Abstract
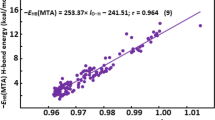
The structural requirements for the binding of steroids to the oestrogen receptor (ER) are important both for the design of new drugs and to assess the health risks of chemicals with ER affinity. In the present QSAR study of receptor binding affinity (RBA) for estradiol derivatives, the atom-level electrotopological state indices have been compared with molecular orbital derived, atom-level parameters for superdelocalisability and atomic charge. The AM1 Hamiltonian was used to calculate molecular orbital parameters. The predictive power of the QSARs indicated that the superdelocalisability indices provide a better model than the electrotopological state indices, and that the atomic charges resulted in the highest prediction error. The most accurate predictions were achieved when other molecular descriptors were also employed in the construction of the QSAR.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghafourian, T., Cronin, M.T. Comparison of electrotopological-state indices versus atomic charge and superdelocalisability indices in a QSAR study of the receptor binding properties of halogenated estradiol derivatives. Mol Divers 8, 343–355 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MODI.0000047499.11033.83
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MODI.0000047499.11033.83