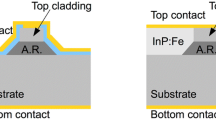
Abstract
We present first results of the investigations of the quantum noise properties of resonant-cavity light-emitting diodes (rcleds). We obtain a quantum noise of up to −0.07dB below the shot noise quantum limit already at moderate pump levels and when being pumped by a quiet current source. This amount of observed sub-shot noise emission is in accordance with the quantum efficiency of the devices. This Sub-Poisson intensity noise ofrcleds together with their narrow beam characteristics make them very attractive for applications in photonics and metrology.
Résumé
Nous présentons les premiers résultats des études du bruit quantique des diodes électroluminescentes à cavité résonante. Nous obtenons un bruit jusqu’à — 0,07 dB au-dessous de la limite quantique du bruit de grenaille même à des niveaux de pompe modérés et avec pompage par une source calme. La valeur observée de ce bruit sous-poissonnien est en accord avec le rendement quantique des diodes électroluminescentes. Finalement, ces résultats démontrent que les diodes électroluminescentes à cavité résonante seront très intéressantes pour des applications en métrologie spectroscopique et en photonique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schubert (E.F.), Wang (Y.-H.), Cho (A.Y.), Tu (L.-W.), Zydzik (G.J.), Resonant cavity light-emitting diode,Appl. Phys. Lett. 60, 921 (1992)
IEEE Sel. Topics Quant. Electron.8 (2002), Special issue on high-efficiency LEDs.
Yamamoto (Y.), Machida (S.), Nilsson (O.), Amplitude squeezing in a pump-noise-suppressed laser oscillator,Phys. Rev. A34, 4025–4042 (1986).
Degen (C.), Vey (J.L.), Elsässer (W.), Schnitzer (P.), Ebeling (K.), Amplitude noise squeezed light from polarisation singlemode VCSEL,Electron. Lett. 34, 353–354 (1998).
Vey (J.-L.), Degen (C.), Auen (K.), Elsässer (W.), Quantum noise and polarization properties of verticalcavity surface-emitting lasers,Phys. Rev. A60, 3284–3295 (1999).
Wiedenmann (D.), Kicherer (M.), Jung (C.), Grabherr (M.), Miller (M.), Jäger (R.), Ebeling (K.J.), Subpoissonian intensity noise from vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers,Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 3075–3077 (1999)
Kilper (D.C.), Ross (P.A.), Carlsten (J.L.), Lear (K.L.), Squeezed light generated by a microcavity laser, Phys. Rev. A55, R3323-R3326 (1997).
Hermier (J.-P.), Bramati (A.), Khoury (A.Z.), Josse (V.), Giacobino (E.), Schnitzer (P.), Michalzik, Ebeling (K.J.), Noise characteristics of oxide-confined vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-37, 87–91 (2001).
Kaiser (J.), Degen (C.), Elsässer (W.), Amplitude-squeezed emission from a transverse single-mode vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser with weakly anticorrelated polarization modes,Opt. Lett. 26, 1720 (2001).
Shinozaki (G.), Abe (J.), Hirano (T.),et al., 3 dB wideband squeezing in photon number fluctuations from a light emitting diode, Jpn.J. Appl. Phys. L36, 6350–6352 (1997).
Abe (J.), Kuga (T.), Hirano (T.), Kobayashi (M.), Yamanishi (M.), Wideband squeezing in photon number fluctuations from a high-speed light-emitting diode,Optics Express 7, 215 (2000).
Wolfl (F.), Schucan (G.M.), Fox (A.M.), Ryan (J.F.), Improved photon-number squeezing in light-emitting diodes, J. Mod.Optics 45, 1147–1153 (1998).
Marin (F.), Bramati (A.), Giacobino (E.), Zhang (T.-Z.), Poizat (J.-P.), Roch (J.-F.), AndGrangier (P.), Squeezing and Intermode Correlations in Laser Diodes,Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 4606 (1995).
Benisty (H.), De Neve (H.);Weisbuch (C.), Impact of planar microcavity effects on light extraction — Part I: Basic concepts and analytical trends, IEEEJ. Quant. Electron. QE-34, 1612 (1998).
Wirth (R.), Karnutsch (C.), Kugler (S.), Streubel (K.), High Efficiency Resonant-Cavity LEDs Emitting at 650nm, IEEE Photon. Technol Lett.13, 421 (2001).
Bachor (H.-A.), A Guide to Experiments in Quantum Optics, (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1998).
Joindot (I.), Measurements of relative intensity noise (RIN) in semiconductor-lasers, J. Phys. III2, 1591–1603 (1992).
Joindot (I.), Amplitude or intensity stability in semiconductor-lasers, J. Phys. IV 1 (C7): 745–748 (1991).
Joindot (I.), Relative intensity noise in semiconductor-lasers, Ann. Telecomm.46, 191–204 (1991).
Kim (J.S.), Kan (H.F.), Yamamoto (Y.), Macroscopic Coulomb-blockade effect in a constant-current driven light-emitting diode,Phys. Rev. B52, 2008–2012 (1995).
Sumitomo (H.), Yamanishi (M.), Kadoya (Y.), Theory of photon-number squeezing in a heterojunction LED by the nonlinear backward pump process,Phys. Rev. B65, 165326 (2002).
Gallion (P.), Vey (J.-L.), Jeremie (F.), Classical optical corpuscular theory of semiconductor laser intensity squeezed-light generator, Ann. Telecomm.52, 235–250 (1997).
Vey (J.-L.), Degen (C.), Auen (K.), Elsässer (W.), Quantum noise and polarization properties of verticalcavity surface-emitting lasers,Phys. Rev. A60, 3284–3295 (1999).
Oulton (R.F.), Gray (J.W.), Stravrinou (P.N.), Parry (G.), Insight into planar microcavity emission as a function of numerical aperture,Opt. Comm. 195, 327–338 (2001).
Kappe (Ph.), Kaiser (J.), Elsässer (W), Spatially correlated light emission from a resonant-cavity light-emitting diode, Opt. Lett.28, 49–51 (2003).
Bramati (A.), Jost (V.), Marin (F.), Hermier (J.-P.), Giacobino (E.), Quantum optics and sub-shot noise spectroscopy with squeezed semiconductor lasers,Laser Physics 8, 703–708 (1998).
Marin (F.), Bramati (A.), Jost (V.), Giacobino (E.), Demonstration of high sensitivity spectroscopy with squeezed semiconductor lasers,Opt. Comm. 140, 146–157 (1997).
Jeremie (F.), Chabran (C.), Gallion (P.), Generation of amplitude-squeezed light from 1550 nm distributed feedback semiconductor laser under wavelength selective optical feedback conditions,App. Phys. Lett. 75, 3614–3616 (1999).
Jeremie (F.), Chabran (C.), Gallion (P.), Room-temperature generation of amplitude-squeezed light from 1550-nm distributed-feedback semiconductor lasers,J. Opt. Soc. Am. B16, 460–464 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kappe, P., Kaiser, J., Elsässer, W. et al. Investigations of the fundamental quantum noise properties of resonant-cavity light-emitting diodes (rcleds). Ann. Télécommun. 58, 1424–1431 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001738
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03001738