Summary
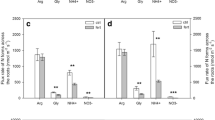
Relationships between root zone temperature, concentrations and uptake rates of NH +4 and NO −3 were studied in non-mycorrhizal roots of 4-year-old Norway spruce under controlled environmental conditions. Additionally, in a forest stand NH +4 and NO −3 uptake rates along the root axis and changes in the rhizosphere pH were measured. In the concentration (Cmin) range of 100–150 μM uptake rates of NH +4 were 3–4 times higher than those of NO −3 The preference for NH +4 uptake was also reflected in the minimum concentration (Cmin) values. Supplying NH4NO3, the rate of NO −3 uptake was very low until the NH +4 concentrations had fallen below about 100 μM. The shift from NH +4 to NO −3 uptake was correlated with a corresponding shift from net H+ production to net H+ consumption in the external solution. The uptake rates of NH +4 were correlated with equimolar net production of H+. With NO −3 nutrition net consumption of H+ was approximately twice as high as uptake rates of NO −3 In the forest stand the NO −3 concentration in the soil solution was more than 10 times higher than the NH +4 concentration (<100 μM), and the rhizosphere pH of non-mycorrhizal roots considerably higher than the bulk soil pH. The rhizosphere pH increase was particularly evident in apical root zones where the rates of water and NO −3 uptake and nitrate reductase activity were also higher. The results are summarized in a model of water and nutrient transport to, and uptake by, non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruce in a forest stand. Model calculations indicate that delivery to the roots by mass flow may meet most of the plant demand of nitrogen and calcium, and that non-mycorrhizal root tips have the potential to take up most of the delivered nitrate and calcium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlström K, Persson H, Börjesson I (1988) Fertilization in a mature Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) stand — effects on fine roots. Plant Soil 106: 179–190
Ashford AE, Peterson CA, Carpenter JL, Cairney JWG, Alloway WG (1988) Structure and permeability of the fungal sheath in the Pisonia mycorrhiza. Protoplasma 147: 149–161
Boxman AW, Roelofs JGM (1988) Some effects of nitrate versus ammonium nutrition on the nutrient fluxes in Pinus sylvestris seedlings. Effects of mycorrhizal infection. Can J Bot 66: 1091–1097
Clarkson DT, Hopper MJ, Jones LHP (1986) The effect of root temperature on the uptake of nitrogen and the relative size of the root system in Lolium perenne. I. Solutions containing both NH +4 and NO −. Plant Cell Environ 9: 535–545
Deane-Drummond CE, Chaffey NJ (1985) Characteristics of nitrate uptake into seedlings of pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Feltham First). Changes in net NO − uptake following inoculation with Rhizobium and growth in low nitrate concentrations. Plant Cell Environ 8: 517–523
Deane-Drummond CE, Glass ADM (1983) Short term studies of nitrate uptake into barley plants using ion-specific electrodes and 36ClO −. II. Regulation of NO− efflux by NH +4 . Plant Physiol 73: 105–110
Drew MC, Saker LR, Barber SA, Jenkins W (1984) Changes in the kinetics of phosphate and potassium absorption in nutrient-deficient barley roots measured by a solution depletion technique. Planta 160: 490–499
Evers FH, Hildebrand EE, Kenk G, Kremer WL (1986) Boden-, ernährungs- und ertragskundliche Untersuchungen in einem stark geschädigten Fichtenbestand des Buntsandstein-Schwarzwaldes. Mitt Ver Forstl Standortskd Forstpflanzenzüchtung 32: 72–80
Finlay RD, Ek H, Odham G, Söderström B (1989) Uptake, translocation and assimilation of nitrogen from 15N-labelled ammonium and nitrate sources by intact ectomycorrhizal systems of Fagus sylvatica infected with Paxillus involutus. New Phytol 113: 47–55
Gijsman AJ (1990a) Rhizosphere pH along different root zones of Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii), as affected by source of nitrogen. Plant Soil 124: 161–167
Gijsman AJ (1990b) Nitrogen nutrition of Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) on strongly acid sandy soil. II. Proton excretion and rhizosphere pH. Plant Soil 126: 63–70
Haug I, Feger KH (1990) Effects of fertilization with MgSO4 and (NH4)2SO4 on soil solution chemistry, mycorrhiza and nutrient content of fine roots in a Norway spruce stand. Water Air Soil Pollut (in press)
Häussling M, Marschner H (1989) Organic and inorganic soil phosphates and acid phosphatase activity in the rhizosphere of 80-year-old Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst.] trees. Biol Fertil Soils 8: 128–133
Häussling M, Leisen E, Marschner H, Römheld V (1985) An improved method for non-destructive measurements of the pH at the root-soil interface (rhizosphere). J Plant Physiol 117: 371–375
Häussling M, Jorns CA, Lehmbecker G, Hecht-Buchholz C, Marschner H (1988) Ion and water uptake in relation to root development in Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst.]. J Plant Physiol 133: 486–491
Jungk A, Claassen N (1989) Availability in soil and acquisition by plants as the basis for phosphorus and potassium supply to plants. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 152: 151–157
Kähr M, Arveby AS (1986) A method for establishing ectomycorrhiza on conifer seedlings in steady-state conditions of nutrition. Physiol Plant 67: 333–339
Kaupenjohann M, Hantschel R (1987) Die kurzfristige pH-Pufferung von gestörten und ungestörten Waldbodenproben. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 150: 156–160
Lee RB, Clarkson DT (1986) Nitrogen-13 studies of nitrate fluxes in barley roots. I. Compartmental analysis from measurements of 13N efflux. J Exp Bot 37: 1753–1767
Lee RB, Drew MC (1989) Rapid, reversible inhibition of nitrate influx in barley by ammonium. J Exp Bot 40: 741–752
Leisen E, Häussling M, Marschner H (1990) Einfluß von Stickstoff-Form und -Konzentration und saurer Benebelung auf pH-Veränderungen in der Rhizosphäre von Fichten [Picea abies (L.) Karst.]. Forstwiss Centralbl 109: 275–286
MacFall JS, Johnson GA, Kramer PJ (1990) Observation of a water-depletion region surrounding loblolly pine roots by magnetic resonance imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 1203–1207
Marschner B, Stahr K, Renger M (1989) Potential hazards of lime application in a damaged pine forest ecosystem in Berlin, Germany. Water Air Soil Pollut 48: 45–57
Marschner H (1989) Effect of soil acidification on root growth, nutrient and water uptake. In: Ulrich B (ed) Forest decline research: state of knowledge and perspectives. Friedrichshafen, pp 381–404
Marschner H, Römheld V (1983) In-vivo measurement of root-induced pH changes of the soil-root interface: effect of plant species and nitrogen source. Z Pflanzenphysiol 111: 241–251
Marschner H, Häussling M, Leisen E (1986) Rhizosphere pH of Norway spruce trees grown under both controlled and field conditions. In: Proceeding of the CEC Workshop, Jülich, 1985 on “Indirect effects of air pollution on forest trees”. Kernforschungsanlage, Jülich, pp 113–118
Martin F, Chemardin M, Godai P (1981) Nitrate assimilation and nitrogen circulation in Australian pine. Physiol Plant 53: 105–110
Matzner E (1988) Der Stoffumsatz zweier Wald-Ökosysteme im Solling. Berichte des Forschungszentrums Waldökosysteme/Waldsterben, Reihe A, vol 40, Göttingen, FRG
McClure PR, Kochian LV, Spanswick RM, Shaff JE (1990) Evidence for cotransport of nitrate and protons in maize roots. II. Measurement of NO− and H+ fluxes with ion-selective microelectrodes. Plant Physiol 93: 290–294
Meyer J, Schneider BU, Werk K, Oren R, Schulze E-D (1988) Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. V. Root tip and ectomycorrhiza development and their relations to above ground and soil nutrients. Oecologia 77: 7–13
Murach D (1984) Die Reaktion der Feinwurzeln von Fichten (Picea abies Karst.) auf zunehmende Bodenversauerung. Göttinger Bodenkundliche Berichte 77
Peuke AD (1987) Der Effect von Schwefeldioxid-, Ozon- und Stickstoffdioxid-Begasung auf den Stickstoff-Metabolismus steril kultivierter Fichtenkeimlinge [Picea abies (L.) Karst.]. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Göttingen
Read DJ, Frances R, Finlay RD (1985) Mycorrhizal mycelia and nutrient cycling in plant communities. In: Fitter AH (ed) Ecological interactions in soil. Special Publication of the British Ecology Society. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 193–218
Read DJ, Leake JR, Longsdale AR (1989) The nitrogen nutrition of mycorrhizal fungi and their host plant. In: Boddy L, Marchant R, Read DJ (eds) Nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur utilization by fungi. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 181–204
Rollwagen BA, Zasoski RJ (1988) Nitrogen source effects on rhizosphere pH and nutrient accumulation by Pacific Northwest conifers. Plant Soil 105: 79–86
Rygiewicz PT, Bledsoe CS, Zasoski RJ (1984a) Effects of ectomycorrhizae and solution pH on (15N)ammonium uptake by coniferous seedlings. Can J For Res 14: 885–892
Rygiewicz PT, Bledsoe CS, Zasoski RJ (1984b) Effects of ectomycorrhizae and solution pH on (15N)nitrate uptake by coniferous seedlings. Can J For Res 14: 893–899
Scheromm P, Plassard C (1988) Nitrogen nutrition of non-mycorrhized pine (Pinus pinaster) grown on nitrate or ammonium. Plant Physiol Biochem 26: 261–269
Schierl R, Kreutzer K (1989) Dolomitische Kalkung eines Fichtenbestandes auf saurer Parabraunerde: Auswirkungen auf Bodenchemie und Vegetation. Kali-Briefe 19: 417–423
Schneider BU, Meyer J, Schulze E-D, Zech W (1989) Root and mycorrhizal development in healthy and declining Norway spruce stands. In: Schulze E-D, Lange OL, Oren R (eds) Forest decline and air pollution (Ecological studies, vol 77) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 370–391
Schulze E-D (1989) Air pollution and forest decline in a spruce (Picea abies) forest. Science 244: 776–783
Schulze E-D, Hantschel R, Werk KS, Horn R (1989) Water relations of two Norway spruce stands at different stages of decline. In: Schulze E-D, Lange OL, Oren R (eds) Forest decline and air pollution. (Ecological studies, vol 77) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 341–351
Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM, Ruth TJ, Fernando M (1989) Studies of the regulation of nitrate influx by barley seedlings using 13NO3 Plant Physiol 90: 806–813
Tachibana S (1987) Effect of root temperature on the rate of water and nutrient absorption in cucumber cultivars and figleaf gourd. J Jpn Soc Hort Sci 55: 461–467
Van Beusichem ML, Baas R, Kirkby EA, Nelemans JA (1985) Intracellular pH regulation during NO− assimilation in shoot and roots of Ricinus communis. Plant Physiol 78: 768–773
Van der Paauw F (1971) An effective water extraction method for the determination of plant-available soil phosphorus. Plant Soil 34: 467–481
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marschner, H., Häussling, M. & George, E. Ammonium and nitrate uptake rates and rhizosphere pH in non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst.]. Trees 5, 14–21 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225330
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225330