Abstract
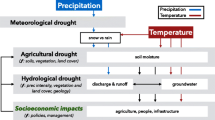
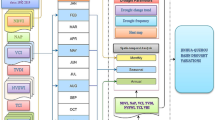
Drought indices are useful for quantifying drought severity and have shown mixed success as an indicator of drought damage and biophysical dryness. While spatial downscaling of drought indicators from the climate divisional level to the county level has been conducted successfully in previous work, little research to date has attempted to “upscale” remotely sensed biophysical indicators to match the downscaled drought indices. This upscaling is important because drought damage and indices are often reported at a coarser scale than the biophysical indicators provide. This research upscales National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer sensor-acquired Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) data to produce a county-level biophysical drought index, for a five-state region of the South Central United States. The county-level NDVI is then correlated with the downscaled drought indices for assessing the degree to which the biophysical data match well-documented drought indicators. Results suggest that the Palmer Drought Severity Index and Palmer Hydrologic Drought Index are effective indicators of biophysical drought in much of the arid western part of the study area and in larger swaths of the study area in summer. In nearly all cases except for autumn months, correlations are weakest in the ecotones, with significant negative correlations in the humid eastern part of the study area. Results generally corroborate the findings of recent research that correlations between drought indices and biophysical drought vary spatially. As long-lead climate forecasts continue to improve, these results can assist environmental planners in preparing for the impacts of drought.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali M, Deo RC, Downs NJ, Maraseni T (2018) An ensemble-ANFIS based uncertainty assessment model for forecasting multi-scalar standardized precipitation index. Atmos Res 207:155–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.02.024
Alley WM (1984) Palmer Drought Severity Index: limitations and assumptions. J Clim Appl Meteorol 23:1100–1109. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1984)023<1100:TPDSIL>2.0.CO;2
Barua S, Ng A, Perera B (2010) Comparative evaluation of drought indexes: case study on the Yarra River catchment in Australia. J Water Resour Plan Manag 137:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000105
Beguería S, Vicente-Serrano SM, Reig F, Latorre B (2014) Standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) revisited: parameter fitting evapotranspiration models, tools, datasets and drought monitoring. Int J Clim 34:3001–3023. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3887
Bhuiyan C, Singh RP, Kogan FN (2006) Monitoring drought dynamics in the Aravalli region (India) using different indices based on ground and remote sensing data. Int J Appl Earth Obs 8:289–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2006.03.002
Brown JF, Wardlow BD, Tadesse T, Hayes MJ, Reed BC (2008) The vegetation drought response index (VegDRI): a new integrated approach for monitoring drought stress in vegetation. GISci Remote Sens 45:16–46. https://doi.org/10.2747/1548-1603.45.1.16
Carrao H, Naumann G, Barbosa P (2016) Mapping global patterns of drought risk: an empirical framework based on sub-national estimates of hazard, exposure and vulnerability. Global Environ Change 39:108–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.04.012
Dai A, Trenberth KE, Qian T (2004) A global dataset of Palmer Drought Severity Index for 1870–2002: relationship with soil moisture and effects of surface warming. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 5:1117–1130. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-386.1
Dembélé M, Zwart SJ (2016) Evaluation and comparison of satellite-based rainfall products in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Int J Remote Sens 37:3995–4014. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1207258
Edossa DC, Woyessa YE, Welderufael WA (2016) Spatiotemporal analysis of droughts using self-calibrating Palmer’s Drought Severity Index in the central region of South Africa. Theor Appl Climatol 126:643–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1604-x
Esri (2012) ArcGIS desktop: release 10.1. Environmental System Research Institute, Redlands, CA
Esri (2016) ArcGIS desktop: release 10.4. Environmental System Research Institute, Redlands, CA
Guttman NB (1991) Sensitivity of the Palmer Hydrologic Drought Index. Water Resour Bull 27:797–807. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1991.tb01478.x
Guttman NB (1997) Comparing the Palmer Drought Index and the Standardized Precipitation Index. J Am Water Resour As 34:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05964.x
Guttman NB (1999) Accepting the standardized precipitation index: a calculation algorithm. J Am Water Resour As 35:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1999.tb03592.x
Guttman NB, Wallis JR, Hosking JRM (1992) Spatial comparability of the Palmer Drought Severity Index. Water Resour Bull 28:1111–1119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1992.tb04022.x
Hayes MJ, Svodoba MD, Wilhite DA, Vanyarkho OV (1999) Monitoring the 1996 drought using the standardized precipitation index. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 80:429–438. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1999)080<0429:MTDUTS>2.0.CO;2
Hayes M, Svoboda M, Wall N, Widhalm M (2011) The Lincoln Declaration on drought indices: universal meteorological drought index recommended. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 92:485–488. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010BAMS3103.1
Herman A, Kumar VB, Arkin PA, Kousky JV (1997) Objectively determined 10-day African rainfall estimates created for famine early warning systems. Int J Remote Sens 18:2147–2159. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311697217800
Hou Y, Niu ZM, Zheng F, Wang NA, Wang JY, Li ZL, Chen HX, Zhang XM (2016) Drought fluctuations based on dendrochronology since 1786 for the Lenglongling Mountains at the northwestern fringe of the East Asian summer monsoon region. J Arid Land 8:492–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-016-0009-8
Ionita M, Scholz P, Chelcea S (2016) Assessment of droughts in Romania using the Standardized Precipitation Index. Nat Hazards 81:1483–1498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-2141-8
Karl TR (1983) Some spatial characteristics of drought duration in the United States. J Clim Appl Meteorol 22:1356–1366. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1983)022<1356:SSCODD>2.0.CO;2
Karl TR (1986) The sensitivity of the Palmer Drought Severity Index and Palmer’s Z-Index to their calibration coefficients including potential evapotranspiration. J Clim Appl Meteorol 25:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1986)025<0077:TSOTPD>2.0.CO;2
Keyantash J, Dracup JA (2002) The quantification of drought: an evaluation of drought indices. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83:1167–1180. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477-83.8.1167
Keyantash J, National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff (eds) (2016) Last modified 02 Mar 2016. The climate data guide: Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI). Retrieved from https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/standardized-precipitation-index-spi. Accessed 06 Aug 2018
Khan MI, Liu D, Fu Q, Faiz MA (2018) Detecting the persistence of drying trends under changing climate conditions using four meteorological drought indices. Meteorol Appl 25:184–194. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1680
Lewinska KE, Ivits E, Schardt M, Zebisch M (2016) Alpine forest drought monitoring in South Tyrol: PCA based synergy between scPDSI data and MODIS derived NDVI and NDII7 timer series. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8080639
Liu Y, Yang XL, Ren LL, Yuan F, Jiang SH, Ma MW (2015) A new physically based self-calibrating Palmer Drought Severity Index and its performance evaluation. Water Resour Manag 29:4833–4847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1093-9
Liu Y, Ren L, Hong Y, Zhu Y, Kiaoli Yang, Yua F, Jiang S (2016) Sensitivity analysis of standardization procedures in drought indices to varied input data selections. J Hydrol 538:817–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.04.073
Liu M, Xu X, Sun AY, Wang KL (2017) Decreasing spatial variability of drought in southwest China during 1959–2013. Int J Climatol 37:4610–4619. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5109
Liu ZY, Zhang X, Fang RH (2018) Multi-scale linkages of winter drought variability to ENSO and the Arctic Oscillation: a case study in Shaanxi, North China. Atmos Res 200:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.10.012
McKee TB, Doeskin NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In: Proceedings 8th conference on applied climatology, 17–22 Jan 1993. American Meteorological Society, Boston, MA, pp 179–184
McKee TB, Doeskin NJ, Kleist J (1995) Drought monitoring with multiple time scales. In: Proceedings 9th conference on applied climatology, 14–20 Jan 1995. American Meteorological Society, Boston, MA, pp 233–236
Meshram SG, Gautam R, Kahya E (2018) Drought analysis in the Tons River Basin, India during 1969–2008. Theor Appl Climatol 132:939–951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2129-2
Mihunov VV, Lam NSN, Zou L, Rohli RV, Bushra N, Reams MA, Argote JE (2018) Community resilience to drought hazard in the south-central United States. Ann Am As Geogr 108:739–755. https://doi.org/10.1080/24694452.2017.1372177
Murthy CS, Singh J, Kumar P, Sesha Sai MVR (2016) Meteorological drought analysis over India using analytical framework on CPC rainfall time series. Nat Hazards 81:573–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-2097-8
Nam WH, Tadesse T, Wardlow BD, Hayes MJ, Svoboda MD, Hong EM, Pachepsky YA, Jang MW (2018) Developing the vegetation drought response index for South Korea (VegDRI-SKorea) to assess the vegetation condition during drought events. Int J Remote Sens 39:1548–1574. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2017.1407047
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (2013). http://www1.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/data/sds/cdr/CDRs/Normalized%20Difference%20Vegetation%20Index/AlgorithmDescription.pdf. Accessed 06 Aug 2018
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (2017). https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/metaview/page?xml=NOAA/NESDIS/NCDC/Geoportal/iso/xml/C00683.xml&view=getDataView&header=none. Accessed 06 Aug 2018
Otkin JA, Anderson MC, Hain C, Svoboda M, Johnson D, Mueller R, Tadesse T, Wardlow B, Brown J (2016) Assessing the evolution of soil moisture and vegetation conditions during the 2012 United States flash drought. Agric For Meteorol 218:230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.12.065
Palmer WC (1965) Meteorological drought. U.S. Weather Bureau Research Paper 45, 65 pp
Park J, Lim Y-J, Kim B-J, Sung JH (2018) Appraisal of drought characteristics of representative drought indices using meteorological variables. KSCE J Civ Eng 22:2002–2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1744-x
Ramkar P, Yadav SM (2018) Spatiotemporal drought assessment of a semi-arid part of middle Tapi River Basin, India. Int J Dis Risk Reduct 28:414–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2018.03.025
Rhee J, Im J, Carbone GJ (2010) Monitoring agricultural drought for arid and humid regions using multi-sensor remote sensing data. Remote Sens Environ 114:2875–2887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2010.07.005
Riebsame WE, Changnon SA, Karl TR (1991) Drought and natural resources management in the United States: impacts and implications of the 1987─89 drought. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Rohli RV, Bushra N, Lam NSN, Zou L, Mihunov V, Reams MA, Argote JE (2016) Drought indices as drought predictors in the south-central United States. Nat Hazards 83:1567–1582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2376-z
Shafer BA, Dezman LE (1982) Development of a surface water supply index (SWSI) to assess the severity of drought conditions in snowpack runoff areas. In: Proceedings 50th annual western snow conference, Reno, NV, Western Snow Conference, pp 164–175
Shin JY, Chen S, Lee J-H, Kim TW (2018) Investigation of drought propagation in South Korea using drought index and conditional probability. Terr Atmos Ocean Sci 29:231–241. https://doi.org/10.3319/TAO.2017.08.23.01
Stahle DW, Cook ER, Burnette DJ, Villanueva J, Cerano J, Burns JN, Griffin D, Cook BI, Acuna R, Torbenson MCA, Szejner P, Howard IM (2016) The Mexican drought atlas: tree-ring reconstructions of the soil moisture balance during the late pre-Hispanic, colonial, and modern eras. Quat Sci Rev 149:34–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.06.018
Tadesse T, Wardlow BD, Brown JF, Svoboda MD, Hayes MJ, Fuchs B, Gutzmer D (2015) Assessing the vegetation condition impacts of the 2011 drought across the U.S. southern Great Plains using the vegetation drought response index (VegDRI). J Appl Meteorol Clim 54:153–169. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-14-0048.1
Thenkabail PS (ed) (2016) Remote sensing of water resources, disasters, and urban studies. Remote sensing handbook, vol III. TCRC Press, Boca Raton
United States Geological Survey (USGS) (2017). https://landsat.usgs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/si_product_guide.pdf. Accessed 06 Aug 2018
van der Schrier G, Barichivich J, Briffa KR, Jones PD (2013) A scPDSI-based global data set of dry and wet spells for 1901–2009. J Geophys Res-Atmos 118:4025–4048. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50355
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, Lόpez-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23:1696–1718. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI2909.1
Vicente-Serrano SM, Schrier GV, Beguería S, Azorin-Molina C, Lopez-Moreno J (2015) Contribution of precipitation and reference evapotranspiration to drought indices under different climates. J Hydrol 526:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.11.025
Wang H, Pan Y, Chen Y (2017) Comparison of three drought indices and their evolutionary characteristics in the arid region of northwestern China. Atmos Sci Lett 18:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1002/asl.735
Wu J, Zhou L, Liu M, Zhang J, Leng S, Diao CY (2013) Establishing and assessing the Integrated Surface Drought Index (ISDI) for agricultural drought monitoring in mid-eastern China. Int J Appl Earth Obs 23:397–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2012.11.003
Yacoub E, Tayfur G (2017) Evaluation and assessment of meteorological drought by different methods in Trarza Region, Mauritania. Water Resour Manag 31:825–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1510-8
Yang Q, Li MX, Zheng ZY (2017) Regional applicability of seven meteorological drought indices in China. Sci China Earth Sci 60:745–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-016-5133-5
Yang P, Xia J, Zhang YY, Zhan CS, Qiao YF (2018) Comprehensive assessment of drought risk in the arid region of northwest China based on the global Palmer Drought Severity Index gridded data. Sci Total Environ 627:951–962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.234
Zarei AR, Moghimi MM, Mahmoudi MR (2016) Analysis of changes in spatial pattern of drought using RDI index in south of Iran. Water Res Manag 30:3723–3743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1380-0
Zargar A, Sadiq R, Naser B, Khan FI (2011) A review of drought indices. Environ Rev 19:333–349. https://doi.org/10.1139/A11-013
Zhang XQ, Yamaguchi Y (2014) Characterization and evaluation of MODIS-derived Drought Severity Index (DSI) for monitoring the 2009/2010 drought over southwestern China. Nat Hazards 74:2129–2145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1278-1
Zhang WJ, Lu QF, Gao ZQ, Peng J (2008) Response of remotely sensed normalized difference water deviation index to the 2006 drought of eastern Sichuan basin. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 51:124–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-008-0037-0
Zhang L, Xiao JF, Zhou Y, Zheng Y, Li J, Xiao H (2016) Drought events and their effects on vegetation productivity in China. Ecosphere. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.1591
Zhang LF, Jiao WZ, Zhang HM, Huang CP, Tong QX (2017) Studying drought phenomena in the continental United States in 2011 and 2012 using various drought indices. Remote Sens Environ 190:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.12.010
Zhao H, Gao G, An W, Zou X, Li H, Hou M (2017) Timescale differences between SC-PDSI and SPEI for drought monitoring in China. Phys Chem Earth 102:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2015.10.022
Acknowledgements
This material is based on work supported by a research grant from the United States Geological Survey/South Central Climate Science Center (Award No. G14AP00087). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bushra, N., Rohli, R.V., Lam, N.S.N. et al. The relationship between the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index and drought indices in the South Central United States. Nat Hazards 96, 791–808 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03569-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03569-5