, M., Taya, Y., Nakayama, K., and Motoyama, N. (1999). pRb phosphorylation is regulated differentially by cyclin-dependent kinase CdK2 and Cdk4 in retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation of P19 cells. Brain Res. 842:342–350.
Yurchenko, V., Zybarth, G., O'Connor, M., Dai, W. W., Franchin, G., Hao, T., Guo, H., Hung, H. C., Toole, B., Gallay, P., Sherry, B., and Bukrinsky, M. (2002). Active site residues of cyclophilin A are crucial for its signaling activity via CD147. J. Biol. Chem. 277:22959–22965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, R., Rey, O., Zheng, JQ. et al. Effects of Altered Expression and Localization of Cyclophilin A on Differentiation of p19 Embryonic Carcinoma Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23, 929–943 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CEMN.0000005321.11544.cc
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CEMN.0000005321.11544.cc