Abstract
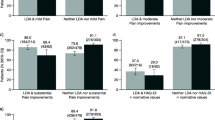
Patient overall satisfaction with health (PSH) was measured by a subset of questions from the Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales II. Based on longitudinal observations for 267 early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients of the United States Western Consortium (WC) cohort receiving first non-biologic DMARD treatment, we estimated the 1-year change in PSH (\(\Updelta\) PSH). Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate the association of improvement in \(\Updelta\) PSH with the core set of clinical and patient-reported components of disease activity scores (DAS). Most patients were more satisfied with health after 1 year of treatment (80%); few achieved DAS28-ESR minimal disease activity (27%) or remission (7%). Laboratory and joint count measures were not associated with improved 12-month PSH. Patients with greater HAQ-DI (P = 0.0473) and self-reported stiffness (P = 0.0669) were more likely to have a perceived overall health benefit from treatment. Regardless of objective disease status, patients are generally satisfied with first-line treatment, which could present a challenge to implementing DAS-guided treatment change. Patients with greater self-reported functional limitations might have lower expectations for treatment benefit and be less willing to modify their current therapy; subjective assessments of function and stiffness could be particularly useful in identifying these patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIMS2:
-
Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales II
- CDAI:
-
Clinical Disease Activity Index
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- DAS:
-
Disease activity score
- DMARD:
-
Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug
- ESR:
-
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- HAQ-DI:
-
Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disease Index
- MDA:
-
Minimal disease activity
- PSH:
-
Patient overall satisfaction with health
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- VAS:
-
Visual analog scale
- WC:
-
Western Consortium
References
Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J, Finney C, Curtis JR, Paulus HE, Mudano A, Pisu M, Elkins-Melton M, Outman R, Allison JJ, Suarez Almazor M, Bridges SLJ, Chatham WW, Hochberg M, MacLean C, Mikuls T, Moreland LW, O’Dell J, Turkiewicz AM, Furst DE (2008) American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 59(6):762–784
Olsen NJ, Stein CM (2004) New drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 350(21):2167–2179
van Tuyl LHD, Vlad SC, Felson DT, Wells G, Boers M (2009) Defining remission in rheumatoid arthritis: results of an initial American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum 61(5):704–710
Shammas RM, Ranganath VK, Paulus HE (2010) Remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 12(5):355–362
ten Wolde S, Breedveld FC, Hermans J, Vandenbroucke JP, van de Laar MA, Markusse HM, Janssen M, van den Brink HR, Dijkmans BA (1996) Randomised placebo-controlled study of stopping second-line drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 347(8998):347–352
Khanna D, Oh M, Furst DE, Ranganath V, Gold RH, Sharp JT, Park GS, Keystone EC, Paulus HE (2007) Evaluation of the preliminary definitions of minimal disease activity and remission in an early seropositive rheumatoid arthritis cohort. Arthritis Rheum 57(3):440–447
Wolfe F, Michaud K (2007) Resistance of rheumatoid arthritis patients to changing therapy: discordance between disease activity and patients’ treatment choices. Arthritis Rheum 56(7):2135–2142
van Tuyl LHD, Plass AMC, Lems WF, Voskuyl AE, Kerstens PJSM, Dijkmans BAC, Boers M (2008) Discordant perspectives of rheumatologists and patients on COBRA combination therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(10):1571–1576
Carbonell J, Badia X (2008) Expectations, preferences and satisfaction of patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving infliximab treatment. Med Clin (Barc) 131(13):493–499
Paulus HE, Oh M, Sharp JT, Gold RH, Wong WK, Park GS, Bulpitt KJ (2003) Correlation of single time-point damage scores with observed progression of radiographic damage during the first 6 years of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 30(4):705–713
Potts MK, Brandt KD (1987) Evidence of the validity of the Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales. Arthritis Rheum 30:93–96
Meenan RF, Mason JH, Anderson JJ, Guccione AA, Kazis LE (1992) AIMS2. The content and properties of a revised and expanded arthritis impact measurement scales health status questionnaire. Arthritis Rheum 35:1–10
Long JA, Husted JA, Gladman DD, Farewell VT (2000) The relationship between patient satisfaction with health and clinical measures of function and disease status in patients with psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol 27(4):958–966
Bruce B, Fries JF (2005) The health assessment questionnaire (HAQ). Clin Exp Rheumatol 23(5 Suppl 39):S14–S18
Aletaha D, Smolen J (2005) The Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI): a review of their usefulness and validity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23(5 Suppl 39):S100–S108
Acknowledgments
The Western Consortium of Practicing Rheumatologists: J. Javier Orozco-Alcala, MD (Guadalajara, Mexico); Karen Basin, MD (Medford, OR); Martin Berry, MD (Bakersfield, CA); Charles Boniske, MD (Visalia, CA); Melvin Britton, MD (Palo Alto, CA); Ken Bulpitt, MD (Torrance, CA); Jeffrey Carlin, MD (Seattle, WA); H. Walter Emori, MD (Medford, OR); Robert Ettlinger, MD (Tacoma, WA); Daniel Furst, MD (Seattle, WA, now in Los Angeles, CA); Gregory Gardner, MD (Seattle, WA); Robert Gerber, MD (Medford, OR); Maria Greenwald, MD (Palm Desert, CA); Karen Kolba, MD (Santa Maria, CA); George Krick, MD (Tacoma, WA); Max Lundberg, MD (Sandy, UT); Anne MacGuire, MD (Casper, WY); Philip Mease, MD (Seattle, WA); Ghislaine Bernard Medina, MD (Guadalajara, Mexico); Raymond Mirise, MD (Los Angeles, CA, now in Glendale, AZ); Ina Oppliger, MD (Seattle, WA, now in Kansas City, MO); Allen Sawitzke, MD (Salt Lake City, UT); Gerald Schoepflin, MD (Portland, OR); John Seaman, MD (Seattle, WA, now in Tacoma, WA); Robert Shapiro, MD (Sacramento, CA); Fredrica Smith, MD (Los Alamos, CA); Marcia Sparling, MD (Vancouver, WA); Elizabeth Tindall, MD (Portland, OR); Michael Weisman, MD (San Diego, CA, now in Los Angeles, CA); Mark Wener, MD (Seattle, WA); Craig Wiesenhutter, MD (Coeur dAlene, ID); Kenneth Wiesner, MD (Sacramento, CA); Robert Willkens, MD (Seattle, WA); Kenneth Wilske, MD (Seattle, WA); Andrew Wong, MD (Northridge, CA); George Young, MD (Boulder, CO). Thank you to Paul Maranian for his assistance with the data analysis. This research was supported by a National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases training grant T32-AI007370.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovalchik, S.A., Charles-Schoeman, C., Khanna, D. et al. An association study of disease activity score components and patient satisfaction with overall health for early RA patients on non-biologic DMARD therapy. Rheumatol Int 32, 2725–2729 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2037-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2037-1