Abstract
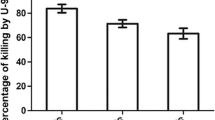
Implant-related infections are a major challenge in clinical routine because of severe complications, for example infective endocarditis (IE). The purpose of this study was to investigate the real-time interaction of S. gordonii with proteins and cells important in the development of IE, in a flow system, by use of a quartz-crystal microbalance (QCM). Acoustic sensors were biologically modified by preconditioning with sterile saliva, platelet-poor plasma (PPP), or platelet-rich plasma (PRP), followed then by perfusion of a bacterial suspension. After perfusion, additional fluorescence and scanning electron microscopic (SEM) studies were performed. The surface structure of S. gordonii was analyzed by atomic force microscopy (AFM). Compared with S. gordonii adhesion on the abiotic sensor surface following normal mass loading indicated by a frequency decrease, adhesion on saliva, PPP, or PRP-conditioned sensors resulted in an increase in frequency. Furthermore, adhesion induced slightly increased damping signals for saliva and PPP-coated sensors but a decrease upon bacterial adhesion to PRP, indicating the formation of a more rigid biofilm. Microscopic analysis confirmed the formation of dense and vital bacterial layers and the aggregation of platelets and bacteria. In conclusion, our study shows that the complex patterns of QCM output data observed are strongly dependent on the biological substrate and adhesion mechanisms of S. gordonii. Overall, QCM sheds new light on the pathways of such severe infections as IE.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tlaskalova-Hogenova H, Stepankova R, Hudcovic T, Tuckova L, Cukrowska B, Lodinova-Zadnikova R, Kozakova H, Rossmann P, Bartova J, Sokol D, Funda DP, Borovska D, Rehakova Z, Sinkora J, Hofman J, Drastich P, Kokesova A (2004) Commensal bacteria (normal microflora), mucosal immunity and chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Immunol Lett 93(2–3):97–108
Krismer B, Peschel A (2011) Does Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization involve biofilm formation? Future Microbiol 6(5):489–493
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(2):95–108
Jung CJ, Yeh CY, Shun CT, Hsu RB, Cheng HW, Lin CS, Chia JS (2012) Platelets enhance biofilm formation and resistance of endocarditis-inducing streptococci on the injured heart valve. J Infect Dis 205(7):1066–1075
Moreillon P, Que YA (2004) Infective endocarditis. Lancet 363(9403):139–149
Grainger DW, van der Mei HC, Jutted PC, van den Dungene JJAM, Schultz MJ, Van der Laang BFAM, Zaath SAJ, Busscher HJ (2013) Critical factors in the translation of improved antimicrobial strategies for medical implantsand devices. Biomaterials. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.043
Kohavi D, Klinger A, Steinberg D, Sela MN (1995) Adsorption of salivary proteins onto prosthetic titanium components. J Prosthet Dent 74(5):531–534
Eichler M, Katzur V, Scheideler L, Haupt M, Geis-Gerstorfer J, Schmalz G, Ruhl S, Muller R, Rupp F (2011) The impact of dendrimer-grafted modifications to model silicon surfaces on protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion. Biomaterials 32(35):9168–9179
Rupp F, Haupt M, Eichler M, Doering C, Klostermann H, Scheideler L, Lachmann S, Oehr C, Wendel HP, Decker E, Geis-Gerstorfer J, von Ohle C (2012) Formation and photocatalytic decomposition of a pellicle on anatase surfaces. J Dent Res 91(1):104–109
Schweikl H, Hiller K-A, Carl U, Schweiger R, Eidt A, Ruhl S, Müller R, Schmalz G (2013) Salivary protein adsorption and Streptococcus gordonii adhesion to dental material surfaces. Dent Mater. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2013.07.021
Fitzgerald JR, Foster TJ, Cox D (2006) The interaction of bacterial pathogens with platelets. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(6):445–457
Ivert TS, Dismukes WE, Cobbs CG, Blackstone EH, Kirklin JW, Bergdahl LA (1984) Prosthetic valve endocarditis. Circulation 69(2):223–232
Kerrigan SW, Cox D (2010) Platelet-bacterial interactions. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(4):513–523
Becker B, Cooper MA (2011) A survey of the 2006–2009 quartz-crystal microbalance biosensor literature. J Mol Recog: JMR 24(5):754–787. doi:10.1002/jmr.1117
Guo X, Lin CS, Chen SH, Ye R, Wu VCH (2012) A piezoelectric immunosensor for specific capture and enrichment of viable pathogens by quartz-crystal microbalance sensor, followed by detection with antibody-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 38(1):177–183
Su XL, Li YB (2004) A self-assembled monolayer-based piezoelectric immunosensor for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. Biosens Bioelectron 19(6):563–574
Knetsch MLW, Koole LH (2011) New Strategies in the Development of Antimicrobial Coatings: The Example of Increasing Usage of Silver and Silver Nanoparticles. Polym Basel 3(1):340–366. doi:10.3390/Polym3010340
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284(5418):1318–1322
Olsson ALJ, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ, Sharma PK (2009) Influence of cell surface appendages on the bacterium-substratum interface measured real-time using QCM-D. Langmuir 25(3):1627–1632
Rheinlaender J, Grabner A, Ott L, Burkovski A, Schaffer TE (2012) Contour and persistence length of Corynebacterium diphtheriae pili by atomic force microscopy. Eur Biophys J Biophys Lett 41(6):561–570
Rodahl M, Hook F, Krozer A, Brzezinski P, Kasemo B (1995) Quartz-Crystal Microbalance setup for frequency and Q-factor measurements in gaseous and liquid environments. Rev Sci Instrum 66(7):3924–3930
Kanazawa KK, Gordon JG (1985) Frequency of a quartz microbalance in contact with liquid. Anal Chem 57(8):1770–1771
Kanazawa KK, Gordon JG (1985) The oscillation frequency of a quartz resonator in contact with a liquid. Anal Chim Acta 175(SEP):99–105
Sinn S, Muller L, Drechsel H, Wandel M, Northoff H, Ziemer G, Wendel HP, Gehring FK (2010) Platelet aggregation monitoring with a newly developed quartz-crystal microbalance system as an alternative to optical platelet aggregometry. Analyst 135(11):2930–2938
Vanhoorelbeke K, Ulrichts H, Van de Walle G, Fontayne A, Deckmyn H (2007) Inhibition of platelet glycoprotein Ib and its Antithrombotic potential. Curr Pharm Des 13(26):2684–2697
Marcus IM, Herzberg M, Walker SL, Freger V (2012) Pseudomonas aeruginosa attachment on QCM-D sensors: The role of cell and surface hydrophobicities. Langmuir 28(15):6396–6402
Boks NP, Norde W, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (2008) Forces involved in bacterial adhesion to hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Microbiology 154(Pt 10):3122–3133. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2008/018622-0
Bos R, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (1999) Physico-chemistry of initial microbial adhesive interactions—its mechanisms and methods for study. FEMS Microbiol Rev 23(2):179–230
Muller R, Eidt A, Hiller KA, Katzur V, Subat M, Schweikl H, Imazato S, Ruhl S, Schmalz G (2009) Influences of protein films on antibacterial or bacteria-repellent surface coatings in a model system using silicon wafers. Biomaterials 30(28):4921–4929. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.05.079
Puckett SD, Taylor E, Raimondo T, Webster TJ (2010) The relationship between the nanostructure of titanium surfaces and bacterial attachment. Biomaterials 31(4):706–713. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.081
Gehring FK (2005) Schwingquarzsensorik in Flüssigkeiten: Entwicklung eines Blutanalysegerätes vol Auflage 1. Cuvillier, E.,
Yombi JC, Belkhir L, Jonckheere S, Wilmes D, Cornu O, Vandercam B, Rodriguez-Villalobos H (2012) Streptococcus gordonii septic arthritis : two cases and review of literature. Bmc Infectious Diseases 12
Sauerbrey G (1959) Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung. Z Phys A Hadrons Nucl 155(2):206–222. doi:10.1007/BF01337937
Voinova MV, Jonson M, Kasemo B (2002) Missing mass effect in biosensor's QCM applications. Biosens Bioelectron 17(10):835–841
Hannig M (1997) Transmission electron microscopic study of in vivo pellicle formation on dental restorative materials. Eur J Oral Sci 105(5):422–433
Olsson ALJ, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ, Sharma PK (2011) Acoustic sensing of the bacterium-substratum interface using QCM-D and the influence of extracellular polymeric substances. J Colloid Interface Sci 357(1):135–138
Dybwad GL (1985) A Sensitive New Method for the Determination of Adhesive Bonding between a Particle and a Substrate. J Appl Phys 58(7):2789–2790. doi:10.1063/1.335874
McNab R, Forbes H, Handley PS, Loach DM, Tannock GW, Jenkinson HF (1999) Cell wall-anchored CshA polypeptide (259 kilodaltons) in Streptococcus gordonii forms surface fibrils that confer hydrophobic and adhesive properties. J Bacteriol 181(10):3087–3095
Nobbs AH, Lamont RJ, Jenkinson HF (2009) Streptococcus adherence and colonization. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews. MMBR 73(3):407–450. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00014-09, Table of Contents
Kolenbrander PE, Palmer RJ Jr, Periasamy S, Jakubovics NS (2010) Oral multispecies biofilm development and the key role of cell-cell distance. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(7):471–480. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2381
Ruhl S, Sandberg AL, Cisar JO (2004) Salivary receptors for the proline-rich protein-binding and lectin-like adhesins of oral actinomyces and streptococci. J Dent Res 83(6):505–510
Ahn SJ, Kho HS, Kim KK, Nahm DS (2003) Adhesion of oral streptococci to experimental bracket pellicles from glandular saliva. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop: Off Publ Am Assoc Orthod Constituent Soc Am Board Orthod 124(2):198–205. doi:10.1016/S0889540603003469
Jenkinson HF, Lamont RJ (1997) Streptococcal adhesion and colonization. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med: Off Publ Am Assoc Oral Biologist 8(2):175–200
Kerrigan SW, Jakubovics NS, Keane C, Maguire P, Wynne K, Jenkinson HF, Cox D (2007) Role of streptococcus gordonii surface proteins SspA/SspB and hsa in platelet function. Infect Immun 75(12):5740–5747
Petersen HJ, Keane C, Jenkinson HF, Vickerman MM, Jesionowski A, Waterhouse JC, Cox D, Kerrigan SW (2010) Human platelets recognize a novel surface protein, PadA, on Streptococcus gordonii through a unique interaction involving fibrinogen receptor GPIIbIIIa. Infect Immun 78(1):413–422
Acknowledgement
The S. gordonii DL1 bacterial strain was kindly provided by Professor Stefan Ruhl (Buffalo, NY, USA). The technical assistance of I. Stephan (University Hospital Tübingen, Germany) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krajewski, S., Rheinlaender, J., Ries, P. et al. Bacterial interactions with proteins and cells relevant to the development of life-threatening endocarditis studied by use of a quartz-crystal microbalance. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 3395–3406 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7769-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7769-9