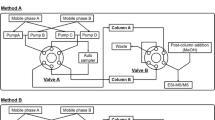
Abstract
Nucleosides and nucleoside triphosphates are the building blocks of nucleic acids and important bioactive metabolites, existing in all living cells. In the present study, two liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry methods were developed to quantify both groups of compounds from the same sample with a shared extraction procedure. After a simple protein precipitation with methanol, the nucleosides were separated with reversed phase chromatography on an Atlantis T3 column while for the separation of the nucleoside triphosphates, an anion exchange column (BioBasic AX) was used. No addition of ion pair reagent was required. A 5500 QTrap was used as analyzer, operating as triple quadrupole. The analytical method for the nucleoside triphosphates has been validated according to the guidelines of the US Food and Drug Administration. The lower limit of quantification values were determined as 10 pg on column (0.5 ng/mL in the injection solution) for deoxyadenosine triphosphate and deoxyguanosine triphosphate, 20 pg (1 ng/mL) for deoxycytidine triphosphate and thymidine triphosphate, 100 pg (5 ng/mL) for cytidine triphosphate and guanosine triphosphate, and 500 pg (25 ng/mL) for adenosine triphosphate und uridine triphosphate respectively. This methodology has been applied to the quantitation of nucleosides and nucleoside triphosphates in primary human CD4 T lymphocytes and macrophages. As expected, the concentrations for ribonucleosides and ribonucleoside triphophates were considerably higher than those obtained for the deoxy derivatives. Upon T cell receptor activation, the levels of all analytes, with the notable exceptions of deoxyadenosine triphosphate and deoxyguanosine triphosphate, were found to be elevated in CD4 T cells.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50(3):414–492
Coulier L, Gerritsen H, van Kampen JJ, Reedijk ML, Luider TM, Osterhaus AD, Gruters RA, Brull L (2011) Comprehensive analysis of the intracellular metabolism of antiretroviral nucleosides and nucleotides using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and method improvement by using ultra performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 879(26):2772–2782
Piret J, Boivin G (2011) Resistance of herpes simplex viruses to nucleoside analogues: mechanisms, prevalence, and management. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(2):459–472
Anderson PL, Kakuda TN, Lichtenstein KA (2004) The cellular pharmacology of nucleoside- and nucleotide-analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors and its relationship to clinical toxicities. Clin Infect Dis 38:743–753
Cohen S, Jordheim LP, Megherbi M, Dumontet C, Guitton J (2010) Liquid chromatographic methods for the determination of endogenous nucleotides and nucleotide analogs used in cancer therapy: a review. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 878(22):1912–1928
Perl A, Gergely P Jr, Puskas F, Banki K (2002) Metabolic switches of T-cell activation and apoptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 4(3):427–443
Dayton JS, Lindsten T, Thompson CB, Mitchell BS (1994) Effects of human T lymphocyte activation on inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase expression. J Immunol 152(3):984–991
Rampazzo C, Miazzi C, Franzolin E, Pontarin G, Ferraro P, Frangini M, Reichard P, Bianchi V (2010) Regulation by degradation, a cellular defense against deoxyribonucleotide pool imbalances. Mutat Res 703(1):2–10
Ferraro P, Franzolin E, Pontarin G, Reichard P, Bianchi V (2010) Quantitation of cellular deoxynucleoside triphosphates. Nucleic Acids Res 38(6):e85
Roy B, Beuneu C (1999) Simultaneous determination of pyrimidine or purine deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates using a polymerase assay. Anal Biochem 269:403–409
Huang D, Zhang Y (2003) Analysis of intracellular nucleoside triphosphate levels in normal and tumor cell lines by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 784:101–109
Padivitage NLT, Dissanayake MK, Armstrong DW (2013) Separation of nucleotides by hydrophilic interaction chromatography using the FRULIC-N column. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:8837–8848
Dd P, Tavazzi B (1995) An Ion pairing HPLC method for the direct simultaneous determination of nucleotides, deoxynucleotides, nicotinic coenzymes, oxypurines, nucleosides, and bases in perchloric acid cell extracts. Anal Biochem 231:407–412
Banoub J (2005) Recent developments in mass spectrometry for the characterization of nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, and nucleic acids. Chem Rev 105:1869–1915
Dudley E, Bond L (2013) Mass spectrometry analysis of nucleosides and nucleotides. Mass Spectrom Rev 33:302–331
Chen P, Liu Z, Liu S, Xie Z, Aimiuwu J, Pang J, Klisovic R, Blum W, Grever MR, Marcucci G, Chan KK (2009) A LC-MS/MS method for the analysis of intracellular nucleoside triphosphate levels. Pharm Res 26(6):1504–1515
Cohen S, Megherbi M, Jordheim LP, Lefebvre I, Perigaud C, Dumontet C, Guitton J (2009) Simultaneous analysis of eight nucleoside triphosphates in cell lines by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 877(30):3831–3840
Henneré G, Becher F, Pruvost A, Goujard C, Grassi J, Benech H (2003) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry assays for intracellular deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate competitors of nucleoside antiretrovirals. J Chromatogr B 789(2):273–281
Cordell RL, Hill SJ, Ortori CA, Barrett DA (2008) Quantitative profiling of nucleotides and related phosphate-containing metabolites in cultured mammalian cells by liquid chromatography tandem electrospray mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 871(1):115–124
Hawkins T, Veikley W, Durand-Gasselin L, Babusis D, Reddy YS, Flaherty JF, Ray AS (2011) Intracellular nucleotide levels during coadministration of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and didanosine in HIV-1-infected patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(4):1549–1555
Coulier L, van Kampen JJ, de Groot R, Gerritsen HW, Bas RC, van Dongen WD, Brull LP, Luider TM (2008) Simultaneous determination of endogenous deoxynucleotides and phosphorylated nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors in peripheral blood mononuclear cells using ion-pair liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Proteomics Clin Appl 2(10–11):1557–1562
Seifar RM, Ras C, van Dam JC, van Gulik WM, Heijnen JJ, van Winden WA (2009) Simultaneous quantification of free nucleotides in complex biological samples using ion pair reversed phase liquid chromatography isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 388(2):213–219
Klawitter J, Schmitz V, Klawitter J, Leibfritz D, Christians U (2007) Development and validation of an assay for the quantification of 11 nucleotides using LC/LC-electrospray ionization-MS. Anal Biochem 365(2):230–239
Kuhlmann FE, Apffel A (1995) Signal enhancement for gradient RP-HPLC-ESI-MS analysis with TFA and other strong acid modifiers by post-column addition of propionic acid and isopropanol. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 6:1221–1225
Zhao Y, Liu G, Liu Y, Yuan L, Hawthorne D, Shen JX, Guha M, Aubry A (2013) Improved ruggedness of an ion-pairing liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry assay for the quantitative analysis of the triphosphate metabolite of a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 27(3):481–488
Machon C, Jordheim LP, Puy JY, Lefebvre I, Dumontet C, Guitton J (2014) Fully validated assay for the quantification of endogenous nucleoside mono- and triphosphates using online extraction coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 406(12):2925–2941
Shi G (2002) Novel direct detection method for the quantitative determination of intracellular NTP-levels by means of WAX-LC-MS/MS. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 16:1092–1099
Gill BD, Indyk HE (2007) Development and application of a liquid chromatographic method for analysis of nucleotides and nucleosides in milk and infant formulas. Int Dairy J 17(6):596–605
Xu G, Enderle H, Liebich H, Lu P (2000) Study of normal and modified nucleosides in serum by RP-HPLC. Chromatographia 52(3/4):152–158
Gill BD, Indyk HE, Manley-Harris M (2013) Analysis of nucleosides and nucleotides in infant formula by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(15):5311–5319
Neubauer S, Rugova A, Chu DB, Drexler H, Ganner A, Sauer M, Mattanovich D, Hann S, Koellensperger G (2012) Mass spectrometry based analysis of nucleotides, nucleosides, and nucleobases—application to feed supplements. Anal Bioanal Chem 404(3):799–808
Studzińska S, Buszewski B (2014) Analysis of normal and modified nucleosides in urine samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with different stationary phases. Biomed Chromatogr 28(8):1140–1146
Chen F, Zhang F, Yang N, Liu X (2013) Simultaneous determination of 10 nucleosides and nucleobases in Antrodia camphorata using QTRAP LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr Sci 52(8):852–861
Zhang LL, Bai YL, Shu SL, Qian DW, Ou-Yang Z, Liu L, Duan JA (2014) Simultaneous quantitation of nucleosides, nucleobases, amino acids, and alkaloids in mulberry leaf by ultra high performance liquid chromatography with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 37(11):1265–1275. doi:10.1002/jssc.201301267
Dudley E, Lemiere F, Van Dongen W (2001) Analysis of urinary nucleosides. II. Comparison of mass spectrometric methods for the analysis of urinary nucleosides. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 15:1701–1707
Yamaoka N, Kudo Y, Inazawa K, Inagawa S, Yasuda M, Mawatari K, Nakagomi K, Kaneko K (2010) Simultaneous determination of nucleosides and nucleotides in dietary foods and beverages using ion-pairing liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 878(23):2054–2060
Badouard C, Masuda M, Nishino H, Cadet J, Favier A, Ravanat J-L (2005) Detection of chlorinated DNA and RNA nucleosides by HPLC coupled to tandem mass spectrometry as potential biomarkers of inflammation. J Chromatogr B 827(1):26–31
Hu J, Zhang W, Ma H, Cai Y, Sheng G, Fu J (2010) Simultaneous determination of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine and 5-methyl-2′-deoxycytidine in DNA sample by high performance liquid chromatography/positive electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 878(28):2765–2769
Weimann A (2002) Quantification of 8-oxo-guanine and guanine as the nucleobase, nucleoside and deoxynucleoside forms in human urine by HPLC-MS/MS. Nucleic Acids Res 30(2):e7
Dudley E, Lemiere F, Van Dongen W, Tuytten R, El-Sharkawi S, Brenton AG, Esmans EL, Newton RP (2004) Analysis of urinary nucleosides. IV. Identification of urinary purine nucleosides by liquid chromatography/electrospray mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18(22):2730–2738
Czarnecka J, Cieslak M, Michal K (2005) Application of solid phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography to qualitative and quantitative analysis of nucleotides and nucleosides in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 822(1–2):85–90
Xing J, Apedo A, Tymiak A, Zhao N (2004) Liquid chromatographic analysis of nucleosides and their mono-, di- and triphosphates using porous graphitic carbon stationary phase coupled with electrospray mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18(14):1599–1606
Weigert A, Johann AM, von Knethen A, Schmidt H, Geisslinger G, Brune B (2006) Apoptotic cells promote macrophage survival by releasing the antiapoptotic mediator sphingosine-1-phosphate. Blood 108(5):1635–1642
US FDA UDoHaHS, FDA, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Rockville, MD, USA (2001) Guidance for industry—analytical method validation. http://www.fdagov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm070107pdf, accessed 04/04/2013
Jan S, Krouwer RR (1984) How to improve estimates of imprecision. Clin Chem 30:290–292
Cohen A, Barankiewicz J, Lederman HM, Gelfand EW (1983) Purine and pyrimidine metabolism in human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 258(20):12334–12340
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Andreas Weigert from the Institute of Biochemistry I of the Goethe University Frankfurt for providing the macrophages. This work was supported by the Else Kroener Fresenius Foundation (Translational Research Innovation Pharma, TRIP) and the LOEWE program from the state of Hesse (Translational Medicine and Pharmacology, TMP). Furthermore, it was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) to O.T.K. (KE 742/5-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 124 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, D., Herold, N., Keppler, O.T. et al. Quantitation of endogenous nucleoside triphosphates and nucleosides in human cells by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 3693–3704 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8588-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8588-3