Abstract
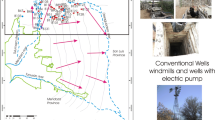
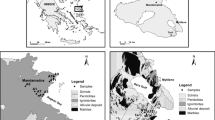
A survey conducted in water wells located in the rhyolithic volcanic area of Mandamados, Lesvos Island, Greece, indicated that significant seasonal variation of arsenic concentration in groundwater exists mainly in wells near the coastal zone. However, there were differences among those coastal wells with regard to the processes and factors responsible for the observed seasonal variability of the element, although they are all located in a small homogeneous area. These processes and factors include (a) a higher rate of silicate weathering and ion exchange during the dry period followed by the dilution by the recharge water during the wet period, (b) enhanced desorption promoted by higher pH in summer and subsequent dilution of As by rainwater infiltration during the wet period, and (c) reductive dissolution of Mn during the wet period and by desorption under high pH values during the dry period. On the other hand, in wells located in higher-relief regions, the concentration of As in groundwater followed a fairly constant pattern throughout the year, which is probably related to the faster flow of groundwater in this part of the area due to a higher hydraulic gradient. In general, seasonal variation of As in groundwater in the study area was found to be related to geology, recharge rate, topography—distance from coast, and well depth.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloupi, M., Angelidis, M., Gavriil, A., Koulousaris, M., & Varnavas, S. (2009). Influence of geology on arsenic concentrations in ground and surface water in central Lesvos, Greece. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 151(1-4), 383–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0280-z.
Anawar, H. M., Akai, J., Komaki, K., Terao, H., Yoshioka, T., Ishizuka, T., Safiullah, S., Kato, K. (2003). Geochemical occurrence of arsenic in groundwater of Bangladesh: sources and mobilization processes. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 77(2-3), 109–131.
APHA, AWWA, WEF. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (1993). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Rotterdam: A. A. Balkema.
Ayotte, J. D., Belaval, M., Olson, S. A., Burow, K. R., Flanagan, S. M., Hinkle, S. R., & Lindsey, B. D. (2015). Factors affecting temporal variability of arsenic in groundwater used for drinking water supply in the United States. Science of the Total Environment, 505, 1370–1379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.057.
Bhattacharya, P., Claesson, M., Bundschuh, J., Sracek, O., Fagerberg, J., Jacks, G., Martin, R., Storniolo, A., & Thir, J. (2006). Distribution and mobility of arsenic in the Rio Dulce alluvial aquifers in Santiago del Estero Province, Argentina. Science of the Total Environment, 358(1-3), 97–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.04.048.
Bhattacharya, P., Hossain, M., Rahman, S. N., Robinson, C., Nath, B., Rahman, M., Islam, M. M., von Brömssen, M., Ahmed, K. M., Chowdhury, D., Rahman, M., Persson, L. A., & Vahter, M. (2011). Temporal and seasonal variability of arsenic in drinking water wells in Matlab, southeastern Bangladesh: a preliminary evaluation on the basis of a 4 year study. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 46(11), 1177–1184.
Biswas, A., Majumder, S., Neidhardt, H., Halder, D., Bhowmick, S., Mukherjee-Goswami, A., Kundu, A., Saha, D., Berner, Z., & Chatterjee, D. (2011). Groundwater chemistry and redox processes: depth dependent arsenic release mechanism. Applied Geochemistry, 26(4), 516–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.01.010.
Biswas, A., Nath, B., Bhattacharya, P., Halder, D., Kundu, A. K., Mandal, U., Mukherjee, A., Chatterjee, D., Mörth, C.-M., & Jacks, G. (2012). Hydrogeochemical contrast between brown and grey sand aquifers in shallow depth of Bengal Basin: consequences for sustainable drinking water supply. Science of the Total Environment, 431, 402–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.031.
Biswas, A., Neidhardt, H., Kundu, A. K., Halder, D., Chatterjee, D., Berner, Z., Jacks, G., & Bhattacharya, P. (2014). Spatial, vertical and temporal variation of arsenic in shallow aquifers of the Bengal Basin: controlling geochemical processes. Chemical Geology, 387, 157–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.08.022.
Blanco, M. D. C., Paoloni, J. D., Morrás, H. J. M., Fiorentino, C. E., & Sequeira, M. E. (2006). Content and distribution of arsenic in soils, sediments and groundwater environments of the southern pampa region, Argentina. Environmental Toxicology, 21(6), 561–574. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20219.
Bondu, R., Cloutier, V., & Rosa, E. (2016). A review and evaluation of the impacts of climate change on geogenic arsenic in groundwater from fractured bedrock aquifers. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227(9), art. no. 296.
Borsi, S., Ferrara, G., Innocenti, F., & Mazzuoli, R. (1972). Geochronology and petrology of recent volcanics in the eastern Aegean Sea (West Anatolia and Lesvos Island). Bulletin Volcanologique, 36(3), 473–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02597122.
Bresciani, E., Ordens, C. M., Werner, A. D., Batelaan, O., Guan, H., & Post, V. E. A. (2014). Spatial variability of chloride deposition in a vegetated coastal area: implications for groundwater recharge estimation. Journal of Hydrology, 519, 1177–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.08.050.
Brikowski, T. H., Neku, A., Shrestha, S. D., & Smith, L. S. (2014). Hydrologic control of temporal variability in groundwater arsenic on the Ganges floodplain of Nepal. Journal of Hydrology, 518, 342–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.09.021.
Bundschuh, J., Farias, B., Martin, R., Storniolo, A., Bhattacharya, P., Cortes, J., Bonorino, G., & Albouy, R. (2004). Groundwater arsenic in the Chaco–Pampean plain, Argentina: case study from Robles country, Santiago del Estero Province. Applied Geochemistry, 19(2), 231–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.09.009.
Bundschuh, J., Litter, M. I., Parvez, F., Roman-Ross, G., Nicolli, H. B., et al. (2012). One century of arsenic exposure in Latin America: a review of history and occurrence from 14 countries. Science of the Total Environment, 429, 2–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.024.
Cheng, Z., van Geen, A., Seddique, A. A., & Ahmed, K. M. (2005). Limited temporal variability of arsenic concentrations in 20 wells monitored for 3 years in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(13), 4759–4766. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048065f.
Costa Goncalves, J. A., de Lena, J. C., Paiva, J. F., Nalini, H. A., & Pereira, J. C. (2007). Arsenic in the groundwater of Ouro Preto (Brazil): its temporal behavior as influenced by the hydric regime and hydrogeology. Environmental Geology, 53(4), 785–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0691-0.
Cullen, W. R., & Reimer, K. J. (1989). Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chemical Reviews, 89(4), 713–764. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00094a002.
Desbarats, A. J., Pal, T., Mukherjee, P. K., & Beckie, R. D. (2017). Geochemical evolution of groundwater flowing through arsenic source sediments in an aquifer system of West Bengal, India. Water Resources Research, 53. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR020863.
Dhar, R. K., Zheng, Y., Stute, M., van Geen, A., Cheng, Z., Shanewaz, M., Shamshudduha, M., Haque, M. A., Rahman, M. W., & Ahmed, K. M. (2008). Temporal variability of groundwater chemistry in shallow and deep aquifers of Araihazar, Bangladesh. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 99(1-4), 97–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2008.03.007.
Diamantis, I. B., & Petalas, C. P. (1989). Seawater intrusion into coastal aquifers of Thrace and its impact on the environment. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 20-21(1), 291–305. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248909357389.
Dzombak, D. A., & Morel, F. M. M. (1990). Surface complexation modelling—hydrous ferric oxide. New York: John Wiley.
EC. Council Directive (98/83/EC). (1998). On the quality of water intended for human consumption. Official Journal of the European Communities, L 330, 32–54.
EPA. (2003). Standard operating procedure (SOP) for ground water sampling. New England: Environmental Protection Agency.
EPA. (2006). Data quality assessment: statistical methods for practitioners, Environmental Protection Agency. EPA QA/G-9S.
Farooq, S. H., Chandrasekharam, D., Norra, S., Berner, Z., Eiche, E., Thambidurai, P., & Stüben, D. (2011). Temporal variations in arsenic concentration in the groundwater of Murshidabad District, West Bengal, India. Environment and Earth Science, 62(2), 223–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0516-4.
García, M. G., Sracek, O., Fernández, D. S., & Hidalgo, M. D. V. (2007). Factors affecting arsenic concentration in groundwaters from northwestern Chaco-Pampean plain, Argentina. Environmental Geology, 52(7), 1261–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0564-y.
Geography of Natural Disasters Laboratory. (2010–2011). Geography of Natural Disasters Laboratory, Department of Geography, University of Aegean. http://meteo.aegean.gr/. Accessed October 2011.
Guo, H., Yang, S., Tang, X., Li, Y., & Shen, Z. (2008). Groundwater geochemistry and its implications for arsenic mobilization in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Science of the Total Environment, 393(1), 131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.12.025.
Guo, H., Zhang, D., Wen, D., Wu, Y., Ni, P., Jiang, Y., Guo, Q., Li, F., Zheng, H., & Zhou, Y. (2014). Arsenic mobilization in aquifers of the southwest Songnen basin, P.R. China: evidences from chemical and isotopic characteristics. Science of the Total Environment, 490, 590–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.050.
Halim, M. A., Majumder, R. K., Nessa, S. A., Oda, K., Hiroshiro, Y., Saha, B. B., Hassain, S. M., Latif, S. A., Islam, M. A., & Jinno, K. (2009). Groundwater contamination with arsenic in Sherajdikhan, Bangladesh: geochemical and hydrological implications. Environmental Geology, 58(1), 73–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1493-8.
Hecht, J. (1971–1974). Geologic map of Lesvos Island (5 sheets). Athens: (Hellenic) National Institute of Geological and Mining Research (IGME).
Hellenic National Meteorological Service. (1955–1997). http://www.hnms.gr/hnms/greek/climatology/climatology_region_diagrams_html?dr_city=Mytilini. Accessed June 2015.
Hellenic Statistical Authority population census (EL.STAT). (2011). http://www.statistics.gr/el/2011-census-pop-hous. Accessed 2017.
Hinkle, S. R., & Polette, D. J. (1999). Arsenic in ground water of the Willamette Basin, Oregon. U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report, 98–4205.
Kallergis, G. A. (1986). Applied hydrogeology. Athens: T.C.G. Publ In Greek.
Katsoyiannis, I. A., Hug, S. J., Ammann, A., Zikoudi, A., & Hatziliontos, C. (2007). Arsenic speciation and uranium concentrations in drinking water supply wells in northern Greece: correlations with redox indicative parameters and implications for groundwater treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 383(1-3), 128–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.04.035.
Katsoyiannis, I. A., Voegelin, A., Zouboulis, A. I., & Hug, S. J. (2015). Enhanced As(III) oxidation and removal by combined use of zero valent iron and hydrogen peroxide in aerated waters at neutral pH values. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 297, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.038.
Kim, K., & Yun, S. T. (2005). Buffering of sodium concentration by cation exchange in the groundwater system of a sandy aquifer. Geochemical Journal, 39(3), 273–284. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.39.273.
Kontis, E. E., & Gaganis, P. (2012). Hydrochemical characteristics and groundwater quality in the island of Lesvos, Greece. Global NEST Journal, 14(4), 422–430.
Lamera S. (2004). The polychnitos ignimbrite of Lesvos Island, Phd Thesis, Department of Geology, University of Patra (in Greek).
Lu, H., Zhu, Z., Zhang, H., & Qiu, Y. (2016). In situ oxidation and efficient simultaneous adsorption of arsenite and arsenate by Mg-Fe-LDH with persulfate intercalation. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227(4), art no. 125.
Manning, B. A., & Goldberg, S. (1996). Modeling competitive adsorption of arsenate with phosphate and molybdate on oxide minerals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 60(1), 121–131. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1996.03615995006000010020x.
McArthur, J. M., Banerjee, D. M., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Mishra, R., Purohit, R., Ravenscroft, P., Cronin, A., Howarth, R. J., Chatterjee, A., Talukder, T., Lowry, D., Houghton, S., & Chadha, D. K. (2004). Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: the example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications. Applied Geochemistry, 19(8), 1255–1293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.02.001.
McArthur, J. M., Sikdar, P. K., Hoque, M. A., & Ghosal, U. (2012). Waste-water impacts on groundwater: Cl/Br ratios and implications for arsenic pollution of groundwater in the Bengal Basin and Red River Basin, Vietnam. Science of the Total Environment, 437, 390–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.068.
Meng, X., Korfiatis, G. P., Christodoulatos, C., & Bang, S. (2001). Treatment of Bangladesh well water using a household co-precipitation and filtration system. Water Research, 35, 2508–2810.
Mtoni, Y., Mjemah, I. C., Bakundukize, C., Van Camp, M., Martens, K., & Walraevens, K. (2013). Saltwater intrusion and nitrate pollution in the coastal aquifer of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70(3), 1091–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2197-7.
Neidhardt, H., Berner, Z., Freikowski, D., Biswas, A., Winter, J., Chatterjee, D., & Norra, S. (2013). Influences of groundwater extraction on the distribution of dissolved As in shallow aquifers of West Bengal, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 262, 941–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.044.
Nickson, R. T., McArthur, J. M., Ravencroft, P., Burgess, W. G., & Ahmed, K. M. (2000). Mechanism of arsenic release to groundwater, Bangladesh and West Bengal. Applied Geochemistry, 15(4), 403–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(99)00086-4.
Nicolli, H. B., Bundschuh, J., Blanco, M. D. C., Tujchneider, O. C., Panarello, H. O., Dapeña, C., & Rusansky, J. E. (2012). Arsenic and associated trace-elements in groundwater from the Chaco-Pampean plain, Argentina: results from 100 years of research. Science of the Total Environment, 429, 36–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.048.
Nordstrom, D. K. (2002). Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in groundwater. Science, 296(5576), 2143–2145. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1072375.
O.G.G. (2001). Quality of water intended for human consumption, in compliance to the Council Directive 98/83/ EC of 3 November 1998 (Joint Ministerial Decision Υ2/2600/2001). Official Government Gazette of the HellenicRepublic (O.G.G.), Issue B’, No 892.
Ormachea Muñoz, M. R., Wern, H., Johnsson, F., Bhattacharya, P., Sracek, O., Thunvik, R., Quintanilla, J., & Bundschuh, J. (2013). Geogenic arsenic and other trace elements in the shallow hydrogeologic system of Southern Poopó Basin, Bolivian. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 262, 924–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.078.
Panno, S. V., Hackley, K. C., Hwang, H. H., Greenberg, S. E., Krapac, I. G., Landsberger, S., & O’Kelly, D. J. (2006). Characterization and identification of Na-Cl sources in ground water. Ground Water, 44(2), 176–187.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. U.S.G.S. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259, Denver, CO, USA.
Pe-Piper, G. (1980). Geochemistry of Shoshonites, Lesbos, Greece. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 72(4), 387–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00371346.
Pujari, P. R., & Soni, A. K. (2009). Sea water intrusion studies near Kovaya limestone mine, Saurashtra coast, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 154(1-4), 93–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0380-9.
Rango, T., Vengosh, A., Dwyer, G., & Bianchini, G. (2013). Mobilization of arsenic and other naturally occurring contaminants in groundwater of the main Ethiopian rift aquifers. Water Research, 47(15), 5801–5818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.07.002.
Raychowdhury, N., Mukherjee, A., Bhattacharya, P., Johannesson, K., Bundschuh, J., Sifuentes, G., Nordberg, E., Martin, R., & Storniolo, A. (2014). Provenance and fate of arsenic and other solutes in the Chaco-Pampean plain of the Andean foreland, Argentina: from perspectives of hydrogeochemical modeling and regional tectonic setting. Journal of Hydrology, 518, 300–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.07.003.
Revelle, R. (1941). Criteria for recognizing sea water in groundwater. American Geophysical Union Transactions, 22, 593–597.
Reyes - Gómez, V. M., Alarcón - Herrera, M. T., Gutiérrez, M., & López, D. N. (2015). Arsenic and fluoride variations in groundwater of an endorheic basin undergoing land-use changes. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 68(2), 292–304.
Rodriguez, R., Ramos, J. A., & Armienta, A. (2004). Groundwater arsenic variation: the role of local geology and rainfall. Applied Geochemistry, 19(2), 245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.09.010.
Savarimuthu, X., Hira-Smith, M. M., Yuan, Y., von Ehrenstein, O. S., Das, S., Ghosh, N., Guha Mazumder, D. N., & Smith, A. H. (2006). Seasonal variation of arsenic concentration in tube wells in West Bengal, India. Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition, 24, 1–5.
Schaefer, M. V., Ying, S. C., Benner, S. G., Duan, Y., Wang, Y., & Fendorf, S. (2016). Aquifer arsenic cycling induced by seasonal hydrologic changes within the Yangtze River basin. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(7), 3521–3529. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04986.
Sdao, F., Parisi, S., Kalisperi, D., Pascale, S., Soupios, P., Lydakis-Simantiris, N., & Kouli, M. (2012). Geochemistry and quality of the groundwater from the karstic and coastal aquifer of Geropotamos River basin at north-central Crete, Greece. Environmental Earth Sciences, 67(4), 1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1558-6.
Sengupta, S., Sracek, O., Jean, J. S., Lu, H. Y., Wang, C. H., Palcsu, L., Liu, C. C., Jen, C. H., & Bhattacharya, P. (2014). Spatial variation of groundwater arsenic distribution in the Chianan plain, SW Taiwan: role of local hydrogeological factors and geothermal sources. Journal of Hydrology, 518, 393–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.03.067.
Shamsudduha, M., Marzen, L. J., Uddin, A., Lee, M. K., & Saunders, J. A. (2009). Spatial relationship of groundwater arsenic distribution with regional topography and water-table fluctuations in the shallow aquifers in Bangladesh. Environmental Geology, 57(7), 1521–1535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1429-3.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behavior and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17(5), 517–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5.
Smedley, P. L., Nicolli, H. B., Macdonald, D. M. J., Barros, A. J., & Tullioc, J. O. (2002). Hydrogeochemistry of arsenic and other inorganic constituents in groundwaters from La Pampa, Argentina. Applied Geochemistry, 17(3), 259–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00082-8.
Smedley, P. L., Kinniburgh, D. G., Macdonald, D. M. J., Nicolli, H. B., Barros, A. J., Tullio, J. O., Pearce, J. M., & Alonso, M. S. (2005). Arsenic associations in sediments from the loess aquifer of La Pampa, Argentina. Applied Geochemistry, 20(5), 989–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.10.005.
Sracek, O., Bhattachayra, P., Jacks, G., Gustafsson, J. P., & von Brömssen, M. (2004). Behavior of arsenic and geochemical modeling of arsenic enrichment in aquatic environments. Applied Geochemistry, 19(2), 169–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.09.005.
Stollenwerk, K. G. (2003). Geochemical processes controlling transport of arsenic in groundwater: a review of adsorption. In A. H. Welch & K. G. Stollenwerk (Eds.), Arsenic in ground water: geochemistry and occurrence (pp. 67–100). New York: Kluwer Academic Publishers. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-47956-7_3.
Stumm, W. (1992). Chemistry of the solid-water interface, processes at the mineral-water and particle-water interface in natural systems. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Interscience.
Stumm, W., & Morgan, J. J. (1996). Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Todd, D. K. (1980). Groundwater hydrology (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
USEPA. (2001). The arsenic and clarifications to compliance and new source contaminants monitoring. US Environmental Protection Agency, 66 FR 6976.
von Brömssen, M., Jakariya, M., Bhattacharya, P., Ahmed, K. M., Hasan, M. A., Sracek, O., Jonsson, L., Lundell, L., & Jacks, G. (2007). Targeting low-arsenic aquifers in Matlab Upazila, southeasten Bangladesh. Science of the Total Environment, 379(2–3), 121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.06.028.
von Brömssen, M., Larsson, S. H., Bhattacharya, P., Hasan, M. A., Ahmed, K. M., Jakariya, M., Sikder, M. A., Sracek, O., Biven, A., Dousova, B., Patriarca, C., Thunvik, R., & Jacks, G. (2008). Geochemical characterisation of shallow aquifer sediments of Matlab Upazila, southeastern Bangladesh—implications for targeting low-As aquifers. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 99(1–4), 137–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2008.05.005.
Welch, A. H., Westjohn, D. B., Helsel, D. R., & Wanty, R. B. (2000). Arsenic in ground water of the United States: occurrence and geochemistry. Ground Water, 38(4), 589–604. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2000.tb00251.x.
WHO. (2001). Environmental health criteria 224, arsenic and arsenic compounds, Inter-organization programme for the sound management of chemicals. Geneva: World Health Organization.
WHO. (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn. On line: http://www.who.int/publications/2011/9789241548151_eng.pdf. Accessed June 2016.
Yokota, H., Tanabe, K., Sezaki, M., Akiyoshi, Y., Miyata, T., Kawahara, K., Tsushima, S., Hironaka, H., Takafuji, H., Rahaman, M., Ahmad, S. K. A., Sayed, M. H. S. U., & Faruquee, M. H. (2001). Arsenic contamination of ground and pond water and water purification system using pond water in Bangladesh. Engineering Geology, 60(1-4), 323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00112-5.
Zkeri, E., Aloupi, M., & Gaganis, P. (2015). Natural occurrence of arsenic in groundwater from Lesvos Island, Greece. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226(9), 1–16.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers for their support and comments that improved the original manuscript.
Funding
E. Zkeri would like to thank the Greek State Scholarships Foundation (I.K.Y.) for funding this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 145 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zkeri, E., Aloupi, M. & Gaganis, P. Seasonal and spatial variation of arsenic in groundwater in a rhyolithic volcanic area of Lesvos Island, Greece. Environ Monit Assess 190, 44 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6395-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6395-3