Abstract
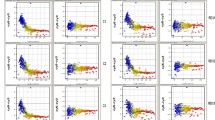
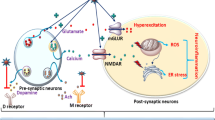
Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) may cause neurobehavioral changes. This study aimed to explore the underlying mechanism of PAH neurotoxicity in coal miners. Urinary PAH metabolites, neurotransmitters, and oxidative stress biomarkers of 652 coal miners were examined. Subjects were divided into high and low-exposure groups based on the median of total urinary PAH metabolites. Differentially expressed miRNAs were screened from 5 samples in the low-exposure group (≤ 4.88 μmol/mol Cr) and 5 samples in the high-exposure group (> 4.88 μmol/mol Cr) using microarray technology, followed by bioinformatics analysis of the potential molecular functions of miRNA target genes. Reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to validate differentially expressed miRNAs. Restricted cubic splines (RCS) were applied to assess the possible dose-response relationships. Compared to the low PAH exposure group, the high-exposure group had higher levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), epinephrine (E), and acetylcholine (ACh), and lower levels of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). 1-OHP had a dose-response relationship with malondialdehyde (MDA), dopamine (DA), 5-HT, and AChE (P for overall associations < 0.05). There were 19 differentially expressed microRNAs in microarray analysis, significantly enriched in the cell membrane, molecular binding to regulate transcription, and several signaling pathways such as PI3K-Akt. And in the validation stage, miR-885-5p, miR-20a-5p, and let-7i-3p showed differences in the low and high-exposure groups (P < 0.05). Changes in neurotransmitters and microRNA expression levels among the coal miners were associated with PAH exposure. Their biological functions are mainly related to the transcriptional regulation of nervous system diseases or signaling pathways of disorders. These findings provide new insights for future research of PAH neurotoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets applied throughout the present research are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
An J, Cai T, Che H et al (2014) The changes of miRNA expression in rat hippocampus following chronic lead exposure. Toxicol Lett 229(1):158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.06.002
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11(10):R106. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106
Blokland A (1995) Acetylcholine: a neurotransmitter for learning and memory? Brain Res Rev 21(3):285–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0173(95)00016-X
Bukke V, Archana M, Villani R et al (2020) The dual role of glutamatergic neurotransmission in Alzheimer’s disease: from pathophysiology to pharmacotherapy. Int J Mol Sci 21(20):7452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207452
Campo L, Rossella F, Pavanello S et al (2010) Urinary profiles to assess polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure in coke-oven workers. Toxicol Lett 192(1):72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.12.018
Cao L, Wang D, Zhu C et al (2020a) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in urban adults: the mediating role of oxidatively damaged DNA. Environ Pollut 265:114860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114860
Cao X, Li J, Cheng L et al (2020b) The associations between prenatal exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites, umbilical cord blood mitochondrial DNA copy number, and children’s neurobehavioral development. Environ Pollut 265:114594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114594
Cavalcante GL, Ferreira FN, da Silva MTB et al (2020) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition prevents alterations in cardiovascular autonomic control and gastric motility in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Life Sci 256:117915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117915
Cheng M, Wang B, Yang M et al (2020) microRNAs expression in relation to particulate matter exposure: a systematic review. Environ Pollut 260:113961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113961
Chepelev NL, Moffat ID, Bowers WJ et al (2015) Neurotoxicity may be an overlooked consequence of benzo[a]pyrene exposure that is relevant to human health risk assessment. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 764:64–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2015.03.001
Cherry N, Aklilu YA, Beach J et al (2019) Urinary 1-hydroxypyrene and skin contamination in firefighters deployed to the Fort McMurray Fire. Ann Work Expo Health 63(4):448–458. https://doi.org/10.1093/annweh/wxz006
Cho J, Sohn J, Noh J et al (2020) Association between exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and brain cortical thinning: The Environmental Pollution-Induced Neurological EFfects (EPINEF) study. Sci Total Environ 737:140097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140097
Costa LG, Cole TB, Coburn J et al (2017) Neurotoxicity of traffic-related air pollution. NeuroToxicology 59:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2015.11.008
Das SK, Aparna S, Patri M (2020) Chronic waterborne exposure to benzo[a]pyrene induces locomotor dysfunction and development of neurodegenerative phenotypes in zebrafish. Neurosci Lett 716:134646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134646
Deng QF, Dai XY, Feng W et al (2019) Co-exposure to metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, microRNA expression, and early health damage in coke oven workers. Environ Int 122:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.056
Falzone L, Lupo G, La Rosa GRM et al (2019) Identification of novel MicroRNAs and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in oral cancer. Cancers (Basel) 11(5):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050610
Ferrúa CP, Giorgi R, da Rosa LC et al (2019) MicroRNAs expressed in depression and their associated pathways: a systematic review and a bioinformatics analysis. J Chem Neuroanat 100:101650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2019.101650
Gizak A, Duda P, Pielka E et al (2020) GSK3 and miRNA in neural tissue: from brain development to neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Mol Cell Res 1867(7):118696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118696
Han F, Guo H, Hu J et al (2020) Sources and health risks of ambient polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China. Sci Total Environ 698:134229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134229
Hauser-Davis RA, Lopes RM, Ziolli RL et al (2019) Inihibition of mullet (M. liza) brain acetylcholinesterase activity by in vitro polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure. Mar Pollut Bull 140:30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.01.027
Inomata Y, Kajino M, Sato K et al (2012) Emission and atmospheric transport of particulate PAHs in Northeast Asia. Environ Sci Technol 46(9):4941–4949. https://doi.org/10.1021/es300391w
Kamal A, Qamar K, Gulfraz M et al (2015) PAH exposure and oxidative stress indicators of human cohorts exposed to traffic pollution in Lahore city (Pakistan). Chemosphere 120:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.021
Kotsyfakis M, Patelarou E (2019) MicroRNAs as biomarkers of harmful environmental and occupational exposures: a systematic review. Biomarkers 24(7):623–630. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750X.2019.1652348
Kuang D, Zhang W, Deng Q et al (2013) Dose-response relationships of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure and oxidative damage to DNA and lipid in coke oven workers. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):7446–7456. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401639x
Kuznetsova M, Wilson C, Hannan AJ et al (2020) How the enriched get richer? Experience-dependent modulation of microRNAs and the therapeutic effects of environmental enrichment. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 195:172940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172940
Liu Y, Tong S, Ding L et al (2019) Serum levels of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and multiple neurotransmitters: in relation to cognitive performance in Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment. Int J Geriatric Psychiatry 35(2):153–162. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.5222
Lizarraga D, Gaj S, Brauers KJ et al (2012) Benzo[a]pyrene-induced changes in microRNA-mRNA networks. Chem Res Toxicol 25(4):838–849. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx2003799
Lu J, Xu Y, Quan Z et al (2017) Dysregulated microRNAs in neural system: implication in pathogenesis and biomarker development in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 365:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.09.033
Magierski R, Sobow T (2016) Serotonergic drugs for the treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms in dementia. Expert Rev Neurother 16(4):375–387. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.2016.1155453
Mendes-Silva AP, Pereira KS, Tolentino-Araujo GT et al (2016) Shared biologic pathways between Alzheimer disease and major depression: a systematic review of microRNA expression studies. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 24(10):903–912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jagp.2016.07.017
Niu Q, Zhang H, Li FX, Li M et al (2010) Benzo[a]pyrene-induced neurobehavioral function and neurotransmitter alterations in coke oven workers. Occup Environ Med 67(7):444–448. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2009.047969
Novikova IN, Manole A, Zherebtsov EA et al (2020) Adrenaline induces calcium signal in astrocytes and vasoconstriction via activation of monoamine oxidase. Free Radic Biol Med 159:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.07.011
Petit P, Maître A, Persoons R et al (2019) Lung cancer risk assessment for workers exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in various industries. Environ Int 124:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.058
Polyakova EA, Zaraiskii MI, Mikhaylov EN et al (2020) Association of myocardial and serum miRNA expression patterns with the presence and extent of coronary artery disease: a cross-sectional study. Int J Cardiol 322:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.08.043
Shen H, Huang Y, Wang R et al (2013) Global atmospheric emissions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from 1960 to 2008 and future predictions. Environ Sci Technol 47(12):6415–6424. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400857z
Singh T, Yadav S (2020) Role of microRNAs in neurodegeneration induced by environmental neurotoxicants and aging. Ageing Res Rev 60:101068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101068
Song Y, Zhang Y, Li R et al (2020) The cellular effects of PM collected in Chinese Taiyuan and Guangzhou and their associations with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), nitro-PAHs and hydroxy-PAHs. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110225
Torma F, Gombos Z, Jokai M et al (2020) The roles of microRNA in redox metabolism and exercise-mediated adaptation. J Sport Health Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2020.03.004
Tsamou M, Nawrot TS, Carollo RM et al (2020) Prenatal particulate air pollution exposure and expression of the miR-17/92 cluster in cord blood: findings from the ENVIRONAGE birth cohort. Environ Int 142:105860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105860
Vaseghi S, Nasehi M, Zarrindast M (2020) How do stupendous cannabinoids modulate memory processing via affecting neurotransmitter systems? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.10.018
Wang F, Fangfang Z, Guo X et al (2017) Effects of volatile organic compounds and carbon monoxide mixtures on learning and memory, oxidative stress, and monoamine neurotransmitters in the brains of mice. Toxicol Ind Health 34(3):178–187. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233717747504
Wang F, Yang L, Zhang B et al (2020) Neurobehavioral performance of PAH exposure in male coal miners in Shanxi, China: a cross-sectional study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 93(6):707–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-020-01521-w
Wei C-W, Luo T, Zou S-S et al (2017) Research progress on the roles of microRNAs in governing synaptic plasticity, learning and memory. Life Sci 188:118–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.033
Wideman CE, Jardine KH, Winters BD (2018) Involvement of classical neurotransmitter systems in memory reconsolidation: focus on destabilization. Neurobiol Learn Mem 156:68–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2018.11.001
Xia Y, Cheng S, He J et al (2011) Effects of subchronic exposure to benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) on learning and memory, and neurotransmitters in male Sprague–Dawley rat. NeuroToxicology 32(2):188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2010.12.015
Yang K, Jiang X, Cheng S et al (2019) Synaptic dopamine release is positively regulated by SNAP-25 that involves in benzo[a]pyrene-induced neurotoxicity. Chemosphere 237:124378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124378
Yu Y, Zhang J, Jin Y et al (2018) MiR-20a-5p suppresses tumor proliferation by targeting autophagy-related gene 7 in neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell Int 18(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-017-0499-2
Zając J, Gomółka E, Szot W (2018) Urinary 1-hydroxypyrene in occupationally-exposed and non-exposed individuals in Silesia, Poland. Ann Agric Environ Med 25(4):625–629. https://doi.org/10.26444/aaem/75940
Zhang Q, Li Q, Ma J et al (2018) PM2.5 impairs neurobehavior by oxidative stress and myelin sheaths injury of brain in the rat. Environ Pollut 242:994–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.031
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the participants.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shanxi Basic Research Project [grant numbers 20210302123317] and the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 81502795].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by FW, TJ, YW, HH, YW, LC, GL, and XS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by FW and TJ. Project administration was written by FW. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The present study was approved by the ethics and human subject committees of Shanxi Medical University (approval 2015LL078).
Consent to participate
Each participant completed a written informed consent form.
Consent for publication
All the patients provided their informed consent for participation in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ludek Blaha
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Differential expression of miRNAs in coal miners exposed to different PAHs groups (N=10). (DOCX 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Jia, T., Wang, Y. et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure was associated with microRNA differential expression and neurotransmitter changes: a cross-sectional study in coal miners. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 14838–14848 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23230-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23230-2