Abstract
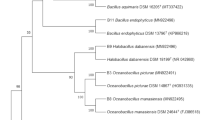
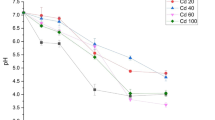
A salt-tolerant microbe strain JYZ-SD2 was investigated to develop biological soil amendments to stimulate salix growth and acclimation in costal salt-affected soils. The salt tolerance mechanism of strain JYZ-SD2 was investigated by detecting the salt-tolerant growth characteristics, biofilm formation, ion distribution, secondary metabolites, and zymogram profiling. The strain was identified by physiological and biochemical characteristics (Biolog), 16S rDNA sequencing, and cry1/7/9 gene expressing. With increasing of NaCl concentration, strain JYZ-SD2 adapted to the increased osmotic pressure by prolonging the retardation period, slowing down the growth rate of the logarithmic phase, increasing spo0A gene expression, increasing biofilm formation, reducing Na+ uptake, and changing the expression of metabolites and intracellular soluble proteins. The results showed that strain JYZ-SD2 could be assigned to Bacillus cereus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59(1):651–681
Nusrat N, Shahbaz M, Perveen S (2014) Modulation in growth, photosynthetic efficiency, activity of antioxidants and mineral ions by foliar application of glycine betaine on pea (Pisum sativum L.) under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 36(11):2985–2998
Mishra S, Upadhyay S, Shukla RK (2017) The role of strigolactones and their potential cross-talk under hostile ecological conditions in plants. Front Physiol 7:691
Ahmad AF, Iqbal A (2018) Plant growth promoting attributes and alleviation of salinity stress to wheat by biofilm forming, Brevibacterium sp. FAB3 isolated from rhizospheric soil. Saudi J Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.08.003
Vaidya S, Dev K, Sourirajan A (2018) Distinct osmoadaptation strategies in the strict halophilic and halotolerant bacteria isolated from lunsu salt water body of north west Himalayas. Curr Microbiol 75(7):888–895
Saum SH, Volker M (2010) Growth phase-dependent switch in osmolyte strategy in a moderate halophile:ectoine is a minor osmolyte but major stationary phase solute in Halobacillus halophilus. Environ Microbiol 10(3):716–726
Ivey DM, Guffanti AA, Bossewitch JS, Padan E, Krulwich TA (1991) Molecular cloning and sequencing of a gene from alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus OF4 that functionally complements an Escherichia coli strain carrying a deletion in the nhaA Na+/H+ antiporter gene. J Biol Chem 266(34):23483
Jiang J, Wang L, Zou Y, Lu W, Zhao B, Zhang B et al (1828) (2013) Identification of important charged residues for alkali cation exchange or pH regulation of NhaH, a Na+/H+ antiporter of Halobacillus dabanensis. BBA-Biomembranes 3:997–1003
Ritika K, Gupta MK, Kumar N, Kanwar S (2017) Analysis of nhaA gene from salt tolerant and plant growth promoting Enterobacter ludwigii. Rhizosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2017.07.002
Wei X, Fang L, Cai P, Huang Q, Chen H, Liang W et al (2011) Influence of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on Cd adsorption by bacteria. Environ Pollut 159(5):1369–1374
Kasim WA, Gaafar RM, Abou-Ali RM, Omar MN, Hewait HM (2016) Effect of biofilm forming plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on salinity tolerance in barley. J Agric Sci Cambridge 61:217–227
Dimkpa C, Weinand T, Asch F (2010) Plant–rhizobacteria interactions alleviate abiotic stress conditions. Plant Cell Environ 32(12):1682–1694
Castelijn GAA, Stijn VDV, Zwietering MH, Moezelaar R, Abee T (2012) Diversity in biofilm formation and production of curli fimbriae and cellulose of Salmonella, typhimurium strains of different origin in high and low nutrient medium. Biofouling 28(1):51–63
Gao T, Foulston L, Chai Y, Wang Q, Losick R (2015) Alternative modes of biofilm formation by plant-associated Bacillus cereus. Microbiology Open 4(3):452–464
Lucking G, Dommel MK, Scherer S, Fouet A, Ehling-Schulz M (2009) Cereulide synthesis in emetic Bacillus cereus is controlled by the transition state regulator abrb, but not by the virulence regulator plcr. Microbiology 155(3):922–931
Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (1974) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th edn. The William & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 729–759
Li GE, Wu XQ, Ye J-R (2013) Isolation and identification of phytate-degrading rhizobacteria with activity of improving growth of poplar and masson pine. World J Microb Biotechnol 29(11):2181–2193
Frank JA, Reich CI, Sharma S, Weisbaum JS, Wilson BA, Olsen GJ (2008) Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(8):2461–2470
Kuo WS, Chak KF (1996) Identification of novel cry-type genes from Bacillus thuringiensis strains on the basis of restriction fragment length polymorphism of the PCR-amplified DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(4):1369–1377
Zeng Q, Wu X, Wen X (2016) Identification and characterization of the rhizosphere phosphate-solubilizing bacterium Peudomonas frederiksbergensis JW-SD2, and its plant growth-promoting effects on poplar seedlings. Ann Microbiol 66(4):1343–1354
Sadeghi A, Soltani BM, Nekouei MK, Jouzani GS, Mirzaei HH, Sadeghizadeh M (2014) Diversity of the ectoines biosynthesis genes in the salt tolerant streptomyces and evidence for inductive effect of ectoines on their accumulation. Microbiol Res 169(9–10):699–708
Shivanand P, Mugeraya G (2011) Halophilic bacteria and their compatible solutes—osmoregulation and potential applications. Curr Sci India 100(10):25–2011
Dow JM, Ryan P (2008) Diffusible signals and interspecies communication in bacteria. Microbiology 154(7):1845
Morikawa M (2006) Beneficial biofilm formation by industrial bacteria Bacillus subtilis and related species. J Biosci Bioeng 101(1):1–8
Zeng Q, Wu X, Wen X (2016) Effects of soluble phosphate on phosphate-solubilizing characteristics and expression of gcd gene in Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis JW-SD2. Curr Microbiol 72(2):198–206
Park EJ, Hussain MS, Wei S, Kwon M (2019) Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of biofilm formation of emetic toxin producing Bacillus cereus strains. Food Control 96:527–534
Widderich N, Rodrigues C, Commichau F, Fischer K, Ramirez-Guadiana FH, Rudner DZ et al (2016) Salt-sensitivity of σH and Spo0A prevents sporulation of Bacillus subtilis at high osmolarity avoiding death during cellular differentiation. Mol Microbiol. 100(1):108–124
Waheed QA, Nasim SA (2012) Bacterial exopolysaccharide and biofilm formation stimulate chickpea growth and soil aggregation under salt stress. Braz J Microbiol 43(3):1183–1191
Li J, Xu H, Chen X, Xu L, Cheng R, Zhang J et al (2017) Characterization of an exopolysaccharide with distinct rheological properties from, Paenibacillus edaphicusnust16. Int J Biol Macromol 105(1):1–8
Kaluzhnaya M, Khmelenina V, Eshinimaev B, Suzina N, Nikitin D, Solonin A et al (2001) Taxonomic characterization of new alkaliphilic and alkalitolerant methanotrophs from soda lakes of the southeastern transbaikal region and description of Methylomicrobium buryatense sp nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 24(2):166–176
Taketo K, Soichi F, Naoki N, Chisato H et al (2009) Biofilm formation by Escherichia coli in hypertonic sucrose media. J Biosci Bioeng 107(6):630–635
Southworth TW, Guffanti AA, Moir A, Krulwich TA (2001) Gern, an endospore germination protein of Bacillus cereus, is an Na+/H+-K+ antiporter. J Bacteriol 183(20):5896–5903
Roeßler M, Müller V (1998) Quantitative and physiological analyses of chloride dependence of growth of Halobacillus halophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(10):3813
Chen Z, Pan X, Chen H, Guan X, Lin Z (2015) Biomineralization of pb(ii) into pb-hydroxyapatite induced by Bacillus cereus 12–2 isolated from lead-zinc mine tailings. J Hazardous Mater 301:531–537
Karunakaran E, Biggs CA (2011) Mechanisms of Bacillus cereus biofilm formation: an investigation of the physicochemical characteristics of cell surfaces and extracellular proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(4):1161–1175
Fang H, Hu B, Nie Y, Tang YQ, Wu XL (2017) The complete genome of Dietzia timorensis id05-a0528(t) revealed the genetic basis for its saline-alkali tolerance. J Biotechnol 241:11–13
Lu W, Zhang B, Zhao B et al (2007) Cloning and characterization of the genes encoding a glycine betaine ABC-type transporter in Halobacillus trueperi DSM10404T. Curr Microbiol 54(2):124–130
Li FY, Ju QJ, Bai SZ, Bo Z (2006) A Na+/H+ antiporter gene of the moderately halophilic bacterium Halobacillus dabanensis D-8T. FEMS Microbiol Lett 255(1):89–95
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFD0600100) and the Priority Academic Development Program of Jiangsu Universities (PAPD). I am grateful to Dr. Prof. Eric C. Brevik, Dickinson State University, for his kind improving this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors hereby declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Ty., Wu, XQ., Xu, Xq. et al. Salt Tolerance Mechanism and Species Identification of the Plant Rhizosphere Bacterium JYZ-SD2. Curr Microbiol 77, 388–395 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01835-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01835-0