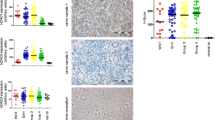
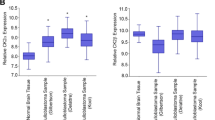
Abstract
Medulloblastomas are the most common malignant brain tumors in childhood. Emerging evidence suggests that medulloblastoma comprises at least four distinct diseases (WNT, SHH, Group 3 and 4) with different biology, clinical presentation, and outcome, with especially poor prognosis in Group 3. The tight connection of biology and clinical behavior in patients emphasizes the need for subgroup-specific preclinical models in order to develop treatments tailored to each subgroup. Herein we report on the novel cell line HD-MB03, isolated from tumor material of a patient with metastasized Group 3 medulloblastoma, and preclinical testing of different histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) in this model. HD-MB03 cells grow long term in vitro and form metastatic tumors in vivo upon orthotopic transplantation. HD-MB03 cells reflect the original Group 3 medulloblastoma at the histological and molecular level, showing large cell morphology, similar expression patterns for markers Ki67, p53, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), a gene expression profile most closely matching Group 3 medulloblastomas, and persistence of typical molecular alterations, i.e., isochromosome 17q [i(17q)] and MYC amplification. Protein expression analysis of HDACs 2, 5, 8, and 9 as well as the predictive marker HR23B showed intermediate to strong expression, suggesting sensitivity to HDACis. Indeed, treatment with HDACis Helminthosporium carbonum (HC)-toxin, vorinostat, and panobinostat revealed high sensitivity to this novel drug class, as well as a radiation-sensitizing effect with significantly increased cell death upon concomitant treatment. In summary, our data indicate that HD-MB03 is a suitable preclinical model for Group 3 medulloblastoma, and HDACis could represent a therapeutic option for this subgroup.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kool M, Koster J, Bunt J, Hasselt NE, Lakeman A, van Sluis P, Troost D, Meeteren NS, Caron HN, Cloos J, Mrsic A, Ylstra B, Grajkowska W, Hartmann W, Pietsch T, Ellison D, Clifford SC, Versteeg R (2008) Integrated genomics identifies five medulloblastoma subtypes with distinct genetic profiles, pathway signatures and clinicopathological features. PLOS One 3:e3088
Northcott P, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Eberhart C, Mack S, Bouffet E, Clifford S, Hawkins C, French P, Rutka J, Pfister S, Taylor M (2010) Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29(11): 1408–1414
Thompson MC, Fuller C, Hogg TL, Dalton J, Finkelstein D, Lau CC, Chintagumpala M, Adesina A, Ashley DM, Kellie SJ, Taylor MD, Curran T, Gajjar A, Gilbertson RJ (2006) Genomics identifies medulloblastoma subgroups that are enriched for specific genetic alterations. J Clin Oncol 24:1924–1931
Cho YJ, Tsherniak A, Tamayo P, Santagata S, Ligon A, Greulich H, Berhoukim R, Amani V, Goumnerova L, Eberhart CG, Lau CC, Olson JM, Gilbertson RJ, Gajjar A, Delattre O, Kool M, Ligon K, Meyerson M, Mesirov JP, Pomeroy SL (2010) Integrative genomic analysis of medulloblastoma identifies a molecular subgroup that drives poor clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol 29:1424–1430
Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M, Jones DT, Schlanstein M, Northcott PA, Cho YJ, Koster J, Schouten-van Meeteren A, van Vuurden D, Clifford SC, Pietsch T, von Bueren AO, Rutkowski S, McCabe M, Collins VP, Backlund ML, Haberler C, Bourdeaut F, Delattre O, Doz F, Ellison DW, Gilbertson RJ, Pomeroy SL, Taylor MD, Lichter P, Pfister SM (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: an international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol 123:473–484
Taylor MD, Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Remke M, Cho YJ, Clifford SC, Eberhart CG, Parsons DW, Rutkowski S, Gajjar A, Ellison DW, Lichter P, Gilbertson RJ, Pomeroy SL, Kool M, Pfister SM (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol 123:465–472
Milde T, Oehme I, Korshunov A, Kopp-Schneider A, Remke M, Northcott P, Deubzer HE, Lodrini M, Taylor MD, von Deimling A, Pfister S, Witt O (2010) HDAC5 and HDAC9 in medulloblastoma: novel markers for risk stratification and role in tumor cell growth. Clin Cancer Res 16:3240–3252
Deubzer HE, Ehemann V, Westermann F, Heinrich R, Mechtersheimer G, Kulozik AE, Schwab M, Witt O (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitor Helminthosporium carbonum (HC)-toxin suppresses the malignant phenotype of neuroblastoma cells. Int J Cancer 122:1891–1900
Jaboin J, Wild J, Hamidi H, Khanna C, Kim CJ, Robey R, Bates SE, Thiele CJ (2002) MS-27-275, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, has marked in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity against pediatric solid tumors. Cancer Res 62:6108–6115
Oehme I, Deubzer HE, Wegener D, Pickert D, Linke JP, Hero B, Kopp-Schneider A, Westermann F, Ulrich SM, von Deimling A, Fischer M, Witt O (2009) Histone deacetylase 8 in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. Clin Cancer Res 15:91–99
Rangwala S, Zhang C, Duvic M (2012) HDAC inhibitors for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Future Med Chem 4:471–486
Fouladi M, Park JR, Stewart CF, Gilbertson RJ, Schaiquevich P, Sun J, Reid JM, Ames MM, Speights R, Ingle AM, Zwiebel J, Blaney SM, Adamson PC (2010) Pediatric phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of vorinostat: a Children’s Oncology Group phase I consortium report. J Clin Oncol 28:3623–3629
Schmitt M, Pawlita M (2009) High-throughput detection and multiplex identification of cell contaminations. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e119
Milde T, Kleber S, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Koch P, Kopp HG, Jugold M, Deubzer HE, Oehme I, Lodrini M, Grone HJ, Benner A, Brustle O, Gilbertson RJ, von Deimling A, Kulozik AE, Pfister SM, Martin-Villalba A, Witt O (2011) A novel human high-risk ependymoma stem cell model reveals the differentiation-inducing potential of the histone deacetylase inhibitor Vorinostat. Acta Neuropathol 122(5):637–650
Shmelkov SV, Butler JM, Hooper AT, Hormigo A, Kushner J, Milde T, St Clair R, Baljevic M, White I, Jin DK, Chadburn A, Murphy AJ, Valenzuela DM, Gale NW, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD, D’Angelica M, Kemeny N, Lyden D, Rafii S (2008) CD133 expression is not restricted to stem cells, and both CD133+ and CD133- metastatic colon cancer cells initiate tumors. J Clin Invest 118:2111–2120
Pfister S, Remke M, Benner A, Mendrzyk F, Toedt G, Felsberg J, Wittmann A, Devens F, Gerber NU, Joos S, Kulozik A, Reifenberger G, Rutkowski S, Wiestler OD, Radlwimmer B, Scheurlen W, Lichter P, Korshunov A (2009) Outcome prediction in pediatric medulloblastoma based on DNA copy-number aberrations of chromosomes 6q and 17q and the MYC and MYCN loci. J Clin Oncol 27:1627–1636
Fattet S, Haberler C, Legoix P, Varlet P, Lellouch-Tubiana A, Lair S, Manie E, Raquin MA, Bours D, Carpentier S, Barillot E, Grill J, Doz F, Puget S, Janoueix-Lerosey I, Delattre O (2009) Beta-catenin status in paediatric medulloblastomas: correlation of immunohistochemical expression with mutational status, genetic profiles, and clinical characteristics. J Pathol 218:86–94
Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, Li J, Liang W, Bhagabati N, Braisted J, Klapa M, Currier T, Thiagarajan M, Sturn A, Snuffin M, Rezantsev A, Popov D, Ryltsov A, Kostukovich E, Borisovsky I, Liu Z, Vinsavich A, Trush V, Quackenbush J (2003) TM4: a free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. Biotechniques 34:374–378
Oehme I, Bosser S, Zornig M (2006) Agonists of an ecdysone-inducible mammalian expression system inhibit Fas Ligand- and Trail-induced apoptosis in the human colon carcinoma cell line RKO. Cell Death Differ 13:189–201
Fotheringham S, Epping MT, Stimson L, Khan O, Wood V, Pezzella F, Bernards R, La Thangue NB (2009) Genome-wide loss-of-function screen reveals an important role for the proteasome in HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Cancer Cell 15:57–66
Khan O, Fotheringham S, Wood V, Stimson L, Zhang C, Pezzella F, Duvic M, Kerr DJ, La Thangue NB (2010) HR23B is a biomarker for tumor sensitivity to HDAC inhibitor-based therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:6532–6537
Fakih MG, Fetterly G, Egorin MJ, Muindi JR, Espinoza-Delgado I, Zwiebel JA, Litwin A, Holleran JL, Wang K, Diasio RB (2010) A phase I, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of two schedules of vorinostat in combination with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in patients with refractory solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 16:3786–3794
Rathkopf D, Wong BY, Ross RW, Anand A, Tanaka E, Woo MM, Hu J, Dzik-Jurasz A, Yang W, Scher HI (2010) A phase I study of oral panobinostat alone and in combination with docetaxel in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 66:181–189
Ryan SL, Schwalbe EC, Cole M, Lu Y, Lusher ME, Megahed H, O’Toole K, Nicholson SL, Bognar L, Garami M, Hauser P, Korshunov A, Pfister SM, Williamson D, Taylor RE, Ellison DW, Bailey S, Clifford SC (2012) MYC family amplification and clinical risk-factors interact to predict an extremely poor prognosis in childhood medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol 123:501–513
von Hoff K, Hartmann W, von Bueren AO, Gerber NU, Grotzer MA, Pietsch T, Rutkowski S (2009) Large cell/anaplastic medulloblastoma: outcome according to myc status, histopathological, and clinical risk factors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 54:369–376
Kawauchi D, Robinson G, Uziel T, Gibson P, Rehg J, Gao C, Finkelstein D, Qu C, Pounds S, Ellison DW, Gilbertson RJ, Roussel MF (2012) A mouse model of the most aggressive subgroup of human medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell 21:168–180
Pei Y, Moore CE, Wang J, Tewari AK, Eroshkin A, Cho YJ, Witt H, Korshunov A, Read TA, Sun JL, Schmitt EM, Miller CR, Buckley AF, McLendon RE, Westbrook TF, Northcott PA, Taylor MD, Pfister SM, Febbo PG, Wechsler-Reya RJ (2012) An animal model of MYC-driven medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell 21:155–167
Zhao X, Liu Z, Yu L, Zhang Y, Baxter P, Voicu H, Gurusiddappa S, Luan J, Su JM, Leung HC, Li XN (2012) Global gene expression profiling confirms the molecular fidelity of primary tumor-based orthotopic xenograft mouse models of medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol 14:574–583
Gessi M, von Bueren AO, Rutkowski S, Pietsch T (2012) p53 expression predicts dismal outcome for medulloblastoma patients with metastatic disease. J Neurooncol 106:135–141
Ray A, Ho M, Ma J, Parkes RK, Mainprize TG, Ueda S, McLaughlin J, Bouffet E, Rutka JT, Hawkins CE (2004) A clinicobiological model predicting survival in medulloblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:7613–7620
Woodburn RT, Azzarelli B, Montebello JF, Goss IE (2001) Intense p53 staining is a valuable prognostic indicator for poor prognosis in medulloblastoma/central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumors. J Neurooncol 52:57–62
Pfaff E, Remke M, Sturm D, Benner A, Witt H, Milde T, von Bueren AO, Wittmann A, Schottler A, Jorch N, Graf N, Kulozik AE, Witt O, Scheurlen W, von Deimling A, Rutkowski S, Taylor MD, Tabori U, Lichter P, Korshunov A, Pfister SM (2010) TP53 mutation is frequently associated with CTNNB1 mutation or MYCN amplification and is compatible with long-term survival in medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28:5188–5196
Kunkele A, De Preter K, Heukamp L, Thor T, Pajtler KW, Hartmann W, Mittelbronn M, Grotzer MA, Deubzer HE, Speleman F, Schramm A, Eggert A, Schulte JH (2012) Pharmacological activation of the p53 pathway by nutlin-3 exerts anti-tumoral effects in medulloblastomas. Neuro Oncol 14:859–869
Hacker S, Karl S, Mader I, Cristofanon S, Schweitzer T, Krauss J, Rutkowski S, Debatin KM, Fulda S (2011) Histone deacetylase inhibitors prime medulloblastoma cells for chemotherapy-induced apoptosis by enhancing p53-dependent Bax activation. Oncogene 30:2275–2281
Furchert SE, Lanvers-Kaminsky C, Juurgens H, Jung M, Loidl A, Fruhwald MC (2007) Inhibitors of histone deacetylases as potential therapeutic tools for high-risk embryonal tumors of the nervous system of childhood. Int J Cancer 120:1787–1794
Sonnemann J, Kumar KS, Heesch S, Muller C, Hartwig C, Maass M, Bader P, Beck JF (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce cell death and enhance the susceptibility to ionizing radiation, etoposide, and TRAIL in medulloblastoma cells. Int J Oncol 28:755–766
Wegener D, Deubzer HE, Oehme I, Milde T, Hildmann C, Schwienhorst A, Witt O (2008) HKI 46F08, a novel potent histone deacetylase inhibitor, exhibits antitumoral activity against embryonic childhood cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 19:849–857
Berry DA, Herbst RS, Rubin EH (2012) Reports from the 2010 Clinical and Translational Cancer Research Think Tank meeting: design strategies for personalized therapy trials. Clin Cancer Res 18:638–644
Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T, Oehme I (2009) HDAC family: what are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett 277:8–21
Weichert W, Roske A, Niesporek S, Noske A, Buckendahl AC, Dietel M, Gekeler V, Boehm M, Beckers T, Denkert C (2008) Class I histone deacetylase expression has independent prognostic impact in human colorectal cancer: specific role of class I histone deacetylases in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 14:1669–1677
Kumar KS, Sonnemann J, le Hong TT, Buurman C, Adler F, Maass M, Volker U, Beck JF (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors, but not vincristine, cooperate with radiotherapy to induce cell death in medulloblastoma. Anticancer Res 27:465–470
Spiller SE, Ditzler SH, Pullar BJ, Olson JM (2008) Response of preclinical medulloblastoma models to combination therapy with 13-cis retinoic acid and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA). J Neurooncol 87:133–141
Blattmann C, Oertel S, Ehemann V, Thiemann M, Huber PE, Bischof M, Witt O, Deubzer HE, Kulozik AE, Debus J, Weber KJ (2010) Enhancement of radiation response in osteosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines by histone deacetylase inhibition. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:237–245
Seo SK, Jin HO, Woo SH, Kim YS, An S, Lee JH, Hong SI, Lee KH, Choe TB, Park IC (2011) Histone deacetylase inhibitors sensitize human non-small cell lung cancer cells to ionizing radiation through acetyl p53-mediated c-myc down-regulation. J Thorac Oncol 6:1313–1319
Chen X, Wong JY, Wong P, Radany EH (2011) Low-dose valproic acid enhances radiosensitivity of prostate cancer through acetylated p53-dependent modulation of mitochondrial membrane potential and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res 9:448–461
Chen X, Wong P, Radany E, Wong JY (2009) HDAC inhibitor, valproic acid, induces p53-dependent radiosensitization of colon cancer cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 24:689–699
Kawano T, Akiyama M, Agawa-Ohta M, Mikami-Terao Y, Iwase S, Yanagisawa T, Ida H, Agata N, Yamada H (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitors valproic acid and depsipeptide sensitize retinoblastoma cells to radiotherapy by increasing H2AX phosphorylation and p53 acetylation-phosphorylation. Int J Oncol 37:787–795
Acknowledgments
We thank Jasmin Wünschel, Markus Sohn, Christina Xanthopoulos, Diana Rieker, Peter van Sluis, and Richard Volckmann for excellent technical assistance. Work was supported by a grant from the University of Heidelberg through the OLYMPIA MORATA program to H.E.D., and a grant from the Interdisciplinary Research Program (NCT-IFP) of the National Center of Tumor Diseases, Heidelberg, Germany, to T.M. and S.M.P. The experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milde, T., Lodrini, M., Savelyeva, L. et al. HD-MB03 is a novel Group 3 medulloblastoma model demonstrating sensitivity to histone deacetylase inhibitor treatment. J Neurooncol 110, 335–348 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0978-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0978-1