Abstract
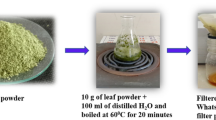
The synthesis of ZnO NPs (zinc oxide nanoparticles) from Hardwickia binata leaves extract using zinc acetate NP (nanoparticle) was verified by a colour change and it was assessed using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer at 365 nm. FTIR (Fourier transform infra-red) analysis was done to demonstrate the existence of several functional groups. XRD (X-ray diffraction) findings support to find the structure of ZnO-NPs. SEM (scanning electron microscopy) data confirmed their synthesis ZnO NPs and its shape. Size range of particles was confirmed by using TEM (transmission electron microscopy). Staphylococcus aureus shows high inhibition compared to other bacterial strains. Antioxidant activity shows highest inhibition in DPPH (2, 2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate) compared to ABTS (2.2’-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) and hydroxyl radical scavenging assay. Anti-inflammatory assay shows highest level of inhibition in HRBC (human red blood cell) membrane stabilization and albumin denaturation. Anti-cancer activity of synthesised ZnO NPs was performed in A431 Human carcinoma cancer cell line and HepG2 liver cancer cell line to evaluate the cytotoxicity of biosynthesized ZnO-NPs. From these findings, it should be noted that synthesised NPs can be utilized for a variety of global biomedical applications in the future.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the finding of this study are included within the manuscript.
References
Kumar JA, Krithiga T, Manigandan S, Sathish S, Renita AA, Prakash P, Prasad BN, Kumar TP, Rajasimman M, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Prabu DA (2021) A focus to green synthesis of metal/metal based oxide nanoparticles: Various mechanisms and applications towards ecological approach. J Clean Prod 324:129198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129198
Naseer M, Aslam U, Khalid B, Chen B (2020) Green route to synthesize Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci Rep 10(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65949-3
Abdelmigid HM, Hussien NA, Alyamani AA, Morsi MM, AlSufyani NM, Kadi HA (2022) Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Pomegranate Fruit Peel and Solid Coffee Grounds vs. Chemical Method of Synthesis, with Their Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Properties Investigation. Molecules 27(4):1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041236
Rastogi A, Zivcak M, Sytar O, Kalaji HM, He X, Mbarki S, Brestic M (2017) Impact of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles on Plant: A Critical Review. Front Chem 5:78. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00078
Shanmugapriya J, Reshma CA, Srinidhi V, Harithpriya K, Ramkumar KM, Umpathy D, Gunasekaran K, Subashini R (2022) Green Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles Using Withania somnifera and Its Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activity. Journal of Nanomaterials 2022:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7967294
Rajendran G, Datta SP, Singh RD, Datta SC, Vakada M (2022) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles – comparison of acetate (precursor) based methods. Inorg Nano-Met Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2021.1891099
Rajendran NK, George BP, Houreld NN, Abrahamse H (2021) Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Rubus fairholmianus Root Extract and Their Activity against Pathogenic Bacteria. Molecules 26(10):–3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26103029
Bukhari A, Ijaz I, Gilani E, Nazir A, Zain H, Saeed R, Alarfaji SS, Hussain S, Aftab R, Naseer Y (2021) Green Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles Using Different Plants’ Parts for Antimicrobial Activity and Anticancer Activity: A Review Article. Coatings 11(11):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111374
Jan H, Shah M, Andleeb A, Faisal S, Khattak A, Rizwan M, Drouet S, Hano C, Abbasi BH (2021) Oxid Med, Plant-Based Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) Using Aqueous Leaf Extract of Aquilegia pubiflora: Their Antiproliferative Activity against HepG2 Cells Inducing Reactive Oxygen Species and Other In Vitro Properties. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4786227
Velumani M, Thiruppathi G, Mohankumar A, Kalaiselvi D, Sundararaj P, Premasudha P (2022) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cananga odorata essential oil and its antibacterial efficacy in vitro and in vivo. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 262:109448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2022.109448
Sharma JL, Dhayal V, Sharma RK (2021) White-rot fungus mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their impregnation on cellulose to develop environmental friendly antimicrobial fibers. 3 Biotech 11(6):269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02840-6
Suba S, Vijayakumar S, Vidhya E, Punitha VN, Nilavukkarasi M (2021) Microbial mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles derived from Lactobacillus spp: Characterizations, antimicrobial and biocompatibility efficiencies. SI 2:100104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100104
Barani B, Lakshminarayanan AK, Subashini R (2019) Microstructural characteristics of chitosan deposited az91 magnesium alloy. Materials Today: Proceedings 16:456–462
Cruz DM, Mostafavi E, Vernet-Crua A, Barabadi H, Shah V, Cholula-Díaz JL, Guisbiers G, Webster TJ (2020) Green nanotechnology-based zinc oxide (ZnO) nanomaterials for biomedical applications: a review. JPhys Materials 3(3):034005. https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7639/ab8186
Babayevska N, Przysiecka Ł, Iatsunskyi I, Nowaczyk G, Jarek M, Janiszewska E, Jurga S (2022) ZnO size and shape effect on antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity profile. Sci Rep 12(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-12134-3
Shaban AS, Owda ME, Basuoni MM, Mousa MA, Radwan AA, Saleh AK (2022) Punica granatum peel extract mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: structure and evaluation of their biological applications. Biomass Convers Biorefin 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03185-7
Chandrasekaran S, Anusuya S, Anbazhagan V (2022) Anticancer, anti-diabetic, antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A comparative analysis. J Mol Struct 1263:133139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133139
Sharifi-Rad M, Anil Kumar NV, Zucca P, Varoni EM, Dini L, Panzarini E, Rajkovic J, Tsouh Fokou PV, Azzini E, Peluso I, Prakash Mishra A (2020) Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Front Physiol 11:694. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00694
Anjum S, Hashim M, Malik SA, Khan M, Lorenzo JM, Abbasi BH, Hano C (2021) Recent Advances in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) for Cancer Diagnosis, Target Drug Delivery, and Treatment. Cancers. 13(18):4570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184570
Tettey CO, Shin HM (2019) Evaluation of the antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using scutellaria baicalensis root. Sci Afr 6:e00157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2019.e00157
Liu H, Kang P, Liu Y, An Y, Hu Y, Jin X, Cao X, Qi Y, Ramesh T, Wang X (2020) Zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesised from the Vernonia amygdalina shows the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities in the mice model. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 48(1):1068–1078. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2020.1809440
Agarwal H, Shanmugam V (2019) A review on anti-inflammatory activity of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticle: Mechanism-based approach. Bioorg Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103423
Shingade SP, Kakde RB (2021) A Review on “Anjan” Hardwickia binata Roxb: Its Phytochemical Studies, Traditional uses and Pharmacological activities. Pharmacogn Rev 15(29):65. https://doi.org/10.5530/phrev.2021.15.7
Deshmukh SV, Ghanawat NA (2019) Cholesterol esterase enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activities of leaves of Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze. using in vitro models. Int J Pharm Pharm. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232
Vijayakumar S, Vaseeharan B, Sudhakaran R, Jeyakandan J, Ramasamy P, Sonawane A, Padhi A, Velusamy P, Anbu P, Faggio C (2019) Bioinspired Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Lycopersicon esculentum for Antimicrobial and Anticancer Applications. J Clust Sci 30(6):1465–1479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01590-z
Saka A, Tesfaye JL, Gudata L, Shanmugam R, Dwarampudi LP, Nagaprasad N, Krishnaraj R, Rajeshkumar S (2022) Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles from Fresh Leaf Extracts of Apocynaceae, Carissa spinarum L. (Hagamsa). J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6230298
Ananthalakshmi R, Rajarathinam SR, Sadiq AM (2019) Antioxidant activity of ZnO Nanoparticles synthesized using Luffa acutangula peel extract. Res J Pharm Technol 12(4):1569–1572. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360X.2019.00260.9
Giao MS, Gonzalez SML, Rivero PMD, Pereira CI, Pintado ME, Malcata FX (2007) Infusions of Portuguese medicinal plants: Dependence of final antioxidant capacity and phenol content on extraction features. J Sci Food Agric 87:2638–2647. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.3023
Soren S, Kumar S, Mishra S, Jena PK, Verma SK, Parhi P (2018) Evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant potential of the zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by aqueous and polyol method. Microb Pathog 119:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.03.048
Islam S, Fahad FI, Sultana A, Sayem SAJ, Roy SB, Islam MN, Roy A, Sayeed MA (2022) Evaluation of Antioxidant, Cytotoxic, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiarthritic, Thrombolytic, and Anthelmintic Activity of Methanol Extract of Lepidagathis hyalina Nees Root. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2022:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2515260
Nagaharika Y, Rasheed S (2013) Anti-inflammatory activity of leaves of Jatropha gossypifolia L. by hrbc membrane stabilization method. J Acute Dis 2(2):156–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-6189(13)60118-3
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
Monks A, Scudiero D, Skehan P, Shoemaker R, Paull K, Vistica D, Hose C, Langley J, Cronise P, Vaigro-Wolff A, Gray-Goodrich M, Campbell H, Mayo J, Boyd M (1991) Feasibility of a High-Flux Anticancer Drug Screen Using a Diverse Panel of Cultured Human Tumor Cell Lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 83:757–766. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/83.11.757
Rajapriya M, Sharmili SA, Baskar R, Balaji R, Alharbi NS, Kadaikunnan S, Khaled JM, Alanzi KF, Vaseeharan B (2020) Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Cynara scolymus Leaves: Enhanced Hemolytic, Antimicrobial, Antiproliferative, and Photocatalytic Activity. J Clust Sci 31(4):791–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01686-6
Datta A, Patra C, Bharadwaj H, Kaur S, Dimri N, Khajuria R (2017) Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Parthenium hysterophorus Leaf Extract and Evaluation of their Antibacterial Properties. J biotechnol Biomater 7(3):271–276. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-952X.1000271
Kwabena DE, Aquisman AE (2019) Morphology of green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles using low temperature hydrothermal technique from aqueous Carica papaya extract. Nanosci Nanotechnol 9(1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.nn.20190901.03
Abdelmigid HM, Hussien NA, Alyamani AA, Morsi MM, AlSufyani NM, Kadi HA (2022) Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Pomegranate Fruit Peel and Solid Coffee Grounds vs. Chemical Method of Synthesis, with Their Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Properties Investigation. Molecules 27(4):1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041236
Patra P, Mitra S, Debnath N, Pramanik P, Goswami A (2014) Ciprofloxacin conjugated zinc oxide nanoparticle: A camouflage towards multidrug resistant bacteria. Bull Mater Sci 37(2):199–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-014-0637-6
Ramesh P, Rajendran A, Ashokkumar M (2022) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Phyllanthus Niruri plant extract for photocatalytic and antioxidant activities. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2022.2041004
Mourdikoudis S, Pallares RM, Thanh NT (2018) Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 10(27):12871–12934. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR02278J
Faisal S, Jan H, Shah SA, Shah S, Khan A, Akbar MT, Rizwan M, Jan F, Wajidullah Akhtar N, Khattak A (2021) Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Fruit Extracts of Myristica fragrans: Their Characterizations and Biological and Environmental Applications. ACS omega 6(14):9709–9722. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00310
Zewde D, Geremew B (2022) Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Hagenia abyssinica leaf extracts; their photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Env Pollut Bioavail 34(1):224–235. https://doi.org/10.1080/26395940.2022.2081261
Gholami M, Esmaeilzadeh M, Kachoei Z, Kachoei M, Divband B (2021) Influence of Physical Dimension and Morphological-Dependent Antibacterial Characteristics of ZnO Nanoparticles Coated on Orthodontic NiTi Wires. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6397698
Jeyabharathi S, Naveenkumar S, Chandramohan S, Venkateshan N, Gawwad MRA, Elshikh MS, Rasheed RA, Al Farraj DA, Muthukumaran A (2022) Biological synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the plant extract, Wattakaka volubilis showed anti-microbial and anti-hyperglycemic effects. J King Saud Univ Sci 34(3):101881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101881
Narendra Kumar HK, Chandra Mohana N, Nuthan BR, Ramesha KP, Rakshith D, Geetha N, Satish S (2019) Phyto-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous plant extract of Ocimum americanum and evaluation of its bioactivity. SN Appl Sci 1(6):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0671-5
Iqbal J, Abbasi BA, Yaseen T, Zahra SA, Shahbaz A, Shah SA Uddin, Ma X, Raouf B, Kanwal S, Amin W (2021) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Elaeagnus angustifolia L. leaf extracts and their multiple in vitro biological applications Sci Rep 11(1):1-13. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-99839-z.
Samuel Z, Ojemaye MO, Okoh OO, Okoh AI (2022) Zinc oxide nanoparticles functionalized with chelating nitrogenous groups for the adsorption of methyl violet in aqueous solutions. Results in Chemistry 4:100579
Gudkov SV, Burmistrov DE, Serov DA, Rebezov MB, Semenova AA, Lisitsyn ABA (2021) A Mini Review of Antibacterial Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. Front Physiol 9:641481. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2021.641481
Hemlata Meena PR, Singh AP, Tejavath KK (2020) Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Cucumis prophetarum Aqueous Leaf Extract and Their Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Activity Against Cancer Cell Lines. ACS omega 5(10):5520–5528. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00155
Gharpure S, Ankamwa B (2020) Synthesis and Antimicrobial Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 20(10):5977–5996. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.18707
Ashwini J, Aswathy TR, Rahul AB, Thara GM, Nair AS (2021) Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Acacia caesia Bark Extract and Its Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Activities. Catalysts 11(12):1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121507
Mthana MS, Mthiyane DM, Onwudiwe DC, Singh M (2022) Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Capsicum Chinense fruit extract and their in vitro cytotoxicity and antioxidant assay. Appl Sci 12(9):4451. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094451
AlNeyadi SS, Amer N, Thomas TG, Al Ajeil R, Breitener P, Munawar N (2020) Biosynthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Capsicum chinense Fruit Extract and Their In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Antioxidant Assay. Heterocycl Comm 26(1):112–122. https://doi.org/10.1515/hc-2020-0112
Bensouici A, Baali N, Bouloudenine R, Speranza G (2022) Decoration of Reduced Graphene Oxide with Magnesium Oxide during Reflux Reaction and Assessment of Its Antioxidant Properties. C 8(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/c8040049
Alam MW, Al Qahtani HS, Aamir M, Abuzir A, Khan MS, Albuhulayqah M, Mushtaq S, Zaidi N, Ramya A (2022) Phyto Synthesis of Manganese-Doped Zinc Nanoparticles Using Carica papaya Leaves: Structural Properties and Its Evaluation for Catalytic, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities. Polymer (Basel) 14(9):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091827
Okeke ES, Enechi OC, Nkwoemeka NE (2020) Membrane Stabilization, Albumin Denaturation, Protease Inhibition, and Antioxidant Activity as Possible Mechanisms for the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoid-Rich Extract of Peltophorum pterocarpum (DC.) K. Heyne (FREPP) Stem Bark. Trop J Nat Prod Res. https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v4i10.25
Jayappa MD, Ramaiah CK, Kumar MAP, Suresh D, Prabhu A, Devasya RP, Sheikh S (2020) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the leaf, stem and in vitro grown callus of Mussaenda frondosa L.: characterization and their applications. Appl Nanosci 10(8):3057–3074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01382-2
Jaithon T, Ruangtong J, Thienprasert JT, Thienprasert NPT (2022) Effects of Waste-Derived ZnO Nanoparticles against Growth of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria and Epidermoid Carcinoma Cells. Crystals 12(6):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12060779
Alhoqail WA, Alothaim AS, Suhail M, Iqbal D, Kamal M, Asmari MM, Jamal A (2023) Husk-like Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Apoptosis through ROS Generation in Epidermoid Carcinoma Cells: Effect of Incubation Period on Sol-Gel Synthesis and Anti-Cancerous Properties. Biomedicines 11(2):320
Shyamalagowri S, Charles P, Manjunathan J, Kamaraj M, Anitha R, Pugazhendhi A (2022) In vitro anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles phyto-fabricated by Hylocereus undatus peel extracts on human liver carcinoma (HepG2) cell lines. Process Biochem 116:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2022.02.022
Shawki MM, El Sadieque A, Elabd S, Moustafa ME (2022) Synergetic Effect of Tumor Treating Fields and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Cell Apoptosis and Genotoxicity of Three Different Human Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 27(14):4384
Ahmed AAH, Maharik N, Valero A, Elsherif W, Kamal SM (2023) Effect of Yoghourt Starter Culture and Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles on the Activity of Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in Domiati Cheese. Applied Sciences 13(6):3935
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges Periyar University for provided University Research Fellowship (URF/000876/2021), Salem, Tamil Nadu, India. This work was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSPD2023R763) King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The authors also thank to Department of Botany, School of Life Sciences, Periyar University, Salem, Tamil Nadu-636 011, India for providing infrastructural facility. This work was supported by Ming Chi University of Technology, Taishan, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peraman Manimegalai: investigation, conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft. Kuppusamy Selvam, Settu Loganathan: conceptualization, data curation, writing—original draft, Dharmalingam Kirubakaran, Muthugounder Subaramanian Shivakumar, Mani Govindasamy, Umamaheswari Rajaji, and Aboud Ahmed Awadh Bahajjaj: formal analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1337 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Manimegalai, P., Selvam, K., Loganathan, S. et al. Green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Hardwickia binata: their characterizations and biological applications. Biomass Conv. Bioref. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04279-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04279-6