Abstract
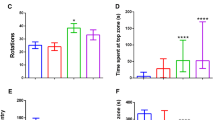
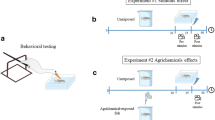
In agriculture intensive areas, fishponds and natural water bodies located in close proximity to these fields receive water with variable amounts of agrichemicals. Consequently, toxic compounds reach nontarget organisms. For instance, aquatic organisms can be exposed to tebuconazole-based fungicides (TBF), glyphosate-based herbicides (GBH), and atrazine-based herbicides (ABH) that are potentially dangerous, which motivates the following question: Are these agrichemicals attractant or aversive to fish? To answer this question, adult zebrafish were tested in a chamber that allows fish to escape from or seek a lane of contaminated water. This attraction and aversion paradigm was evaluated with zebrafish in the presence of an acute contamination with these compounds. We showed that only GBH was aversive to fish, whereas ABH and TBF caused neither attraction nor aversion for zebrafish. Thus, these chemicals do not impose an extra toxic risk by being an attractant for fish, although TBF and ABH can be more deleterious, because they induce no aversive response. Because the uptake and bioaccumulation of chemicals in fish seems to be time- and dose-dependent, a fish that remains longer in the presence of these substances tends to absorb higher concentrations than one that escapes from contaminated sites.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu MS, Giacomini ACV, Gusso D, Rosa JGS, Koakoski G, Kalichak F, Idalencio R, Oliveira TA, Barcellos HHA, Bonan CD, Barcellos LJG (2016) Acute exposure to waterborne psychoactive drugs attracts zebrafish. Comp Biochem Physiol C 179:37–43. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.08.009
Al-Sawafi AGA, Yan Y (2013) Bioconcentration and antioxidant status responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio) under atrazine exposure. Int J Chem Eng Appl 4:204–208. doi:10.7763/IJCEA.2013.V4.295
Armiliato N, Ammar D, Nezzi L, Straliotto M, Muller YMR, Nazari EM (2014) Changes in ultrastructure and expression of steroidogenic factor-1 in ovaries of zebrafish Danio rerio exposed to glyphosate. J Toxicol Environ Health A 77:405–414. doi:10.1080/15287394.2014.880393
Blazina AR, Vianna MR, Lara DR (2013) The spinning task: a new protocol to easily assess motor coordination and resistance in zebrafish. Zebrafish 10:480–485. doi:10.1089/zeb.2012.0860
Cericato L, Neto JGM, Fagundes M, Kreutz LC, Quevedo RM, Finco J, Rosa JGS, Koakoski G, Centenaro L, Pottker E, Anziliero D, Barcellos LJG (2008) Cortisol response to acute stress in jundia (Rhamdia quelen) acutely exposed to sublethal concentrations of agrichemicals. Comp Biochem Physiol C 148:281–286. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.06.008
Cericato L, Neto JGM, Kreutz LC, Quevedo RM, Rosa JGS, Koakoski G, Centenaro L, Marqueze A, Barcellos LJG (2009) Responsiveness of the interrenal tissue of jundia (Rhamdia quelen) to an in vivo ACTH test following acute exposure to sublethal concentrations of agrichemicals. Comp Biochem Physiol C 149:363–367. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.09.002
Døving KB, Hamdani EH, Hoglund E, Kasumyan A, Tuvikene AO (2005) Review of the chemical and physiological basis of alarm reactions in cyprinids. In: von der Emde G, Mogdans J, Kapoor BG (eds) Senses of fish. Narosa, New Delhi, pp 131–163
Elsaesser D, Schulz R (2008) Mitigation of fungicide pollution in vegetated agricultural surface waters: GIS modeling and monitoring in the field. In: Conference proceeding from the SETAC Europe 18th annual meeting. SETAC, Warsaw, pp 406–407
Ferreira D, Motta AC, Kreutz LC, Toni C, Loro VL, Barcellos LJG (2010) Assessment of oxidative stress in Rhamdia quelen exposed to agrichemicals. Chemosphere 79:914–921. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.03.024
Ferreira D, Unfer TC, Rocha HC, Kreutz LC, Koakoski G, Barcellos LJG (2012) Antioxidant activity of bee products added to water in tebuconazole-exposed fish. Neotrop Ichthyol 10:215–220. doi:10.1590/S1679-62252012000100021
Ferreira D, Rocha HC, Kreutz LC, Loro VL, Marqueze A, Koakoski G, Rosa JGS, Gusso D, Oliveira TA, Abreu MS, Barcellos LJG (2013) Bee products prevent agrichemical-induced oxidative damage in fish. PLoS ONE 8(10):e74499. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074499
Folmar LC, Sanders HO, Julin AM (1979) Toxicity of the herbicide glyphosate and several of its formulations to fish and aquatic invertebrates. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 8:269–278. doi:10.1007/BF01056243
Geyer HJ, Rimkus GG, Scheunert I, Kaune A, Schramm K, Kettrup A, Zeeman M, Muir DCG, Hansen LG, Mackay D (2000) Bioaccumulation and occurrence of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), persistent organic pollutants (POPs), and other organic compounds in fish and other organisms including humans. In: Beek B (ed) The handbook of environmental chemistry, bioaccumulation. Springer, Berlin, p 166
Glusczak L, Miron DS, Moraes BS, Simões RR, Schetinger MRC, Morsch VM, Loro VL (2007) Acute effects of glyphosate herbicide on metabolic and enzymatic parameters of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen). Comp Biochem Physiol C 146:519–524. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.06.004
Goerke H, Weber K, Bornemann H, Ramdohr S, Plötz J (2004) Increasing levels and biomagnification of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in Antarctic biota. Mar Poll Bull 48:295–302
Hamelink JL, Spacie A (1977) Fish and chemicals: the process of accumulation. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 17:167–177. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.001123
Hidaka H, Tatsukawa R (1989) Avoidance by olfaction in a fish, Medaka (Oryzias latipes), to aquatic contaminants. Environ Poll 56:299–309. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(89)90075-4
Hidalgo C, Rios C, Hidalgo M, Salvado V, Sancho JV, Hernández F (2004) Improved coupled-column liquid chromatographic method for the determination of glyphosate and aminomethyl-phosphonic acid residues in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1035:153–157. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.02.044
Jiraungkoorskul W, Upatham ES, Kruatrachue M, Sahaphong S, Vichasri-Grams S, Pokethitiyook P (2002) Histopathological effects of Roundup, a glyphosate herbicide, on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Sci Asia 28:121–127
Kelly BC, Ikonomou MG, Blair JD, Morin AE, Gobas FAPC (2007) Food web–specific biomagnification of persistent organic pollutants. Science 317:236–239
Kessler D, Kallenbach M, Diezel C, Rothe E, Murdock M, Baldwin IT (2015) How scent and nectar influence floral antagonists and mutualists. eLife 4:e07641. doi:10.7554/eLife.07641
Koakoski G, Quevedo RM, Ferreira D, Oliveira TA, Rosa JGS, Abreu MS, Gusso D, Marqueze A, Kreutz LC, Giacomini ACV, Fagundes M, Barcellos LJG (2014) Agrichemicals chronically inhibit the cortisol response to stress in fish. Chemosphere 112:85–91. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.083
Korver RM, Sprague JB (1989) Zinc avoidance by fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas): computerized tracking and greater ecological relevance. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46:494–502. doi:10.1139/f89-066
Kreutz LC, Barcellos LJG, Marteninghe A, dos Santos ED, Zanatta R (2010) Exposure to sublethal concentration of glyphosate or atrazine-based herbicides alters the phagocytic function and increases the susceptibility of silver catfish fingerlings (Rhamdia quelen) to Aeromonas hydrophila challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:694–697. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2010.06.003
Langiano VM, Martinez CBR (2008) Toxicity and effects of a glyphosate-based herbicide on the neotropical fish, Prochilodus lineatus. Comp Biochem Physiol C 147:222–231. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.09.009
Lebokowska MZ, Radziwill M, Narozniak AR, Kobiela S (2003) Toxicity assessment of wood preservatives. Environ Int 28:801–802. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00113-7
Morgan JD, Vigers GA, Farrell AP, Janz DM, Manville JF (1991) Acute avoidance reactions and behavioral responses of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to Garlon 4®, Garlon 3® and Vision® herbicides. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:73–79. doi:10.1002/etc.5620100109
Moyle PB, Cech JJ (2000) Fishes: an introduction to ichthyology, 4th edn. Prentice Hall Canada Inc., Toronto
Niethammer KR, White DH, Baskett TS, Sayre MW (1984) Presence and biomagnification of organochlorine chemical residues in oxbow lakes of Northeastern Louisiana. Arc Environ Contam Toxicol 13:63–74
Paterson G, Metcalfe CD (2008) Uptake and depuration of the anti-depressant fluoxetine by the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere 74:125–130. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.08.022
Pratt JR, Melendez AE, Barreiro R, Bowers NJ (1997) Predicting the ecological effects of herbicides. Ecol Appl 7:1117–1124. doi:10.2307/2641200
Readman GD, Owen SF, Murrell JC, Knowles TG (2013) Do fish perceive anesthetics as aversive? PLoS ONE 8(9):e73773. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073773
Sánchez AO, Paraíba LC, Jonsson CM, Carrasco JM (2012) Acute toxicity and bioconcentration of fungicide tebuconazole in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Toxicol 27:109–116. doi:10.1002/tox.20618
Sorensen PW, Stacey NE (1999) Evolution and specialization in fish hormonal pheromones. In: Johnston RE, Müller-Schwarze D, Sorensen PW (eds) Advances in chemical signals in vertebrates. Plenum, New York, pp 15–48
Soumis N, Lucotte M, Sampaio D, Almeida DC, Giroux D, Morais S, Pichet P (2003) Presence of organophosphate insecticides in fish of the Amazon river. Acta Amazon 33:325–338. doi:10.1590/1809-4392200332338
Stacey NE, Sorensen PW (2005) Hormones, pheromones, and reproductive behaviors. In: Sloman KS, Balshine S, Wilson RW (eds) Behaviour: interactions with fish physiology (24). In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ, Farrell AP (series eds) Fish physiology. Academic, New York, pp 359–412
Strieck F (1924) Untersuchungen über den Geruchsund Geschmackssinn der Ellritze (Phoxinus laevis A.). J Comp Physiol A 2:122–154. doi:10.1007/BF00339042
Tierney KB, Singh CR, Ross PS, Kennedy CJ (2007) Relating olfactory neurotoxicity to altered olfactory-mediated behaviors in rainbow trout exposed to three currently-used pesticide. Aquat Toxicol 81:55–64
Tierney KB, Sekela MA, Cobbler CE, Xhabija B, Gledhill M, Ananvoranich S, Zielinski BS (2009) Evidence for behavioral preference toward environmental concentrations of urban-use herbicides in a model adult fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 9999:1–9. doi:10.1002/etc.588
Toni C, Ferreira D, Kreutz LC, Loro VL, Barcellos LJG (2011) Assessment of oxidative stress and metabolic changes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) acutely exposed to different concentrations of the fungicide, tebuconazole. Chemosphere 83:579–584. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.022
Vera MS, Lagomarsino L, Sylvester M, Pérez GL, Rodríguez P, Mugni H, Sinistro R, Ferraro M, Bonetto C, Zagarese H, Pizarro H (2010) New evidences of Roundup (glyphosate formulation) impact on the periphyton community and the water quality of freshwater ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 19:710–721. doi:10.1007/s10646-009-0446-7
Zanella R, Primel EG, Goncalves FF, Kurtz MHS, Mistura CM (2003) Development and validation of a high-performance liquid chromatographic procedure for the determination of herbicide residues in surface and agriculture waters. J Sep Sci 26:935–938. doi:10.1002/jssc.200301309
Zhao YG, Zhang Y, Zhang BB, Hu GJ, Zhang XZ, Zhou CH, Li J (2008) Determination of tebuconazole in water using solid phase extraction and HPLC. China National Knowl Infrastruct J 47(4):271
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Universidade de Passo Fundo and CNPq. L.J.G.B. holds a CNPq research fellowship (301992/2014-2).
Author Contributions
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. L.J.G.B., M.S.A, R.E.B., and J.G.S.R. conceptualized the study, interpreted the data, and wrote the paper. M.S.A., A.C.V.G., G.K., F.K., T.A.O., and H.H.A.B. collected and analyzed the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Rosa, J.G.S., de Abreu, M.S., Giacomini, A.C.V. et al. Fish Aversion and Attraction to Selected Agrichemicals. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 71, 415–422 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0300-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-016-0300-x