Abstract
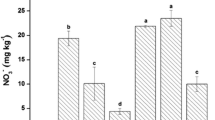
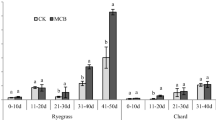
To our knowledge, this is the first report on exploring the interactive effects of various biochars (BCs) and nanomaterials (NMs) on plant growth and bioavailability of trace elements in soil. This study evaluated the bioavailability and toxicity of arsenic (As), lead (Pb), and NMs to cabbage plants. The BCs were produced from rice husk (RB), sewage sludge, and bamboo wood (WB). The BCs at 2.5 and 5% (w w−1), NMs for removing As (NMs-As) and heavy metals (NMs-HM) at 3000 mg kg−1, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNT) at 1000 mg kg−1 were applied in bioassay and incubation experiments (40 days), along with the unamended soil as the control. Results showed that the NMs-As and NMs-HM decreased seed germination at 3 days after sowing; however, their toxicity was eliminated by BCs. Growth parameters of cabbage revealed that the CNT was the most toxic NMs, as it was translocated in root and leaf cells, which was confirmed by transmission electron microscopic images. Bioavailable Pb was reduced by 1.2–3.8-folds in all amended rhizosphere and bulk soils. Amendments of 2.5% WB + NMs-As and 2.5% RB + NMs-As significantly decreased both bioavailable As and Pb.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 December 2017
Unfortunately, in the original publication of the article, Prof. Yong Sik Ok’s affiliation was incorrectly published. The author’s affiliation is as follows.
References
Abid, M., Niazi, N. K., Bibi, I., Farooqi, A., Ok, Y. S., Kunhikrishnan, A., et al. (2016). Arsenic (V) biosorption by charred orange peel in aqueous environments. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 18(5), 442–449.
Ahmad, M., Hashimoto, Y., Moon, D. H., Lee, S. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2012a). Immobilization of lead in a Korean military shooting range soil using eggshell waste: an integrated mechanistic approach. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 209, 392–401.
Ahmad, M., Lee, S. S., Yang, J. E., Ro, H.-M., Lee, Y. H., & Ok, Y. S. (2012b). Effects of soil dilution and amendments (mussel shell, cow bone, and biochar) on Pb availability and phytotoxicity in military shooting range soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 79, 225–231.
Ahmad, M., Moon, D. H., Lim, K. J., Shope, C. L., Lee, S. S., Usman, A. R., et al. (2012c). An assessment of the utilization of waste resources for the immobilization of Pb and Cu in the soil from a Korean military shooting range. Environmental Earth Sciences, 67(4), 1023–1031.
Ahmad, M., Ok, Y. S., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lim, J. E., Kim, B.-Y., Ahn, J.-H., et al. (2016). Lead and copper immobilization in a shooting range soil using soybean stover-and pine needle-derived biochars: Chemical, microbial and spectroscopic assessments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 301, 179–186.
Ahmad, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lim, J. E., Zhang, M., Bolan, N., Mohan, D., et al. (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere, 99, 19–33.
Almaroai, Y. A., Usman, A. R., Ahmad, M., Moon, D. H., Cho, J.-S., Joo, Y. K., et al. (2014a). Effects of biochar, cow bone, and eggshell on Pb availability to maize in contaminated soil irrigated with saline water. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(3), 1289–1296.
Almaroai, Y. A., Vithanage, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lee, S. S., Dou, X., Lee, Y. H., et al. (2014b). Natural and synthesised iron-rich amendments for As and Pb immobilisation in agricultural soil. Chemistry and Ecology, 30(3), 267–279.
Atkinson, C. J., Fitzgerald, J. D., & Hipps, N. A. (2010). Potential mechanisms for achieving agricultural benefits from biochar application to temperate soils: A review. Plant and Soil, 337(1–2), 1–18.
Awad, Y. M., Abdelhafez, A. A., Ahmad, M., Lee, S.-S., Kim, R.-Y., Sung, J.-K., et al. (2010). Synthesis of nanoscale zerovalent iron particle and its application to Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions. Korean Journal of Environmental Agriculture, 29(4), 402–407.
Awad, Y. M., Lee, S. E., Ahmed, M. B. M., Vu, N. T., Farooq, M., Kim, I. S., et al. (2017). Biochar, a potential hydroponic growth substrate, enhances the nutritional status and growth of leafy vegetables. Journal of Cleaner Production, 156, 581–588.
Bandara, T., Herath, I., Kumarathilaka, P., Hseu, Z.-Y., Ok, Y. S., & Vithanage, M. (2016). Efficacy of woody biomass and biochar for alleviating heavy metal bioavailability in serpentine soil. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39(2), 391–401.
Bandyopadhyaya, R., Nativ-Roth, E., Regev, O., & Yerushalmi-Rozen, R. (2002). Stabilization of individual carbon nanotubes in aqueous solutions. Nano Letters, 2(1), 25–28.
Beesley, L., & Marmiroli, M. (2011). The immobilisation and retention of soluble arsenic, cadmium and zinc by biochar. Environmental Pollution, 159(2), 474–480.
Beesley, L., Moreno-Jiménez, E., Gomez-Eyles, J. L., Harris, E., Robinson, B., & Sizmur, T. (2011). A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 159(12), 3269–3282.
Beiyuan, J., Awad, Y. M., Beckers, F., Tsang, D. C., Ok, Y. S., & Rinklebe, J. (2017). Mobility and phytoavailability of As and Pb in a contaminated soil using pine sawdust biochar under systematic change of redox conditions. Chemosphere, 178, 110–118.
Bernal, M., Clemente, R., & Walker, D. (2007). The role of organic amendments in the bioremediation of heavy metal-polluted soils. In A. B. Gore (Ed.), Environmental research at the leading edge (pp. 1–57). New York: Nova Science Publisher, Inc.
Cañas, J. E., Long, M., Nations, S., Vadan, R., Dai, L., Luo, M., et al. (2008). Effects of functionalized and nonfunctionalized single‐walled carbon nanotubes on root elongation of select crop species. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27(9), 1922–1931.
Cao, X., Ma, L., Liang, Y., Gao, B., & Harris, W. (2011). Simultaneous immobilization of lead and atrazine in contaminated soils using dairy-manure biochar. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(11), 4884–4889.
Chaney, R. L., Kim, W. I., Kunhikrishnan, A., Yang, J. E., & Ok, Y. S. (2016). Integrated management strategies for arsenic and cadmium in rice paddy environments. Geoderma, 270, 1–2.
Clough, T. J., Condron, L. M., Kammann, C., & Müller, C. (2013). A review of biochar and soil nitrogen dynamics. Agronomy, 3(2), 275–293.
Deedar, N., & Aslam, I. (2009). Evaluation of the adsorption potential of titanium dioxide nanoparticles for arsenic removal. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21(3), 402–408.
Frohne, T., Rinklebe, J., & Diaz-Bone, R. A. (2014). Contamination of floodplain soils along the Wupper River, Germany, with As Co, Cu, Ni, Sb, and Zn and the impact of pre-definite redox variations on the mobility of these elements. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 23(7), 779–799.
Giammar, D. E., Maus, C. J., & Xie, L. (2007). Effects of particle size and crystalline phase on lead adsorption to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environmental Engineering Science, 24(1), 85–95.
Greene, J., Bartels, C., Warren-Hicks, W., Parkhurst, B., & Linder, G. (1988). Protocols for short-term toxicity screening of hazardous-waste sites. Environmental Protection Agency, Corvallis, OR (USA). New York: Environmental Research Lab.
Hartley, W., Dickinson, N. M., Riby, P., & Lepp, N. W. (2009). Arsenic mobility in brownfield soils amended with green waste compost or biochar and planted with Miscanthus. Environmental Pollution, 157(10), 2654–2662.
Igalavithana, A. D., Lee, S.-E., Lee, Y. H., Tsang, D. C., Rinklebe, J., Kwon, E. E., et al. (2017). Heavy metal immobilization and microbial community abundance by vegetable waste and pine cone biochar of agricultural soils. Chemosphere, 174, 593–603.
Jade 5. (1999). XRD Pattern Processing. Irvine, CA: Materials Data Inc.
Joseph, S., & Lehmann, J. (2009). Biochar for environmental management: Science and technology. London: Earthscan.
Karami, N., Clemente, R., Moreno-Jiménez, E., Lepp, N. W., & Beesley, L. (2011). Efficiency of green waste compost and biochar soil amendments for reducing lead and copper mobility and uptake to ryegrass. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 191(1), 41–48.
Kern, J., Mukhina, I., Dicke, C., Lanza, G., & Kalderis, D. (2015). Effects of rice husks and their chars from hydrothermal carbonization on the germination rate and root length of Lepidium sativum. In EGU general assembly conference abstracts, 2015 (Vol. 17, p. 10002).
Khodakovskaya, M., Dervishi, E., Mahmood, M., Xu, Y., Li, Z., Watanabe, F., et al. (2009). Carbon nanotubes are able to penetrate plant seed coat and dramatically affect seed germination and plant growth. ACS Nano, 3(10), 3221–3227.
Khodakovskaya, M. V., de Silva, K., Nedosekin, D. A., Dervishi, E., Biris, A. S., Shashkov, E. V., et al. (2011). Complex genetic, photothermal, and photoacoustic analysis of nanoparticle-plant interactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(3), 1028–1033.
Khodakovskaya, M. V., Kim, B. S., Kim, J. N., Alimohammadi, M., Dervishi, E., Mustafa, T., et al. (2013). Carbon nanotubes as plant growth regulators: effects on tomato growth, reproductive system, and soil microbial community. Small, 9(1), 115–123.
Kim, H.-S., Kim, K.-R., Kim, H.-J., Yoon, J.-H., Yang, J. E., Ok, Y. S., et al. (2015). Effect of biochar on heavy metal immobilization and uptake by lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in agricultural soil. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(2), 1249–1259.
Kim, H. S., Kim, K. R., Yang, J. E., Ok, Y. S., Kim, W. I., Kunhikrishnan, A., et al. (2017). Amelioration of horticultural growing media properties through rice hull biochar incorporation. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 8(2), 483–492.
Klaine, S. J., Alvarez, P. J., Batley, G. E., Fernandes, T. F., Handy, R. D., Lyon, D. Y., et al. (2008). Nanomaterials in the environment: Behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27(9), 1825–1851.
Larue, C., Pinault, M., Czarny, B., Georgin, D., Jaillard, D., Bendiab, N., et al. (2012). Quantitative evaluation of multi-walled carbon nanotube uptake in wheat and rapeseed. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 227, 155–163.
Lee, S. S., Shah, H. S., Awad, Y. M., Kumar, S., & Ok, Y. S. (2015). Synergy effects of biochar and polyacrylamide on plants growth and soil erosion control. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(3), 2463–2473.
Lehmann, J., Kuzyakov, Y., Pan, G., & Ok, Y. S. (2015). Biochars and the plant-soil interface. Plant and Soil, 395, 1–5.
Lehmann, J., Rillig, M. C., Thies, J., Masiello, C. A., Hockaday, W. C., & Crowley, D. (2011). Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43(9), 1812–1836.
Liang, S.-X., Jin, Y., Liu, W., Li, X., Shen, S.-G., & Ding, L. (2017). Feasibility of Pb phytoextraction using nano-materials assisted ryegrass: Results of a one-year field-scale experiment. Journal of Environmental Management, 190, 170–175.
Liu, X., Zhang, A., Ji, C., Joseph, S., Bian, R., Li, L., et al. (2013). Biochar’s effect on crop productivity and the dependence on experimental conditions—A meta-analysis of literature data. Plant and Soil, 373(1–2), 583–594.
Ma, X., Geiser-Lee, J., Deng, Y., & Kolmakov, A. (2010). Interactions between engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) and plants: Phytotoxicity, uptake and accumulation. Science of the Total Environment, 408(16), 3053–3061.
McBeath, A. V., Smernik, R. J., Krull, E. S., & Lehmann, J. (2014). The influence of feedstock and production temperature on biochar carbon chemistry: A solid-state 13C NMR study. Biomass and Bioenergy, 60, 121–129.
Miralles, P., Church, T. L., & Harris, A. T. (2012). Toxicity, uptake, and translocation of engineered nanomaterials in vascular plants. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(17), 9224–9239.
Moon, D. H., Cheong, K. H., Koutsospyros, A., Chang, Y.-Y., Hyun, S., Ok, Y. S., et al. (2016). Assessment of waste oyster shells and coal mine drainage sludge for the stabilization of As-, Pb-, and Cu-contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(3), 2362–2370.
Moon, D. H., Wazne, M., Cheong, K. H., Chang, Y.-Y., Baek, K., Ok, Y. S., et al. (2015). Stabilization of As-, Pb-, and Cu-contaminated soil using calcined oyster shells and steel slag. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(14), 11162–11169.
Ok, Y. S., Chang, S. X., Gao, B., & Chung, H.-J. (2015). SMART biochar technology—A shifting paradigm towards advanced materials and healthcare research. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 4, 206–209.
Ok, Y. S., Oh, S. E., Ahmad, M., Hyun, S., Kim, K. R., Moon, D. H., et al. (2010). Effects of natural and calcined oyster shells on Cd and Pb immobilization in contaminated soils. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61(6), 1301–1308.
Oleszczuk, P., Ćwikła-Bundyra, W., Bogusz, A., Skwarek, E., & Ok, Y. S. (2016). Characterization of nanoparticles of biochars from different biomass. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 121, 165–172.
Otte, M., Haarsma, M., Broekman, R., & Rozema, J. (1993). Relation between heavy metal concentrations in salt marsh plants and soil. Environmental Pollution, 82(1), 13–22.
Pan, B., & Xing, B. (2012). Applications and implications of manufactured nanoparticles in soils: A review. European Journal of Soil Science, 63(4), 437–456.
Paz-Ferreiro, J., Gascó, G., Gutiérrez, B., & Méndez, A. (2012). Soil biochemical activities and the geometric mean of enzyme activities after application of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar to soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 48(5), 511–517.
Purwanto, A., Hidayat, D., Terashi, Y., & Okuyama, K. (2008). Synthesis of monophasic Ca x Ba (1 − x) TiO3 nanoparticles with high Ca content (x > 23%) and their photoluminescence properties. Chemistry of Materials, 20(24), 7440–7446.
Rajapaksha, A. U., Ahmad, M., Vithanage, M., Kim, K.-R., Chang, J. Y., Lee, S. S., et al. (2015). The role of biochar, natural iron oxides, and nanomaterials as soil amendments for immobilizing metals in shooting range soil. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(6), 931–942.
Rajapaksha, A. U., Chen, S. S., Tsang, D. C., Zhang, M., Vithanage, M., Mandal, S., et al. (2016). Engineered/designer biochar for contaminant removal/immobilization from soil and water: Potential and implication of biochar modification. Chemosphere, 148, 276–291.
Rajkovich, S., Enders, A., Hanley, K., Hyland, C., Zimmerman, A. R., & Lehmann, J. (2012). Corn growth and nitrogen nutrition after additions of biochars with varying properties to a temperate soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 48(3), 271–284.
Rinklebe, J., Shaheen, S. M., & Frohne, T. (2016). Amendment of biochar reduces the release of toxic elements under dynamic redox conditions in a contaminated floodplain soil. Chemosphere, 142, 41–47.
Rizwan, M., Ali, S., Qayyum, M. F., Ibrahim, M., Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Abbas, T., et al. (2016). Mechanisms of biochar-mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: A critical review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(3), 2230–2248.
Rizwan, M., Ali, S., Qayyum, M. F., Ok, Y. S., Adrees, M., Ibrahim, M., et al. (2017). Effect of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on growth and physiology of globally important food crops: A critical review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 322, 2–16.
SAS. (2004). SAS/STAT user’s guide, version 9.1. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
Schimmelpfennig, S., & Glaser, B. (2012). One step forward toward characterization: Some important material properties to distinguish biochars. Journal of Environmental Quality, 41(4), 1001–1013.
Seneviratne, M., Weerasundara, L., Ok, Y. S., Rinklebe, J., & Vithanage, M. (2017). Phytotoxicity attenuation in Vigna radiata under heavy metal stress at the presence of biochar and N fixing bacteria. Journal of Environmental Management, 186, 293–300.
Servin, A. D., De la Torre-Roche, R., Castillo-Michel, H., Pagano, L., Hawthorne, J., Musante, C., et al. (2017). Exposure of agricultural crops to nanoparticle CeO2 in biochar-amended soil. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 110, 147–157.
Shainberg, I., Sumner, M., Miller, W., Farina, M., Pavan, M., & Fey, M. (1989). Use of gypsum on soils: A review. In B. A. Stewart (Ed.), Advances in soil science (pp. 1–111). Berlin: Springer.
Shieldrick, B., & Wang, C. (1993). Particle size distribution. Soil sampling and methods of analysis. In M. R. Carter (Ed.), Canadian society of soil science (pp. 499–513). Boca Raton, FL: Lewis Publishers.
Stefaniuk, M., Oleszczuk, P., & Ok, Y. S. (2016). Review on nano zerovalent iron (nZVI): From synthesis to environmental applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 287, 618–632.
Sumner, M., Miller, W., Sparks, D., Page, A., Helmke, P., Loeppert, R., et al. (1996). Cation exchange capacity and exchange coefficients. In R. S. Swift & D. L. Sparks (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 3-chemical methods. Volume 5 of Soil Science Society of America books series (pp. 1201–1229). Madison, WI: Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy.
USEPA. (1995). Method 3051: Microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices. In: SW-846 (3rd Eds.), Test methods for evaluating solid waste: Physical/chemical methods, update III, 1995 (pp. 122–142). Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Usman, A., Kuzyakov, Y., & Stahr, K. (2005). Effect of clay minerals on immobilization of heavy metals and microbial activity in a sewage sludge-contaminated soil. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 5(4), 245–252.
Van Zwieten, L., Kimber, S., Morris, S., Chan, K., Downie, A., Rust, J., et al. (2010). Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant and Soil, 327(1–2), 235–246.
Vangronsveld, J., Herzig, R., Weyens, N., Boulet, J., Adriaensen, K., Ruttens, A., et al. (2009). Phytoremediation of contaminated soils and groundwater: Lessons from the field. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 16(7), 765–794.
Veihmeyer, F., & Hendrickson, A. (1931). The moisture equivalent as a measure of the field capacity of soils. Soil Science, 32(3), 181–194.
Wang, C., Liu, H., Chen, J., Tian, Y., Shi, J., Li, D., et al. (2014). Carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes aggravated biochemical and subcellular damages in leaves of broad bean (Vicia faba L.) seedlings under combined stress of lead and cadmium. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 274, 404–412.
Wang, W.-J., He, H.-S., Zu, Y.-G., Guan, Y., Liu, Z.-G., Zhang, Z.-H., et al. (2011). Addition of HPMA affects seed germination, plant growth and properties of heavy saline-alkali soil in northeastern China: Comparison with other agents and determination of the mechanism. Plant and Soil, 339(1–2), 177–191.
Wu, H., Che, X., Ding, Z., Hu, X., Creamer, A. E., Chen, H., et al. (2016). Release of soluble elements from biochars derived from various biomass feedstocks. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(2), 1905–1915.
Xu, Y., Fang, Z., & Tsang, E. P. (2016). In situ immobilization of cadmium in soil by stabilized biochar-supported iron phosphate nanoparticles. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(19), 19164–19172.
Zhang, W. X., & Elliott, D. W. (2006). Applications of iron nanoparticles for groundwater remediation. Remediation Journal, 16(2), 7–21.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (NRF-2015R1A2A2A11001432).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awad, Y.M., Vithanage, M., Niazi, N.K. et al. Potential toxicity of trace elements and nanomaterials to Chinese cabbage in arsenic- and lead-contaminated soil amended with biochars. Environ Geochem Health 41, 1777–1791 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-9989-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-9989-3