Abstract
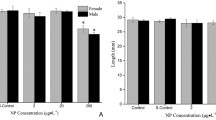
There is still controversy whether adverse effects by genotoxic anthropogenic pollutants are linked to the decline of fish populations. Further investigations into the relationship between genotoxic stress and detrimental effects on development and reproduction in fish are required. For this end, zebrafish (F0 generation) were exposed in vivo to the alkylating model genotoxin methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) from fertilization to the age of 1 year. F0 fish were mated over 6 months to check for reproductive capacities. F1 fish grew up without exposure in order to allow for regeneration. Mortality of F0 fish depended on MMS concentrations. In MMS-exposed F0 fish, times of first spawning were delayed and fertility was reduced. Using the alkaline comet assay and the micronucleus test, significant genotoxic effects were found in the livers, gills and gonads of either sex in the F0 generation. No detrimental effects on growth were found. In F1 fish with parental exposure, teratogenic effects were increased, and larval survival was reduced. However, fertility capacities of the non-exposed F1 generation had recovered. Development and survival rates further recovered in the F2 generation. Anthropogenic genotoxicants may thus play a considerable role in the decline of wild fish populations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson SL, Wild GC (1994) Linking genotoxic responses and reproductive success in ecotoxicology. Environ Health Perspect 102(Suppl. 12):9–12
Baroiller JF, D’Cotta H, Saillant E (2009) Environmental effects on fish sex determination and differentiation. Sex Dev 3(2–3):118–135
Bätscher R, Studer C, Fent K (1999) Stoffe mit endokriner Wirkung in der Umwelt. Schriftenreihe Umwelt Nr. 308. EAWAG/BUWAL, Bern
Beranek DT (1990) Distribution of methyl and ethyl adducts following alkylation with monofunctional alkylating agents. Mutat Res 231(1):11–30
Billiard SM, Querbach K, Hodson PV (1999) Toxicity of retene to early life stages of two freshwater fish species. Environ Toxicol Chem 18(9):2070–2077
Bony S, Gaillard I, Devaux A (2010) Genotoxicity assessment of two vineyard pesticides in zebrafish. Int J Environ Anal Chem 90(3–6):421–428
Braunbeck T, Storch V (1992) Senescence of hepatocytes isolated from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in primary culture—an ultrastructural study. Protoplasma 170(3–4):138–159
Budavari S (ed) (1996) The Merck Index, vol 12. Merck & Co., Whitehouse Station, p 1040
Burkhardt-Holm P, Peter A, Segner H (2002) Decline of fish catch in Switzerland. Aquat Sci 64:36–54
Chen G, White PA (2004) The mutagenic hazards of aquatic sediments: a review. Mutat Res 567:151–225
Cumming RB, Walton MF (1970) Fate and metabolism of some mutagenic alkylating agents in the mouse I. Ethyl methanesulfonate and methyl methanesulfonate at sublethal dose in hybrid males. Mutat Res 10(4):365–377
Depledge MH (1996) Genetic ecotoxicology: an overview. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 200(1–2):57–66
Devaux A, Fiat L, Gillet C, Bony S (2011) Reproduction impairment following paternal genotoxin exposure in brown trout (Salmo trutta) and Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Aquat Toxicol 101(2):405–411
Deventer K (1996) Detection of genotoxic effects on cells of liver and gills of B. rerio by means of single cell gel electrophoresis. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56(6):911–918
Diekmann M, Hultsch V, Nagel R (1999) Wirkung von Benzo(a)pyren auf Fischpopulationen: Ergebnisse eines kompletten Life-Cycle-Tests mit dem Zebrabärbling Danio rerio. In: Oehlmann J, Markert B (eds) Ökotoxikologie—ökosystemare Ansätze und Methoden. Ecomed Verlagsgesellschaft, München, pp 197–203
Diekmann M, Hultsch V, Nagel R (2004a) On the relevance of genotoxicity for fish populations I: effects of a model genotoxicant on zebrafish (Danio rerio) in a complete life-cycle test. Aquat Toxicol 68(1):13–26
Diekmann M, Waldmann P, Schnurstein A, Grummt T, Braunbeck T, Nagel R (2004b) On the relevance of genotoxicity for fish populations II: genotoxic effects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide in a complete life-cycle test. Aquat Toxicol 68(1):27–37
Donnelly ET, McClure N, Lewis SEM (2000) Glutathione and hypotaurine in vitro: effects on human sperm motility, DNA integrity and production of reactive oxygen species. Mutagenesis 15(1):61–68
Fischnetz (2004) Schlussbericht. Trägerschaft des Projekts “Fischnetz”, Switzerland
Friedl C (1999) Fischrückgang in schweizerischen Fliessgewässern. Swiss. Federal Office of Environment, Forests and. Landscape, Bern
Gómez-Bombarelli R, González-Pérez M, Arenas-Valgañón J, Céspedes-Camacho IF, Calle E, Casado J (2011) DNA-damaging disinfection byproducts: alkylation mechanism of mutagenic mucohalic acids. Environ Sci Technol 45(20):9009–9016
Gross-Sorokin MY, Roast SD, Brighty GC (2006) Assessment of feminization of male fish in English rivers by the environment agency of England and wales. Environ Health Perspect 114:147–151
Heeb M, Escher B (2007) Evaluation of the aquatic ecotoxicology of fullerenes and nanotubes. Termpaper, major in biogeochemistry and pollutant dynamics. Department of Environmental Science ETH Zürich, Zürich
Helma C, Knasmüller S, Schulte-Hermann R (1994) Die Belastung von Wässern mit gentoxischen Substanzen. Umweltwiss Schadst Forsch 6(5):277–288
Hemsworth BN, Wardhaugh AA (1978) The induction of dominant lethal mutations in Tilapia mossambica by alkane sulphonic esters. Mutat Res 58(2–3):263–268
Jobling S, Beresford N, Nolan M, Rodgers-Gray T, Brighty GC, Sumpter JP, Tyler CR (2002) Altered sexual maturation and gamete production in wild roach (Rutilus rutilus) living in rivers that receive treated sewage effluents. Biol Reprod 66:272–281
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Keiter S, Rastall A, Kosmehl T, Wurm K, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2006) Ecotoxicological assessment of sediment, suspended matter and water samples in the upper Danube River. A pilot study in search for the causes for the decline of fish catches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13(5):308–319
Kosmehl T, Krebs F, Manz W, Erdinger L, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2004) Comparative genotoxicity testing of Rhine River sediment extracts using the comet assay with permanent fish cell lines (RTG-2 and RTL-W1) and the Ames test. J Soils Sediments 4(1):84–94
Kuehl DW, Serrano J, Naumann S (1994) Identification of potentially mutagenic contaminants in the aquatic environment by liquid chromatographic-thermospray mass spectrometric characterization of in vitro DNA adducts. J Chrom A 684(1):113–119
Lawrence C, Ebersole J, Kesseli R (2008) Rapid growth and out-crossing promote female development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Biol Fish 81(2):239–246
Lundin C, North M, Erixon K, Walters K, Jenssen D, Goldman ASH, Helleday T (2005) Methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) produces heat-labile DNA damage but no detectable in vivo DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res 33(12):3799–3811
Mitchelmore CL, Chipman JK (1998) DNA strand breakage in aquatic organisms and the potential value of the comet assay in environmental monitoring. Mutat Res 399:135–147
Munns WR, Black DE, Gleason TR, Salomon K, Bengtson D, Gutjahr-Gobell R (1997) Evaluation of the effects of dioxin and PCBs on Fundulus heteroclitus populations using a modelling approach. Environ Toxicol Chem 16(5):1074–1081
Nagel R (2002) DarT: the embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio—a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. Altex 19(Suppl 1/02):38–48
Nagel R, Isberner K (1998) Testing of chemicals with fish—a critical evaluation of tests with special regard to zebrafish. In: Braunbeck T, Hinton DE, Streit B (eds) Fish Ecotoxicology. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, pp 338–352
Rich JT, Neely JG, Paniello RC, Voelker CCJ, Nussenbaum B, Wang EW (2010) A practical guide to understanding Kaplan–Meier curves. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143(3):331–336
Rydberg B (2000) Radiation-induced heat-labile sites that convert into DNA double-strand breaks. Radiat Res 153(6):805–812
Schäfers C, Nagel R (1991) Effects of 3,4-dichloroaniline on fish populations. Comparison between r- and K-strategists: a complete life cycle test with the guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21(2):297–302
Schnurstein A, Braunbeck T (2001) Tail moment versus tail length—application of an in vitro version of the comet assay in biomonitoring for genotoxicity in native surface waters using primary hepatocytes and gill cells from zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotox Environ Saf 49(2):187–196
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Solomon FP, Faustman EM (1987) Developmental toxicity of four model alkylating agents on Japanese medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) embryos. Environ Toxicol Chem 6(10):747–753
Sonnenschein C, Soto AM (1998) An updated review of environmental estrogen and androgen mimics and antagonists. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 65(1–6):143–150
Strauss GHS (1991) Non-random cell killing in cryopreservation: implication for performance of the battery of leucocyte tests (BLT). I. Toxic and immunotoxic effects. Mutat Res 252:1–15
Sun LW, Qu MM, Li YQ, Wu YL, Chen YG, Kong ZM, Liu ZT (2004) Toxic effects of aminophenols on aquatic life using the zebrafish embryo test and the comet assay. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73:628–634
Theodorakis CW, Blaylock BG, Shugart LR (1997) Genetic ecotoxicology I: dNA integrity and reproduction in mosquitofish exposed in situ to radionuclides. Ecotoxicology 6(4):205–218
van den Belt K, Wester PW, van der Ven LTM, Verheyen R, Witters H (2002) Effects of ethynylestradiol on the reproductive physiology in zebrafish (Danio rerio): time dependency and reversibility. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(4):767–775
Van den Belt K, Verheyen R, Witters H (2003) Effects of 17α-ethynylestradiol in a partial life-cycle test with zebrafish (Danio rerio): effects on growth, gonads and female reproductive success. Sci Total Environ 309(1–3):127–137
Vos JG, Dybing E, Greim HA, Ladefoged O, Lambré C, Tarazona JV, Brandt I, Vethaak AD (2000) Health effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on wildlife, with special reference to the European situation. Crit Rev Toxicol 30(1):71–133
White PA, Robitaille S, Rasmussen JB (1999) Heritable reproductive effects of benzo[a]pyrene on the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ Toxicol Chem 18(8):1843–1847
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Dr. Henner Hollert for co-supervision. For chemical analysis, the authors thank Prof. Dr. Heinfried Schöler and Dr. Sabine Studenroth from the Organic Environmental Chemistry section of the Institute of Earth Sciences at the University of Heidelberg. The first author is grateful to the Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (DBU) for scholarship.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faßbender, C., Braunbeck, T. Reproductive and genotoxic effects in zebrafish after chronic exposure to methyl methanesulfonate in a multigeneration study. Ecotoxicology 22, 825–837 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1057-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1057-x