Abstract
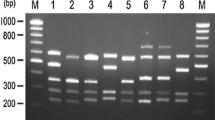
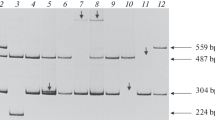
This is the first capillary electrophoresis (CE) analysis for diagnosis of hemophilia A (HA). The intron 22 inversion of factor VIII gene (F8) causes 40–50 % of severe bleeding disorder of HA in all human populations. Consequently, identification of the disease-causing mutations is becoming increasingly important for accurate genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis. In this study, the key steps of inverse-shifting polymerase chain reaction (IS-PCR) and of short-end injection capillary electrophoresis were used for more specific and rapid genotyping of intron 22 inversion of F8. In IS-PCR, three specific primers were used to amplify 512-bp amplicon for wild type and 584-bp amplicon for patients with intron 22 inversion. The capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE) system was performed using 1× Tris–borate–EDTA (TBE) buffer containing 0.3 % (w/v) polyethylene oxide (PEO). The PCR amplicons were electrokinetically injected at 10 kV for 10 s at a temperature of 25 °C. The optimal short-end injection CGE was applied to detect the F8 gene of HA patients and carriers within 5 min. Intron 22 inversion was indeed found on some HA patients (13/35, 37.1 %). All genotyping results showed good agreement with DNA sequencing method and long-distance polymerase chain reaction (LD-PCR). The IS-PCR combined with short-end injection CGE method was feasible and efficient for intron 22 inversion screening of F8 in the HA populations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renault NK, Dyack S, Dobson MJ, Costa T, Lam WL, Greer WL (2007) Eur J Hum Genet 15:628–637
Hedner U, Ginsburg D, Lusher JM, High KA (2000) Hematology 1:241–265
Ng HJ, Lee LH (2009) Ann Acad Med Singap 38:378–379
Chen YC, Hu SH, Cheng SN, Chao TY (2010) Haemophilia 16:538–544
Kemball-Cook G, Tuddenham EGD, Wacey AI (1998) Nucleic Acids Res 26:216–219
Liu Q, Nozari G, Sommer SS (1998) Blood 92:1458–1459
Rost S, Loffler S, Pavlova A, Muller CR, Oldenburg J (2008) J Thromb Haemost 6:1996–1999
Petkova RD, Chakarov SA, Kremensky IM (2008) Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 22:1008–1010
Rossetti LC, Radic CP, Larripa IB, Brasi CDD (2008) J Thromb Haemost 6:830–836
Bond GL, Hirshfield KM, Kirchhoff T, Alexe G, Bond EE, Robins H, Bartel F, Taubert H, Wuerl P, Hait W, Toppmeyer D, Offit K, Levine AJ (2006) Cancer Res 66:5104–5110
Dharel N, Kato N, Muroyama R, Moriyama M, Shao RX, Kawabe T, Omata M (2006) Clin Cancer Res 12:4867–4871
Ruijs MWG, Schmidt MK, Nevanlinna H, Tommiska J, Aittomäki K, Pruntel R, Verhoef S, Veer LJVT (2007) Eur J Hum Genet 15:110–114
Lind H, Zienolddiny S, Ekstrøm PO, Skaug V, Haugen A (2006) Int J Cancer 119:718–721
Schwaab R, Oldenburg J, Lalloz MRA, Schwaab U, Pemberton S, Hanfland P, Brackmann HH, Tuddenham EGD, Michaelides K (1997) Hum Genet 101:323–332
Oldenburg J, Ivaskevicius V, Rost S, Fregin A, White K, Holinski-Feder E (2001) J Biochem Biophys Methods 47:39–51
Kasai K, Nakamura Y, White R (1990) J Forensic Sci 35:1196–1200
Liu Q, Sommer SS (1998) Bio Tech 25:1022–1028
Bergholdt AB, Jørgensen KW, Wendel L, Lehmann SV (2000) J Chromatogr A 875:403–410
Nishl H, Terabe S (1995) J Chromatogr A 694:245–276
Vespalec R, Boček P (1997) Electrophoresis 18:843–852
Strege M, Lagu A (1997) Anal Chem 63:1233–1236
Altria KD, Kelly MA, Clark BJ (1998) Trends Anal Chem 17:204–212
Chen YL, Jong YJ, Hsien JS, Shih CJ, Feng CH, Wu MT, Wu SM (2008) Electrophoresis 29:634–640
Chen YL, Shih CJ, Chang YS, Chang JG, Wu SM (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:1206–1212
Wang CC, Chao KH, Chen YL, Chang JG, Wu SM (2012) J Chromatogr A 1256:276–279
Wang CC, Jong YJ, Chang JG, Chen YL, Wu SM (2010) Anal Bioanal Chem 397:2375–2383
Lausch R, Scheper T (1993) J Chromatogr A 654:190–195
Altria KD (1993) J Chromatogr A 636:125–132
Perrett D, Ross GA (1995) J Chromatogr A 700:179–186
Cahours X, Viron C, Morin P, Renimel I, André P, Lafosse M (2001) Anal Chim Acta 441:15–21
Thornhill AR, Snow K (2002) J Mol Diagn 4:11–29
Ole O, Henrik Z (1992) Tissue Antigens 39:225–235
Wells D, Sherlock JK (1998) Prenat Diagn 18:1389–1401
Wang CC, Chang JG, Ferrance J, Chen HY, You CY, Chang YF, Jong YJ, Wu SM, Yeh CH (2008) Electrophoresis 29:2904–2911
Wang CC, Chang JG, Jong YJ, Wu SM (2009) Electrophoresis 30:1102–1110
Chen YL (2010) Electrophoresis 32:379–385
Ren J, Ueland PM (1999) Hum Mutat 13:458–463
Lin SR, Chang SC, Lee CC, Shen MC, Lin SW (1995) Br J Haematol 91:722–727
Gai JP, Hsu HC, Ho CH (2003) J Chin Med Assoc 66:518–522
Lin SY, Su YN, Hung CC, Tsay W, Chiou SS, Chang CT, Ho HN, Lee CN (2008) BMC Med Genet 9:1–14
Acknowledgments
We deeply extend our sincere thanks to the families who kindly contributed samples that were crucial to this study. We gratefully acknowledge the support of the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MoST), Kaohsiung Medical University, and NSYSU-KMU 103-P023 JOINT RESEARCH PROJECT (#NSYSUKMU103-P023) by way of funding of this work, and the help of Kaohsiung Medical University Chung-Ho Memorial Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, TY., Wang, CC., Shih, CJ. et al. Genotyping of intron 22 inversion of factor VIII gene for diagnosis of hemophilia A by inverse-shifting polymerase chain reaction and capillary electrophoresis. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 5447–5454 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7969-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7969-3