Abstract
Advancing the understanding of stability behavior and aggregation mechanisms of quantum dot (QD) nanoparticles in natural systems is fundamental to elucidate their fate and transport, bioavailability, environmental toxicity, and subsequent risks to environmental and public health. This study investigates the aggregation kinetics and colloidal stability of QDs as a function of pH and organic ligands—acetate, oxalate, and citrate. Results indicated an influence of solution chemistry upon both the aggregation kinetics and colloidal stability of QDs. The zeta potential of QDs, with a point of zero charge (pHPZC) between pH 1.5 and 3.5, decreased (from positive to negative) with increasing solution pH. The diameter of QD aggregates was ~500 nm in the region of pHPZC and decreased with pH when pH > pHPZC to 40–50 nm. Organic ligands enhanced the negative zeta potentials of QDs at pH = 1.5 and pH = 3.5. The impact of ligands on the levels and rates of aggregation was pH dependent; furthermore, the presence of ligands increased the diameters of all QD nanoaggregates at pH 3.5 (e.g., 817 nm for 0.001 M citrate). QDs and organic ligand-QD nanoparticle complexes remained stable across pH values 5–9. In terms of environmental and toxicological risk assessments, results revealed that QDs and organic ligand-QD nanoparticle complexes remain stable across a significant range of pH values (5–9), indicating that this stability behavior could enhance the mobility, transport, and residence time of QDs in terrestrial and aqueous environments, and facilitate the bioavailability of QDs, therefore augmenting the adverse effects of QDs in the environment.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshinnia K, Marrone B, Baalousha M (2018) Potential impact of natural organic ligands on the colloidal stability of silver nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 625:1518–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.299
Akaighe N, MacCuspie RI, Navarro DA, Aga DS, Banerjee S, Sohn M, Sharma VK (2011) Humic acid-induced silver nanoparticle formation under environmentally relevant conditions. Environ Sci Technol 45:3895–3901. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103946g
Akaighe N, Depner SW, Banerjee S, Sharma VK, Sohn M (2012) The effects of monovalent and divalent cations on the stability of silver nanoparticles formed from direct reduction of silver ions by Suwannee River humic acid/natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 441:277–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.09.055
Akaighe N, Depner SW, Banerjee S, Sohn M (2013) Transport and deposition of Suwannee River humic acid/natural organic matter formed silver nanoparticles on silica matrices: the influence of solution pH and ionic strength. Chemosphere 92:406–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.12.077
Akturk O (2020) Colloidal stability and biological activity evaluation of microbial exopolysaccharide Levan-capped gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 192:111061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111061
Albanese A, Tang PS, Chan WCW (2012) The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 14:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071811-150124
Alderighi L, Gans P, Ienco A, Peters D, Sabatini A, Vacca A (1999) Hyperquad simulation and speciation (HySS): a utility program for the investigation of equilibria involving soluble and partially soluble species. Coord Chem Rev 184:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-8545(98)00260-4
Anikeeva PO, Halpert JE, Bawendi MG, Bulović V (2009) Quantum dot light-emitting devices with electroluminescence tunable over the entire visible spectrum. Nano Lett 9:2532–2536. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl9002969
Arenas-Lago D, Monikh FA, Vijver MG, Peijnenburg WJGM (2019) Dissolution and aggregation kinetics of zero valent copper nanoparticles in (simulated) natural surface waters: simultaneous effects of pH, NOM and ionic strength. Chemosphere 226:841–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.190
Baalousha M (2009) Aggregation and disaggregation of iron oxide nanoparticles: influence of particle concentration, pH and natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 407:2093–2101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.11.022
Baalousha M, Manciulea A, Cumberland S, Kendall K, Lead JR (2008) Aggregation and surface properties of iron oxide nanoparticles: influence of pH and natural organic matter. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1875–1882. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-559.1
Baalousha M, Nur Y, Römer I, Tejamaya M, Lead JR (2013) Effect of monovalent and divalent cations, anions and fulvic acid on aggregation of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 454-455:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.093
Badawy AME, Luxton TP, Silva RG, Scheckel KG, Suidan MT, Tolaymat TM (2010) Impact of environmental conditions (pH, ionic strength, and electrolyte type) on the surface charge and aggregation of silver nanoparticles suspensions. Environ Sci Technol 44:1260–1266. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902240k
Bagalkot V, Zhang L, Levy-Nissenbaum E, Jon S, Kantoff PW, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2007) Quantum dot−aptamer conjugates for synchronous cancer imaging, therapy, and sensing of drug delivery based on bi-fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Nano Lett 7:3065–3070. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl071546n
Bai L, Li C, Korte C, Huibers BMJ, Pales AR, Liang W-Z, Ladner D, Daigle H, Darnault CJG (2017) Effects of silica-based nanostructures with raspberry-like morphology and surfactant on the interfacial behavior of light, medium, and heavy crude oils at oil-aqueous interfaces. Appl Nanosci 7:947–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0630-7
Batley GE, Kirby JK, McLaughlin MJ (2013) Fate and risks of nanomaterials in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Acc Chem Res 46:854–862. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar2003368
Baun A, Hartmann NB, Grieger K, Kusk KO (2008) Ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to aquatic invertebrates: a brief review and recommendations for future toxicity testing. Ecotoxicology 17:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0208-y
Baveye P, Laba M (2008) Aggregation and toxicology of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Health Perspect 116:A152–A152. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10915
Beaton GC, Bottomley AJ, Prezgot D, Ianoul A, Stamplecoskie KG (2020) Shape control of silver nanoparticles and their stability on Al2O3. J Mater Chem C 8:10755–10760. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tc01280g
Becker-Koch D, Albaladejo-Siguan M, Lami V, Paulus F, Xiang HY, Chen ZY, Vaynzof Y (2020) Ligand dependent oxidation dictates the performance evolution of high efficiency PbS quantum dot solar cells. Sustain Energy Fuels 4:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9se00602h
Bian S-W, Mudunkotuwa IA, Rupasinghe T, Grassian VH (2011) Aggregation and dissolution of 4 nm ZnO nanoparticles in aqueous environments: influence of pH, ionic strength, size, and adsorption of humic acid. Langmuir 27:6059–6068. https://doi.org/10.1021/la200570n
Bottrill M, Green M (2011) Some aspects of quantum dot toxicity. Chem Commun 47:7039–7050. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CC10692A
Brandeburova P, Grencikova A, Mackul'ak T (2019) Nanoparticles and their ecotoxic effects on the environment. Chem List 113:97–103
Breza M, Simon P (2020) On shape dependence of the toxicity of rutile nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 22:58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-4773-1
Bundschuh M et al (2019) Nanoparticles transported from aquatic to terrestrial ecosystems via emerging aquatic insects compromise subsidy quality. Sci Rep 9:15676. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52096-7
Celiz MD, Colón LA, Watson DF, Aga DS (2011) Study on the effects of humic and fulvic acids on quantum dot nanoparticles using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Environ Sci Technol 45:2917–2924. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1031097
Chekli L, Phuntsho S, Roy M, Shon HK (2013) Characterisation of Fe-oxide nanoparticles coated with humic acid and Suwannee River natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 461-462:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.083
Chekli L, Phuntsho S, Tijing LD, Zhou JL, Kim JH, Shon HK (2014) Stability of Fe-oxide nanoparticles coated with natural organic matter under relevant environmental conditions. Water Sci Technol 70:2040–2046. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.454
Chen KL, Elimelech M (2007) Influence of humic acid on the aggregation kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolyte solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 309:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.01.074
Chen KL, Elimelech M (2008) Interaction of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles with humic acid and alginate coated silica surfaces: measurements, mechanisms, and environmental implications. Environ Sci Technol 42:7607–7614. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8012062
Chen KL, Mylon SE, Elimelech M (2006) Aggregation kinetics of alginate-coated hematite nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolytes. Environ Sci Technol 40:1516–1523. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0518068
Chen Y, Thakar R, Snee PT (2008) Imparting nanoparticle function with size-controlled amphiphilic polymers. J Am Chem Soc 130:3744–3745. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja711252n
Chen M, Yin H, Bai P, Miao P, Deng X, Xu Y, Hu J, Yin J (2016) ABC transporters affect the elimination and toxicity of CdTe quantum dots in liver and kidney cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 303:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2016.04.017
Choi SH, Kim DH, Raghu AV, Reddy KR, Lee HI, Yoon KS, Jeong HM, Kim BK (2012) Properties of graphene/waterborne polyurethane nanocomposites cast from colloidal dispersion mixtures. J Macromol Sci B 51:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2011.583193
Clarke SJ, Hollmann CA, Zhang Z, Suffern D, Bradforth SE, Dimitrijevic NM, Minarik WG, Nadeau JL (2006) Photophysics of dopamine-modified quantum dots and effects on biological systems. Nat Mater 5:409–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1631
Conway JR, Adeleye AS, Gardea-Torresdey J, Keller AA (2015) Aggregation, dissolution, and transformation of copper nanoparticles in natural waters. Environ Sci Technol 49:2749–2756. https://doi.org/10.1021/es504918q
Courtois P, Rorat A, Lemiere S, Guyoneaud R, Attard E, Levard C, Vandenbulcke F (2019) Ecotoxicology of silver nanoparticles and their derivatives introduced in soil with or without sewage sludge: a review of effects on microorganisms, plants and animals. Environ Pollut 253:578–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.053
Döllefeld H, Hoppe K, Kolny J, Schilling K, Weller H, Eychmüller A (2002) Investigations on the stability of thiol stabilized semiconductor nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 4:4747–4753. https://doi.org/10.1039/B202101C
Dollo G, Boucaud Y, Amela-Cortes M, Molard Y, Cordier S, Brandhonneur N (2020) PLGA nanoparticles embedding molybdenum cluster salts: influence of chemical composition on physico-chemical properties, encapsulation efficiencies, colloidal stabilities and in vitro release. Int J Pharm 576:119025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119025
Domingos RF, Tufenkji N, Wilkinson KJ (2009) Aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: role of a fulvic acid. Environ Sci Technol 43:1282–1286. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8023594
Dunphy Guzman KA, Finnegan MP, Banfield JF (2006) Influence of surface potential on aggregation and transport of titania nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 40:7688–7693. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060847g
Echeverria C, Peppas NA, Mijangos C (2012) Novel strategy for the determination of UCST-like microgels network structure: effect on swelling behavior and rheology. Soft Matter 8:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1SM06489D
Elimelech M, Gregory J, Jia X, Williams RA (1998) Particle deposition and aggregation: measurement, modelling and simulation. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Erhayem M, Sohn M (2014) Stability studies for titanium dioxide nanoparticles upon adsorption of Suwannee River humic and fulvic acids and natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 468-469:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.038
Fernando I, Zhou Y (2019) Impact of pH on the stability, dissolution and aggregation kinetics of silver nanoparticles. Chemosphere 216:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.122
Fisher BR, Eisler H-J, Stott NE, Bawendi MG (2004) Emission intensity dependence and single-exponential behavior in single colloidal quantum dot fluorescence lifetimes. J Phys Chem B 108:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp035756
Franchi A, O'Melia CR (2003) Effects of natural organic matter and solution chemistry on the deposition and reentrainment of colloids in porous media. Environ Sci Technol 37:1122–1129. https://doi.org/10.1021/es015566h
French RA, Jacobson AR, Kim B, Isley SL, Penn RL, Baveye PC (2009) Influence of ionic strength, pH, and cation valence on aggregation kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 43:1354–1359. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802628n
Furman O, Usenko S, Lau BLT (2013) Relative importance of the humic and fulvic fractions of natural organic matter in the aggregation and deposition of silver nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 47:1349–1356. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303275g
Godinez IG, Darnault CJG (2011) Aggregation and transport of nano-TiO2 in saturated porous media: effects of pH, surfactants and flow velocity. Water Res 45:839–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.013
Godinez IG, Darnault CJG, Khodadoust AP, Bogdan D (2013) Deposition and release kinetics of nano-TiO2 in saturated porous media: effects of solution ionic strength and surfactants. Environ Pollut 174:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.002
Gogos A, Wielinski J, Voegelin A, Emerich H, Kaegi R (2019) Transformation of cerium dioxide nanoparticles during sewage sludge incineration. Environ Sci Nano 6:1765–1776. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en00281b
Green M (2010) The nature of quantum dot capping ligands. J Mater Chem 20:5797–5809. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JM00007H
Han SJ, Lee HI, Jeong HM, Kim BK, Raghu AV, Reddy KR (2014) Graphene modified lipophilically by stearic acid and its composite with low density polyethylene. J Macromol Sci B 53:1193–1204. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2013.879804
Hanaor D, Michelazzi M, Leonelli C, Sorrell CC (2012) The effects of carboxylic acids on the aqueous dispersion and electrophoretic deposition of ZrO2. J Eur Ceram Soc 32:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.08.015
Hiemenz PC, Rajagopalan R (1997) Principles of colloid and surface chemistry, revised and expanded, Third edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hotze EM, Phenrat T, Lowry GV (2010) Nanoparticle aggregation: challenges to understanding transport and reactivity in the environment. J Environ Qual 39:1909–1924. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2009.0462
Hsiung C-E, Lien H-L, Galliano AE, Yeh C-S, Shih Y-H (2016) Effects of water chemistry on the destabilization and sedimentation of commercial TiO2 nanoparticles: role of double-layer compression and charge neutralization. Chemosphere 151:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.046
Hu J-D, Zevi Y, Kou X-M, Xiao J, Wang X-J, Jin Y (2010) Effect of dissolved organic matter on the stability of magnetite nanoparticles under different pH and ionic strength conditions. Sci Total Environ 408:3477–3489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.03.033
Huibers BMJ, Pales AR, Bai LY, Li CY, Mu LL, Ladner D, Daigle H, Darnault CJG (2017) Wettability alteration of sandstones by silica nanoparticle dispersions in light and heavy crude oil. J Nanopart Res 19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-4011-7
Huynh KA, Chen KL (2011) Aggregation kinetics of citrate and polyvinylpyrrolidone coated silver nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolyte solutions. Environ Sci Technol 45:5564–5571. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200157h
Ife AF, Harding IH, Shah RM, Palombo EA, Eldridge DS (2018) Effect of pH and electrolytes on the colloidal stability of stearic acid-based lipid nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 20:318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4425-x
Illés E, Tombácz E (2006) The effect of humic acid adsorption on pH-dependent surface charging and aggregation of magnetite nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 295:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.08.003
Jatana S, Callahan LM, Pentland AP, DeLouise LA (2016) Impact of cosmetic lotions on nanoparticle penetration through ex vivo C57BL/6 hairless mouse and human skin: a comparison study. Cosmetics 3:6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics3010006
Jean J (2020) Getting high with quantum dot solar cells. Nat Energy 5:10–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-019-0534-8
Ji X, Copenhaver D, Sichmeller C, Peng X (2008) Ligand bonding and dynamics on colloidal nanocrystals at room temperature: the case of alkylamines on CdSe nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 130:5726–5735. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja710909f
Jiang J, Oberdörster G, Biswas P (2009) Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J Nanopart Res 11:77–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9446-4
Joo SH, Zhao DY (2017) Environmental dynamics of metal oxide nanoparticles in heterogeneous systems: a review. J Hazard Mater 322:29–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.068
Ju-Nam Y, Lead JR (2008) Manufactured nanoparticles: an overview of their chemistry, interactions and potential environmental implications. Sci Total Environ 400:396–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.042
Jung Y, Schaumann GE, Baik S, Metreveli G (2020) Effects of hydrophobicity-based fractions of Pony Lake fulvic acid on the colloidal stability and dissolution of oppositely charged surface-coated silver nanoparticles. Environ Chem 17:400–412. https://doi.org/10.1071/En19178
Kamat PV (2008) Quantum dot solar cells. Semiconductor nanocrystals as light harvesters. J Phys Chem C 112:18737–18753. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp806791s
Katsumiti A, Gilliland D, Arostegui I, Cajaraville MP (2014) Cytotoxicity and cellular mechanisms involved in the toxicity of CdS quantum dots in hemocytes and gill cells of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat Toxicol 153:39–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.02.003
Keller AA, Wang H, Zhou D, Lenihan HS, Cherr G, Cardinale BJ, Miller R, Ji Z (2010) Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ Sci Technol 44:1962–1967. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902987d
Kim S, Fisher B, Eisler H-J, Bawendi M (2003) Type-II quantum dots: CdTe/CdSe(core/shell) and CdSe/ZnTe(core/shell) heterostructures. J Am Chem Soc 125:11466–11467. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0361749
Kister T, Monego D, Mulvaney P, Widmer-Cooper A, Kraus T (2018) Colloidal stability of apolar nanoparticles: the role of particle size and ligand shell structure. ACS Nano 12:5969–5977. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b02202
Koeneman BA, Zhang Y, Hristovski K, Westerhoff P, Chen Y, Crittenden JC, Capco DG (2009) Experimental approach for an in vitro toxicity assay with non-aggregated quantum dots. Toxicol in Vitro 23:955–962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2009.05.007
Kohn RA, Dunlap TF (1998) Calculation of the buffering capacity of bicarbonate in the rumen and in vitro. J Anim Sci 76:1702–1709. https://doi.org/10.2527/1998.7661702x
Laguecir A, Ulrich S, Labille J, Fatin-Rouge N, Stoll S, Buffle J (2006) Size and pH effect on electrical and conformational behavior of poly(acrylic acid): simulation and experiment. Eur Polym J 42:1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2005.11.023
Lai Y-C, Lai CS, Tai JT, Nguyen TP, Wang HL, Lin CY, Tsai TY, Ho HC, Wang PH, Liao YC, Tsai DH (2015) Understanding ligand–nanoparticle interactions for silica, ceria, and titania nanopowders. Adv Powder Technol 26:1676–1686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2015.10.005
Lee YR, Raghu AV, Jeong HM, Kim BK (2009) Properties of waterborne polyurethane/functionalized graphene sheet nanocomposites prepared by an in situ method. Macromol Chem Phys 210:1247–1254. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.200900157
Lee J, Bartelt-Hunt SL, Li Y, Gilrein EJ (2016) The influence of ionic strength and organic compounds on nanoparticle TiO2 (n-TiO2) aggregation. Chemosphere 154:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.059
Lewis NS, Crabtree G (2005) Basic research needs for solar energy utilization: report of the basic energy sciences workshop on solar energy utilization, April 18-21, 2005. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/899136. Accessed March 10, 2019
Li X, Yang X, Yuwen L, Yang W, Weng L, Teng Z, Wang L (2016) Evaluation of toxic effects of CdTe quantum dots on the reproductive system in adult male mice. Biomaterials 96:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.04.014
Li B, Chen Y, Liang W-Z, Mu L, Bridges WC, Jacobson AR, Darnault CJG (2017) Influence of cerium oxide nanoparticles on the soil enzyme activities in a soil-grass microcosm system. Geoderma 299:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.03.027
Li B, Pales AR, Clifford HM, Kupis S, Hennessy S, Liang W-Z, Moysey S, Powell B, Finneran KT, Darnault CJG (2018) Preferential flow in the vadose zone and interface dynamics: impact of microbial exudates. J Hydrol 558:72–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.12.065
Li C, Hassan A, Palmai M, Xie Y, Snee P, Powell B, Murdoch L, Darnault CJG (2020a) Experiments and simulations of transport of nanocrystal CdSe/ZnS quantum dots in porous media: effects of pH, organic ligand, and natural organic matter. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11097-0
Li X et al (2020b) Interactions of CeO2 nanoparticles with natural colloids and electrolytes impact their aggregation kinetics and colloidal stability. J Hazard Mater 386:121973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121973
Li ZX, Shakiba S, Deng N, Chen JW, Louie SM, Hu YD (2020c) Natural organic matter (NOM) imparts molecular-weight-dependent steric stabilization or electrostatic destabilization to ferrihydrite nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 54:6761–6770. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c01189
Lin D, Liu N, Yang K, Zhu L, Xu Y, Xing B (2009) The effect of ionic strength and pH on the stability of tannic acid-facilitated carbon nanotube suspensions. Carbon 47:2875–2882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.06.036
Liu W, He Z, Liang J, Zhu Y, Xu H, Yang X (2008) Preparation and characterization of novel fluorescent nanocomposite particles: CdSe/ZnS core‐shell quantum dots loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A 84:1018–1025. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.31205
Liu J, Legros S, Ma G, Veinot JGC, von der Kammer F, Hofmann T (2012) Influence of surface functionalization and particle size on the aggregation kinetics of engineered nanoparticles. Chemosphere 87:918–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.045
Liu W, Sun W, Borthwick AGL, Ni J (2013) Comparison on aggregation and sedimentation of titanium dioxide, titanate nanotubes and titanate nanotubes-TiO2: influence of pH, ionic strength and natural organic matter. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 434:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.05.010
Liu J, Dai C, Hu Y (2018) Aqueous aggregation behavior of citric acid coated magnetite nanoparticles: effects of pH, cations, anions, and humic acid. Environ Res 161:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.10.045
Liu X, Yang ZY, Sun JC, Ma T, Hua F, Shen ZY (2019) A brief review of cytotoxicity of nanoparticles on mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine. Int J Nanomedicine 14:3875–3892. https://doi.org/10.2147/Ijn.S205574
Lowry GV, Gregory KB, Apte SC, Lead JR (2012) Transformations of nanomaterials in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 46:6893–6899. https://doi.org/10.1021/es300839e
Lu S, Yang DJ, Wang M, Yan MZ, Qian Y, Zheng DF, Qiu XQ (2020) Pickering emulsions synergistic-stabilized by amphoteric lignin and SiO2 nanoparticles: stability and pH-responsive mechanism. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 585:124158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124158
Maiga DT, Nyoni H, Nkambule TT, Mamba BB, Msagati TAM (2020) Impact of zinc oxide nanoparticles in aqueous environments: influence of concentrations, natural organic matter and ionic strength. Inorg Nano-Met Chem 50:680–692. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1724145
Majumdar S, Pagano L, Wohlschlegel JA, Villani M, Zappettini A, White JC, Keller AA (2019) Proteomic, gene and metabolite characterization reveal the uptake and toxicity mechanisms of cadmium sulfide quantum dots in soybean plants. Environ Sci Nano 6:3010–3026. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en00599d
Markiewicz M, Kumirska J, Lynch I, Matzke M, Köser J, Bemowsky S, Docter D, Stauber R, Westmeier D, Stolte S (2018) Changing environments and biomolecule coronas: consequences and challenges for the design of environmentally acceptable engineered nanoparticles. Green Chem 20:4133–4168. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8GC01171K
Mateos H, Picca RA, Mallardi A, Dell'Aglio M, De Giacomo A, Cioffi N, Palazzo G (2020) Effect of the surface chemical composition and of added metal cation concentration on the stability of metal nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in water. Appl Sci 10:4169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124169
McBride J, Treadway J, Feldman LC, Pennycook SJ, Rosenthal SJ (2006) Structural basis for near unity quantum yield core/shell nanostructures. Nano Lett 6:1496–1501. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl060993k
Mehta A, Mishra A, Basu S, Shetti NP, Reddy KR, Saleh TA, Aminabhavi TM (2019) Band gap tuning and surface modification of carbon dots for sustainable environmental remediation and photocatalytic hydrogen production - a review. J Environ Manag 250:109486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109486
Metreveli G, Philippe A, Schaumann GE (2015) Disaggregation of silver nanoparticle homoaggregates in a river water matrix. Sci Total Environ 535:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.058
Mishra A, Basu S, Shetti NP, Reddy KR, Aminabhavi TM (2019) Photocatalysis of graphene and carbon nitride-based functional carbon quantum dots. Micro Nano Technol:759–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813926-4.00035-5
Montaño MD, Lowry GV, von der Kammer F, Blue J, Ranville JF (2014) Current status and future direction for examining engineered nanoparticles in natural systems. Environ Chem 11:351–366. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN14037
Morelli E, Cioni P, Posarelli M, Gabellieri E (2012) Chemical stability of CdSe quantum dots in seawater and their effects on a marine microalga. Aquat Toxicol 122-123:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.06.012
Mulvihill MJ, Habas SE, Jen-La Plante I, Wan J, Mokari T (2010) Influence of size, shape, and surface coating on the stability of aqueous suspensions of CdSe nanoparticles. Chem Mater 22:5251–5257. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm101262s
Naidu R, Harter RD (1998) Effect of different organic ligands on cadmium sorption by and extractability from soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62:644–650. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1998.03615995006200030014x
Nardi S, Concheri G, Pizzeghello D, Sturaro A, Rella R, Parvoli G (2000) Soil organic matter mobilization by root exudates. Chemosphere 41:653–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00488-9
Nason JA, McDowell SA, Callahan TW (2012) Effects of natural organic matter type and concentration on the aggregation of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles. J Environ Monit 14:1885–1892. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2EM00005A
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao A-J, Quigg A, Santschi PH, Sigg L (2008) Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17:372–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0214-0
Navarro DAG, Watson DF, Aga DS, Banerjee S (2009) Natural organic matter-mediated phase transfer of quantum dots in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 43:677–682. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8017623
Navarro DA, Banerjee S, Watson DF, Aga DS (2011) Differences in soil mobility and degradability between water-dispersible CdSe and CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Environ Sci Technol 45:6343–6349. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201010f
Navarro DA, Bisson MA, Aga DS (2012) Investigating uptake of water-dispersible CdSe/ZnS quantum dot nanoparticles by Arabidopsis thaliana plants. J Hazard Mater 211-212:427–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.012
Naveed M, Brown LK, Raffan AC, George TS, Bengough AG, Roose T, Sinclair I, Koebernick N, Cooper L, Hackett CA, Hallett PD (2017) Plant exudates may stabilize or weaken soil depending on species, origin and time. Eur J Soil Sci 68:806–816. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12487
Nellist PD et al (2004) Direct sub-angstrom imaging of a crystal lattice. Science 305:1741–1741. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1100965
Nguyen DA, Lee YR, Raghu AV, Jeong HM, Shin CM, Kim BK (2009) Morphological and physical properties of a thermoplastic polyurethane reinforced with functionalized graphene sheet. Polym Int 58:412–417. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.2549
Nie XF, Zhu KC, Zhao S, Dai YC, Tian HX, Sharma VK, Jia HZ (2020) Interaction of Ag+ with soil organic matter: elucidating the formation of silver nanoparticles. Chemosphere 243:125413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125413
Nowack B, Bucheli TD (2007) Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut 150:5–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.006
Nur Y, Lead JR, Baalousha M (2015) Evaluation of charge and agglomeration behavior of TiO2 nanoparticles in ecotoxicological media. Sci Total Environ 535:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.057
Omar FM, Aziz HA, Stoll S (2014) Aggregation and disaggregation of ZnO nanoparticles: influence of pH and adsorption of Suwannee River humic acid. Sci Total Environ 468:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.044
Oriekhova O, Stoll S (2016) Effects of pH and fulvic acids concentration on the stability of fulvic acids – cerium (IV) oxide nanoparticle complexes. Chemosphere 144:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.057
Paesano L et al (2020) Differences in toxicity, mitochondrial function and miRNome in human cells exposed in vitro to Cd as CdS quantum dots or ionic Cd. J Hazard Mater 393:122430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122430
Pales AR, Kinsey E, Li C, Mu L, Bai LC, Clifford HM, Darnault CJG (2017) Rheological properties of silica nanoparticles in brine and brine-surfactant systems. J Nanofluids 6:795–803
Pales AR, Li BT, Clifford HM, Kupis S, Edayilam N, Montgomery D, Liang W-Z, Dogan M, Tharayil N, Martinez N, Moysey S, Powell B, Darnault CJG (2018) Preferential flow systems amended with biogeochemical components: imaging of a two-dimensional study. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 22:2487–2509. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-22-2487-2018
Part F, Zaba C, Bixner O, Zafiu C, Hann S, Sinner E-K, Huber-Humer M (2016) Traceability of fluorescent engineered nanomaterials and their fate in complex liquid waste matrices. Environ Pollut 214:795–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.032
Peng Z, Yang H (2009) Designer platinum nanoparticles: control of shape, composition in alloy, nanostructure and electrocatalytic property. Nano Today 4:143–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2008.10.010
Peng C-W, Tian Q, Yang G-F, Fang M, Zhang Z-L, Peng J, Li Y, Pang D-W (2012) Quantum-dots based simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers of tumor stromal features to predict clinical outcomes in gastric cancer. Biomaterials 33:5742–5752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.04.034
Petersen EJ, Zhang L, Mattison NT, O’Carroll DM, Whelton AJ, Uddin N, Nguyen T, Huang Q, Henry TB, Holbrook RD, Chen KL (2011) Potential release pathways, environmental fate, and ecological risks of carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 45:9837–9856. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201579y
Phenrat T, Saleh N, Sirk K, Kim H-J, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2008) Stabilization of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions by anionic polyelectrolytes: adsorbed anionic polyelectrolyte layer properties and their effect on aggregation and sedimentation. J Nanopart Res 10:795–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-007-9315-6
Pons T, Medintz IL, Wang X, English DS, Mattoussi H (2006) Solution-phase single quantum dot fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J Am Chem Soc 128:15324–15331. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0657253
Pradip, Maltesh C, Somasundaran P, Kulkarni RA, Gundiah S (1991) Polymer-polymer complexation in dilute aqueous solutions: poly (acrylic acid)—poly (ethylene oxide) and poly (acrylic acid)—poly (vinylpyrrolidone). Langmuir 7:2108–2111. https://doi.org/10.1021/la00058a024
Puzder A, Williamson AJ, Zaitseva N, Galli G, Manna L, Alivisatos AP (2004) The effect of organic ligand binding on the growth of CdSe nanoparticles probed by Ab initio calculations. Nano Lett 4:2361–2365. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0485861
Qin SY, Yong X (2019) Controlling the stability of Pickering emulsions by pH-responsive nanoparticles. Soft Matter 15:3291–3300. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8sm02407c
Qiu YH, Mu ZT, Wang N, Wang XJ, Xu ML, Li HL (2020) The aggregation and sedimentation of two different sized copper oxide nanoparticles in soil solutions: dependence on pH and dissolved organic matter. Sci Total Environ 731:139215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139215
Quevedo IR, Tufenkji N (2009) Influence of solution chemistry on the deposition and detachment kinetics of a CdTe quantum dot examined using a quartz crystal microbalance. Environ Sci Technol 43:3176–3182. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803388u
Quevedo IR, Tufenkji N (2012) Mobility of functionalized quantum dots and a model polystyrene nanoparticle in saturated quartz sand and loamy sand. Environ Sci Technol 46:4449–4457. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2045458
Quevedo IR, Olsson ALJ, Tufenkji N (2013) Deposition kinetics of quantum dots and polystyrene latex nanoparticles onto alumina: role of water chemistry and particle coating. Environ Sci Technol 47:2212–2220. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303392v
Raghu AV, Lee YR, Jeong HM, Shin CM (2008) Preparation and physical properties of waterborne polyurethane/functionalized graphene sheet nanocomposites. Macromol Chem Phys 209:2487–2493. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.200800395
Ramiro I, Ozdemir O, Christodoulou S, Gupta S, Dalmases M, Torre I, Konstantatos G (2020) Mid- and long-wave infrared optoelectronics via intraband transitions in PbS colloidal quantum dots. Nano Lett 20:1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b04130
Read DB, Bengough AG, Gregory PJ, Crawford JW, Robinson D, Scrimgeour CM, Young IM, Zhang K, Zhang X (2003) Plant roots release phospholipid surfactants that modify the physical and chemical properties of soil. New Phytol 157:315–326. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00665.x
Reddy K, Darnault CJG, Darko-Kagya K (2014) Transport of lactate-modified nanoscale iron particles in porous media. J Geotech Geoenviron 140:04013013. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001015
Reddy NL, Rao VN, Vijayakumar M, Santhosh R, Anandan S, Karthik M, Shankar MV, Reddy KR, Shetti NP, Nadagouda MN, Aminabhavi TM (2019) A review on frontiers in plasmonic nano-photocatalysts for hydrogen production. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:10453–10472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.02.120
Reddy NR et al (2020) Highly efficient solar light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production over Cu/FCNTs-titania quantum dots-based heterostructures. J Environ Manag 254:109747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109747
Reiss P, Protière M, Li L (2009) Core/shell semiconductor nanocrystals. Small 5:154–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200800841
Ren M, Horn H, Frimmel FH (2017) Aggregation behavior of TiO2 nanoparticles in municipal effluent: influence of ionic strengthen and organic compounds. Water Res 123:678–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.021
Ryman-Rasmussen JP, Riviere JE, Monteiro-Riviere NA (2007) Surface coatings determine cytotoxicity and irritation potential of quantum dot nanoparticles in epidermal keratinocytes. J Investig Dermatol 127:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5700508
Santos AR, Miguel AS, Tomaz L, Malhó R, Maycock C, Vaz Patto MC, Fevereiro P, Oliva A (2010) The impact of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots in cells of Medicago sativa in suspension culture. J Nanobiotechnol 8:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-8-24
Santschi PH, Balnois E, Wilkinson KJ, Zhang J, Buffle J, Guo L (1998) Fibrillar polysaccharides in marine macromolecular organic matter as imaged by atomic force microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Limnol Oceanogr 43:896–908. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1998.43.5.0896
Sharma VK, Sayes CM, Guo B, Pillai S, Parsons JG, Wang C, Yan B, Ma X (2019) Interactions between silver nanoparticles and other metal nanoparticles under environmentally relevant conditions: a review. Sci Total Environ 653:1042–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.411
Slaveykova VI, Startchev K (2009) Effect of natural organic matter and green microalga on carboxyl-polyethylene glycol coated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots stability and transformations under freshwater conditions. Environ Pollut 157:3445–3450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.06.017
Snee PT, Chan Y, Nocera DG, Bawendi MG (2005) Whispering - gallery - mode lasing from a semiconductor nanocrystal/microsphere resonator composite. Adv Mater 17:1131–1136. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200401571
Snee PT, Somers RC, Nair G, Zimmer JP, Bawendi MG, Nocera DG (2006) A ratiometric CdSe/ZnS nanocrystal pH sensor. J Am Chem Soc 128:13320–13321. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0618999
Snee PT, Tyrakowski CM, Page LE, Isovic A, Jawaid AM (2011) Quantifying quantum dots through Förster resonant energy transfer. J Phys Chem C 115:19578–19582. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp205833q
Su YM, Ashworth V, Kim C, Adeleye AS, Rolshausen P, Roper C, White J, Jassby D (2019) Delivery, uptake, fate, and transport of engineered nanoparticles in plants: a critical review and data analysis. Environ Sci Nano 6:2311–2331. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en00461k
Talapin DV, Lee J-S, Kovalenko MV, Shevchenko EV (2010) Prospects of colloidal nanocrystals for electronic and optoelectronic applications. Chem Rev 110:389–458. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900137k
Tang S, Allagadda V, Chibli H, Nadeau JL, Mayer GD (2013a) Comparison of cytotoxicity and expression of metal regulatory genes in zebrafish (Danio rerio) liver cells exposed to cadmium sulfate, zinc sulfate and quantum dots. Metallomics 5:1411–1422. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3MT20234H
Tang Y, Han S, Liu H, Chen X, Huang L, Li X, Zhang J (2013b) The role of surface chemistry in determining in vivo biodistribution and toxicity of CdSe/ZnS core-shell quantum dots. Biomaterials 34:8741–8755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.07.087
Tatsi K, Hutchinson TH, Handy RD (2020) Consequences of surface coatings and soil ageing on the toxicity of cadmium telluride quantum dots to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 201:110813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110813
Thio BJR, Zhou D, Keller AA (2011) Influence of natural organic matter on the aggregation and deposition of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 189:556–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.072
Torkzaban S, Kim Y, Mulvihill M, Wan J, Tokunaga TK (2010) Transport and deposition of functionalized CdTe nanoparticles in saturated porous media. J Contam Hydrol 118:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2010.10.002
Torkzaban S, Wan J, Tokunaga TK, Bradford SA (2012) Impacts of bridging complexation on the transport of surface-modified nanoparticles in saturated sand. J Contam Hydrol 136-137:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2012.05.004
Torkzaban S, Bradford SA, Wan J, Tokunaga T, Masoudih A (2013) Release of quantum dot nanoparticles in porous media: role of cation exchange and aging time. Environ Sci Technol 47:11528–11536. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402075f
Ubaid KA, Zhang XX, Sharma VK, Li LXY (2020) Fate and risk of metal sulfide nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Chem Lett 18:97–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-019-00920-x
Uyusur B, Darnault CJG, Snee PT, Kokën E, Jacobson AR, Wells RR (2010) Coupled effects of solution chemistry and hydrodynamics on the mobility and transport of quantum dot nanomaterials in the vadose zone. J Contam Hydrol 118:184–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2010.09.013
Uyuşur B, Snee PT, Li C, Darnault CJG (2016) Quantitative imaging and in situ concentration measurements of quantum dot nanomaterials in variably saturated porous media. J Nanomater 2016:10–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8237029
Van Hoecke K, De Schamphelaere KAC, Van der Meeren P, Smagghe G, Janssen CR (2011) Aggregation and ecotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles in synthetic and natural waters with variable pH, organic matter concentration and ionic strength. Environ Pollut 159:970–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.12.010
Vijayaraj V, Liné C, Cadarsi S, Salvagnac C, Baqué D, Elger A, Barret M, Mouchet F, Larue C (2018) Transfer and ecotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems: a microcosm study. Environ Sci Technol 52:12757–12764. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02970
Vikesland PJ, Rebodos RL, Bottero JY, Rose J, Masion A (2016) Aggregation and sedimentation of magnetite nanoparticle clusters. Environ Sci Nano 3:567–577. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00155B
Wang L, Zheng H, Long Y, Gao M, Hao J, Du J, Mao X, Zhou D (2010) Rapid determination of the toxicity of quantum dots with luminous bacteria. J Hazard Mater 177:1134–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.001
Wang Y, Zhu H, Becker MD, Englehart J, Abriola LM, Colvin VL, Pennell KD (2013) Effect of surface coating composition on quantum dot mobility in porous media. J Nanopart Res 15:1805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1805-0
Wang Y, Becker MD, Colvin VL, Abriola LM, Pennell KD (2014) Influence of residual polymer on nanoparticle deposition in porous media. Environ Sci Technol 48:10664–10671. https://doi.org/10.1021/es500523p
Wang JY, Yuan YC, Zhu H, Cai T, Fang Y, Chen O (2020a) Three-dimensional macroporous photonic crystal enhanced photon collection for quantum dot-based luminescent solar concentrator. Nano Energy 67:104217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104217
Wang XG, Sun TS, Zhu H, Han T, Wang J, Dai HL (2020b) Roles of pH, cation valence, and ionic strength in the stability and aggregation behavior of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J Environ Manag 267:110656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110656
Werlin R, Priester JH, Mielke RE, Krämer S, Jackson S, Stoimenov PK, Stucky GD, Cherr GN, Orias E, Holden PA (2011) Biomagnification of cadmium selenide quantum dots in a simple experimental microbial food chain. Nat Nanotechnol 6:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2010.251
Xu R, Li C, Ji G (2004) Effect of low-molecular-weight organic anions on electrokinetic properties of variable charge soils. J Colloid Interface Sci 277:243–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.04.020
Yan M, Zhang Y, Qin H, Liu K, Guo M, Ge Y, Xu M, Sun Y, Zheng X (2016) Cytotoxicity of CdTe quantum dots in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: the involvement of cellular uptake and induction of pro-apoptotic endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int J Nanomedicine 11:529–542. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S93591
Yang W, Shang J, Sharma P, Li B, Liu K, Flury M (2019) Colloidal stability and aggregation kinetics of biochar colloids: effects of pyrolysis temperature, cation type, and humic acid concentrations. Sci Total Environ 658:1306–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.269
Yang GH, Zhao JL, Yi SZ, Wan XJ, Tang JN (2020a) Biodegradable and photostable Nb2C MXene quantum dots as promising nanofluorophores for metal ions sensing and fluorescence imaging. Sensors Actuators B Chem 309:127735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127735
Yang WQ et al (2020b) Surface modification induced by perovskite quantum dots for triple-cation perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 67:104189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104189
Yang YL, Mao GB, Ji XH, He ZK (2020c) DNA-templated quantum dots and their applications in biosensors, bioimaging, and therapy. J Mater Chem B 8:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tb01870k
You G, Hou J, Wang P, Xu Y, Wang C, Miao L, Lv B, Yang Y, Luo H (2016) Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on sludge aggregation and the role of extracellular polymeric substances – explanation based on extended DLVO. Environ Res 151:698–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.08.023
Yu TY, Wei DM, Li Z, Pan LJ, Zhang ZL, Tian ZQ, Liu ZH (2020) Target-modulated sensitization of upconversion luminescence by NIR-emissive quantum dots: a new strategy to construct upconversion biosensors. Chem Commun 56:1976–1979. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc09220j
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Westerhoff P, Crittenden J (2009) Impact of natural organic matter and divalent cations on the stability of aqueous nanoparticles. Water Res 43:4249–4257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.005
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Westerhoff P, Crittenden JC (2007) Stability and removal of water soluble CdTe quantum dots in water. Environ Sci Technol 42:321–325
Zhang S, Jiang Y, Chen C-S, Spurgin J, Schwehr KA, Quigg A, Chin W-C, Santschi PH (2012) Aggregation, dissolution, and stability of quantum dots in marine environments: importance of extracellular polymeric substances. Environ Sci Technol 46:8764–8772. https://doi.org/10.1021/es301000m
Zhang W, Yang L, Kuang H, Yang P, Aguilar ZP, Wang A, Fu F, Xu H (2016) Acute toxicity of quantum dots on late pregnancy mice: effects of nanoscale size and surface coating. J Hazard Mater 318:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.048
Zhang D, Zhang ZF, Wu Y, Fu K, Chen Y, Li WH, Chu MQ (2019) Systematic evaluation of graphene quantum dot toxicity to male mouse sexual behaviors, reproductive and offspring health. Biomaterials 194:215–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.12.001
Zhao ZJ, Wang WB, Xiao J, Chen YJ, Cao Y (2020) Interfacial engineering of Pickering emulsion co-stabilized by Zein nanoparticles and Tween 20: effects of the particle size on the interfacial concentration of gallic acid and the oxidative stability. Nanomaterials 10:1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061068
Zhu M, Wang H, Keller AA, Wang T, Li F (2014) The effect of humic acid on the aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles under different pH and ionic strengths. Sci Total Environ 487:375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.036
Acknowledgments
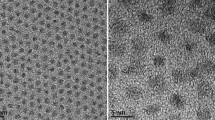
We wish to acknowledge the technical assistance of Eun Byoel Kim for TEM measurements of CdSe quantum dots.
Funding
We wish to convey our appreciation to Clemson University for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Hassan, A., Palmai, M. et al. Colloidal stability and aggregation kinetics of nanocrystal CdSe/ZnS quantum dots in aqueous systems: effects of pH and organic ligands. J Nanopart Res 22, 349 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05080-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05080-6