Abstract
Cholesterol is a waxy steroid metabolite substance and plays an important role in the brain, nervous, and immune systems of humans. The level of cholesterol in human serum has become an important index for clinical diagnosis and prevention of cardiovascular disease. In this study, a highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor for cholesterol measurement has been developed based on reduced graphene oxide-chitosan-ferrocene carboxylic acid/platinum nanoparticle (RGO-CS-Fc/Pt NPs) modified screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE). Under the effect of cholesterol oxidase (CHOD) and cholesterol esterase (CHER), the cholesterol was oxidized to generate hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which can be disintegrated into H2O with the synergistic catalysis of RGO-CS-Fc/Pt NPs and produce the redox response current of H2O2 that could be determined by electrochemical amperometric (i-t) method. The prepared cholesterol biosensor was achieved by integrating of the high electrocatalytic efficiency of Pt NPs, high electronic conductivity and large surface area of RGO, the reversible electrochemical behavior of Fc, and good biocompatibility of CS. The measured of redox response current and cholesterol concentration have a good linearity in the range of 0.5–4.0 mg/mL, low detection limit of 5.70 μg/mL (S/N = 3), and good sensitivity of 0.871 nA/mM/cm2. Moreover, the RGO-CS-Fc/Pt NPs cholesterol biosensor exhibited excellent specificity, acceptable reproducibility, and higher recoveries in the detection of clinical serum samples, showing great potential for clinical diagnosis.

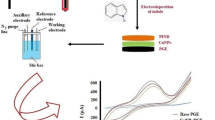
Schematic presentation of an electrochemical biosensor based on RGO-CS-Fc/Pt NPs for cholesterol detection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad R, Tripathy N, Kim SH, Umar A, Al-Hajry A, Hahn YB (2014) High performance cholesterol sensor based on ZnO nanotubes grown on Si/Ag electrodes. Electrochem Commun 38:4–7
Arya SK, Datta M, Malhotra DB (2008) Recent advances in cholesterol biosens. Bioelectron 23:1083–1100
Bai ZH, Li GY, Liang JT, Su J, Zhang Y, Chen HZ, Huang Y, Sui WG, Zhao YX (2016) Non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensor based on Pt NPs/RGO-CS-Fc nano-hybrids for the detection of hydrogen peroxide in living cells. Biosens Bioelectron 82:185–194
Bairagi PK, Verma N (2018) Electrochemically deposited dendritic poly (methyl orange) nanofilm on metal-carbon-polymer nanocomposite: a novel non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensor for cholesterol. J Electroanal Chem 814:134–143
Batra N, Tomar M, Gupta V (2015) ZnO-CuO composite matrix based reagentless biosensor for detection of Total cholesterol. Biosens Bioelectron 67:263–271
Fan L, Zhang Q, Wang K, Li F, Niu L (2012) Ferrocene functionalized graphene: preparation, characterization and efficient Electron transfer toward sensors of H2O2. J Mater Chem 22:6165–6170
Hassanzadeh J, Khataee A, Eskandari H (2018) Encapsulated cholesterol oxidase in metal-organic framework and biomimetic ag nanocluster decorated MoS2 nanosheets for sensitive detection of cholesterol. Sens Actuator B-Chem 259:402–410
Hsieh C, Chena Y, Hwang DW (2013) Effects of cholesterol on membrane molecular dynamics studied by fast field cycling NMR relaxometry. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:16634–16640
Huan J, Liu Q, Fei A, Qian J, Dong X, Qiu B, Mao H, Wang K (2015) Amplified solid-state electrochemiluminescence detection of cholesterol in near-infrared range based on CdTe quantum dots decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes@reduced graphene oxide nanoribbons. Biosens Bioelectron 73:221–227
Huang Y, Xue YW, Zeng JX, Li SS, Wang ZH, Dong CY, Li GY, Liang JT, Zhou ZD (2018) Non-enzymatic electrochemical hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on reduction graphene oxide-persimmon tannin-platinum nanocomposite. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 92:590–598
Karthick NA, Thangappan R, Arivanandhan M, Gnanamani A, Jayavel R (2018) A facile synthesis of ferrocene functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposite for electrochemical sensing of lead. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 28:1021–1028
Kaur G, Tomar M, Gupta V (2018) Development of a microfluidic electrochemical biosensor: prospect for point-of-care cholesterol monitoring. Sensors Actuator B Chem 261:460–466
Li C, Wu Z, Yang H, Deng L, Chen X (2017) Reduced graphene oxide-cyclodextrin-chitosan electrochemical sensor: effective and simultaneous determination of o- and p-nitrophenols. Sensors Actuator B Chem 251:446–454
Liu J, Yang C, Shang Y, Zhang P, Liu J, Zheng J (2018) Preparation of a nanocomposite material consisting of cuprous oxide, polyaniline and reduced graphene oxide, and its application to the electrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185(3):172–179
Novak A, Gutiérrez-Zamora M, Domenech L, Suñé-Negre JM, Miñarro M, García-Montoya E, Llop JM, Ticó JR, Pérez-Lozano P (2018) Development and validation of a simple high-performance liquid chromatography analytical method for simultaneous determination of phytosterols, cholesterol and squalene in parenteral lipid emulsions. Biomed Chromatogr 32(2):4084–4092
Qiu J, Huang J, Liang R (2011) Nanocomposite film based on graphene oxide for high performance flexible glucose biosensor. Sensors Actuator B Chem 160:287–294
Qureshi RN, Kaal E, Janssen HG, Schoenmakers PJ, Kok WT (2011) Determination of cholesterol and triglycerides in serum lipoproteins using flow field-flow fractionation coupled to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 706:361–366
Rajabzadeh S, Rounaghi GH, Arbab-Zavar MH, Ashraf N (2014) Development of a dimethyl disulfide electrochemical sensor based on electrodeposited reduced graphene oxide-chitosan modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim Acta 135:543–549
Razzazi-Fazeli E, Kleineisen S, Luf W (2000) Determination of cholesterol qxides in processed food using highperformance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. J Chromatogr A 896:321–334
Ruecha N, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O (2011) A fast and highly sensitive detection of cholesterol using polymer microfluidic devices and amperometric system. Talanta 84(5):1323–1328
Sharma D, Lee J, Seo J, Shin H (2017) Development of a sensitive electrochemical enzymatic reaction-based cholesterol biosensor using nano-sized carbon interdigitated electrodes decorated with gold nanoparticles. Sensors 17:2128–2143
Shrestha BK, Ahmad R, Shrestha S, Park CH, Kim CS (2017) In situ synthesis of cylindrical spongy polypyrrole doped protonated graphitic carbon nitride for cholesterol sensing application. Biosens Bioelectron 94:686–693
Soorya VC, Berchmans S (2016) Flower like bi structures on Pt surface facilitating effective cholesterol biosensing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 64:183–189
Soylemez S, Udum YA, Kesik M, Hizliates CG, Ergun Y, Toppare L (2015) Electrochemical and optical properties of a conducting polymer and its use in a novel biosensor for the detection of cholesterol. Sensors Actuator B Chem 212:425–433
Wang C, Tan X, Chen S, Yuan R, Hu F, Yuan D, Xiang Y (2012) Highly-sensitive cholesterol biosensor based on platinum-gold hybrid functionalized ZnO nanorods. Talanta 94:263–270
Wang L, Zhang YY, Cheng CS, Liu XL, Jiang H, Wang XM (2015) Highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor for evaluation of oxidative stress based on the nanointerface of graphene nanocomposites blended with gold, Fe3O4, and platinum nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:18441–18449
Wang Z, Xie F, Liu Z, Du G, Asiri AM, Sun X (2017) High-performance non-enzyme hydrogen peroxide detection in neutral solution: using a nickel borate nanoarray as a 3D electrochemical sensor. Chemistry 23(64):16179–16183
Wisitsoraat A, Karuwan C, Wong-Ek K, Phokharatkul D, Sritongkham P, Tuantranont A (2009) High sensitivity electrochemical cholesterol sensor utilizing a vertically aligned carbon nanotube electrode with electropolymerized enzyme immobilization. Sensors 9:8658–8668
Wu ZM, Zhang L, Guan QQ, Ning P, Ye DQ (2014) Preparation of alpha-zirconium phosphate-pillared reduced graphene oxide with increased adsorption towards methylene blue. Chem Eng J 258:77–84
Yang JH, Myoung N, Hong HG (2012) Facile and controllable synthesis of Prussian blue on chitosan-functionalized graphene nanosheets for the electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. Electrochim Acta 81:37–43
Yang M, Kim DS, Lee TJ, Lee SJ, Lee KG, Choi BG (2016) Polyoxometalate-grafted graphene nanohybrid for electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. J Colloid Interface Sci 468:51–56
Yang Y, Liu Q, Liu Y, Cui J, Liu H, Wang P, Li Y, Chen L, Zhao Z, Dong Y (2017) A novel label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for carcinoembryonic antigen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 90:31–38
Yang S, Zhang F, Wang Z, Liang Q (2018) A graphene oxide-based label-free electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of alpha-fetoprotein. Biosens Bioelectron 112:186–192
Yildirimoglu F, Arslan F, Cete S, Yasar A (2009) Preparation of a polypyrrole-polyvinylsulphonate composite film biosensor for determination of cholesterol based on entrapment of cholesterol oxidase. Sensors 9:6435–6445
Zhao Z, Lei W, Zhang X, Wang B, Jiang H (2010) ZnO-based amperometric enzyme biosensors. Sensors 10:1216–1231
Zhao C, Zhang H, Zheng J (2017) A non-enzymatic electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensor based on Ag decorated boehmite nanotubes/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. J Electroanal Chem 784:55–61
Zhu L, Xu LL, Tan L, Tan H, Yang SF, Yao SZ (2013) Direct electrochemistry of cholesterol oxidase immobilized on gold nanoparticles-decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes and cholesterol sensing. Talanta 106:192–199
Zou J, Chen XQ, Zhao GQ, Jiang XY, Jiao FP, Yu JG (2019a) A novel electrochemical chiral interface based on the synergistic effect of polysaccharides for the recognition of tyrosine enantiomers. Talanta 195:628–637
Zou J, Zhao GQ, Teng J, Liu Q, Jiang XY, Jiao FP, Yu JG (2019b) Highly sensitive detection of bisphenol A in real water samples based on in-situ assembled graphene nanoplatelets and gold nanoparticles composite. Microchem J 145:693–702
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (nos. 81460451 and 8176053), the National Science Foundation of Guangxi Province of China (2016GXNSFAA380080), and the Innovation Project of GUET Graduate Education (nos. 2017YJCX90 and 2017YJCX100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the topical collection: “Nanoparticles in Biotechnology and Medicine"
Xiaoshan (Sean) Zhu, University of Nevada, Guest Editor
Research highlights
• A cholesterol electrochemical biosensor based on RGO-CS-Fc/Pt NPs was developed.
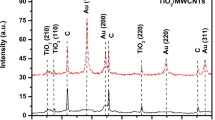
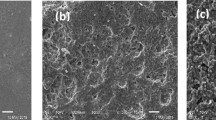
• The RGO-CS-Fc/Pt NPs cholesterol biosensor was characterized by SEM, XPS, and CV.
• The RGO-CS-Fc/Pt NPs cholesterol biosensor demonstrated a good linear calibration curve with R2 of 0.99897.
• The RGO-CS-Fc/Pt NPs cholesterol biosensor showed lower detection limit, higher specificity, acceptable stability, and good recovery.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Zeng, J., Zhao, L. et al. Amperometric cholesterol biosensor based on reduction graphene oxide-chitosan-ferrocene/platinum nanoparticles modified screen-printed electrode. J Nanopart Res 21, 162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4602-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4602-6