Abstract
Aims
Phosphorus resources have to be managed sustainably and therefore the recycling of P from waste streams is essential. A thermo-chemical recycling process has been developed to produce a P fertilizer from sewage sludge ash (SSA) but its plant availability is unknown.
Methods
Two SSA products prepared with either CaCl2 (SSACa) or MgCl2 (SSAMg) as chemical reactant during the thermal treatment were mixed with three soils previously labeled with 33P. Reference treatments with water-soluble P added at equal amounts of total P were included. The transfer of P from SSACa and SSAMg to Lolium multiflorum or P pools of sequentially extracted soil-fertilizer incubations were quantified.
Results
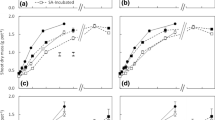
The shoot P uptake from SSAMg was higher than from SSACa. For SSAMg the relative effectiveness compared to a water-soluble P fertilizer was 88 % on an acidic and 71 % on a neutral soil but only 4 % on an alkaline soil. The proportion of P derived from the fertilizer in the plant and in the first two extraction pools of soil-fertilizer incubations were strongly correlated, suggesting that it is sufficient to conduct an incubation study to obtain robust information on plant P availability.
Conclusions
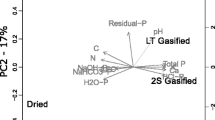
We conclude that under acidic to neutral conditions SSAMg presents an appropriate alternative to conventional P fertilizers and the dissolution of P from SSAMg seems to be governed by protons and cations in the soil solution.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSA:
-
Sewage sludge ash
- SA:
-
Specific activity
- Pdf seed:
-
P derived from the seed
- Pdf fertilizer:
-
P derived from the fertilizer
- Pdf soil:
-
P derived from the soil
- Pupt:
-
Shoot P uptake
- FertPRec:
-
Fertilizer P recovery
References
Adam C, Peplinski B, Michaelis M, Kley G, Simon FG (2009) Thermochemical treatment of sewage sludge ashes for phosphorus recovery. Waste Manage 29:1122–1128
Barrow NJ (1985) Comparing the effectiveness of fertilizers. Fert Res 8:85–90
Bergmann W (1993) Ernährungsstörungen bei Kulturpflanzen, 3rd edn. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena
Bierman PM, Rosen CJ, Bloom PR, Nater EA (1995) Soil solution chemistry of sewage-sludge incinerator ash and phosphate fertilizer amended soil. J Environ Qual 24:279–285
Bright DA, Healey N (2003) Contaminant risks from biosolids land application: contemporary organic contaminant levels in digested sewage sludge from five treatment plants in Greater Vancouver, British Columbia. Environ Pollut 126:39–49
Brookes PC (1982) Correction for seed-phosphorus effects in L-value determinations. J Sci Food Agric 33:329–335
Brookes PC, Mattingly GEG, White RP, Mitchell JD (1983) Relationships between labile-P, NaHCO3-soluble-P, and mobilization of non-labile-P in soils treated with inorganic-phosphate fertilizers and organic manures. J Sci Food Agric 34:335–344
Bühler S, Oberson A, Rao IM, Friesen DK, Frossard E (2002) Sequential phosphorus extraction of a P-33-labeled oxisol under contrasting agricultural systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:868–877
Bühler S, Oberson A, Sinaj S, Friesen DK, Frossard E (2003) Isotope methods for assessing plant available phosphorus in acid tropical soils. Eur J Soil Sci 54:605–616
Bünemann EK, Steinebrunner F, Smithson PC, Frossard E, Oberson A (2004) Phosphorus dynamics in a highly weathered soil as revealed by isotopic labeling techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:1645–1655
Cabeza R, Steingrobe B, Römer W, Claassen N (2011) Effectiveness of recycled P products as P fertilizers, as evaluated in pot experiments. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 91:173–184
Condron LM, Goh KM (1989) Effects of long-term phosphatic fertilizer applications on amounts and forms of phosphorus in soils under irrigated pasture in New-Zealand. J Soil Sci 40:383–395
Cordell D, Drangert JO, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Global Environ Change (A Hum Policy Dimens) 19:292–305
Dann PR, Dear BS, Cunningham RB (1989) Comparison of sewage ash, crushed limestone and cement kiln dust as ameliorants for acid soils. Aust J Exp Agric 29:541–549
Daroub SH, Pierce FJ, Ellis BG (2000) Phosphorus fractions and fate of phosphorus-33 in soils under plowing and no-tillage. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:170–176
Douxchamps S, Frossard E, Bernasconi SM, van der Hoek R, Schmidt A, Rao IM, Oberson A (2011) Nitrogen recoveries from organic amendments in crop and soil assessed by isotope techniques under tropical field conditions. Plant Soil 341:179–192
Fardeau JC, Guiraud G, Marol C (1996) The role of isotopic techniques on the evaluation of the agronomic effectiveness of P fertilizers. Fert Res 45:101–109
Forschungsanstalten Agroscope (2004) Referenzmethoden der Forschungsanstalten Agroscope. Vol 1–4. Forschungsanstalt Agroscope Reckenholz-Tänikon (ART) and Changins-Wädenswil (ACW), Zurich, Changings, Wädenswil
Fraissler G, Joller M, Mattenberger H, Brunner T, Obernberger I (2009) Thermodynamic equilibrium calculations concerning the removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge ash by chlorination. Chem Eng Process 48:152–164
Frossard E, Achat DL, Bernasconi SM, Bünemann EK, Fardeau J-C, Jansa J, Morel C, Rabeharisoa L, Randriamanantsoa L, Sinaj S, Tamburini F, Oberson A (2011) The Use of tracers to investigate phosphate cycling in soil-plant systems. In: Bünemann E, Oberson A, Frossard E (eds) Phosphorus in action: biological processes in soil phosphorus cycling, vol 100, Soil Biology. Springer, Berlin, pp 59–91
Frossard E, Bünemann E, Jansa J, Oberson A, Feller C (2009) Concepts and practices of nutrient management in agro-ecosystems: can we draw lessons from history to design future sustainable agricultural production systems? Bodenkultur 60:43–60
Frossard E, Fardeau JC, Brossard M, Morel JL (1994) Soil isotopically exchangeable phosphorus - a comparison between E and L-values. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:846–851
Frossard E, Sinaj S, Zhang LM, Morel JL (1996) The fate of sludge phosphorus in soil-plant systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1248–1253
Gallet A, Flisch R, Ryser JP, Nösberger J, Frossard E, Sinaj S (2003) Uptake of residual phosphate and freshly applied diammonium phosphate by Lolium perenne and Trifolium repens. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 166:557–567
Gerba CP, Smith JE (2005) Sources of pathogenic microorganisms and their fate during land application of wastes. J Environ Qual 34:42–48
Harley AD, Gilkes RJ (2000) Factors influencing the release of plant nutrient elements from silicate rock powders: a geochemical overview. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 56:11–36
Hedley MJ, Mortvedt JJ, Bolan NS, Syers JK (1995) Phosphorus fertility management in agroecosystems. In: Tiessen H (ed) Phosphorus in the global environment transfers, cycles and management. SCOPE, vol 54. Wiley, Chichester, pp 59–92
Hedley MJ, Stewart JWB, Chauhan BS (1982) Changes in inorganic and organic soil-phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:970–976
Kratz S, Haneklaus S, Schnug E (2010) Chemical solubility and agricultural performance of P-containing recycling fertilizers. Landbauforschung 60:227–240
Lamprecht H, Lang DJ, Binder CR, Scholz RW (2011) The trade-Off between phosphorus recycling and health protection during the BSE crisis in Switzerland a “disposal dilemma”. GAIA 20:112–121
Lederer J, Rechberger H (2010) Comparative goal-oriented assessment of conventional and alternative sewage sludge treatment options. Waste Manag 30:1043–1056
Mattenberger H, Fraissler G, Brunner T, Herk P, Hermann L, Obernberger I (2008) Sewage sludge ash to phosphorus fertiliser: variables influencing heavy metal removal during thermochemical treatment. Waste Manag 28:2709–2722
Mattenberger H, Fraissler G, Joller M, Brunner T, Obernberger I, Herk P, Hermann L (2010) Sewage sludge ash to phosphorus fertiliser (II): influences of ash and granulate type on heavy metal removal. Waste Manag 30:1622–1633
McBride MB (1995) Toxic metal accumulation from agricultural use of sludge - are USEPA regulations protective. J Environ Qual 24:5–18
Mihelcic JR, Fry LM, Shaw R (2011) Global potential of phosphorus recovery from human urine and feces. Chemosphere 84:832–839
Morel C, Fardeau JC (1989a) Native soil and fresh fertilizer phosphorus uptake as affected by rate of application and phosphorus fertilizers. Plant Soil 115:123–128
Morel C, Fardeau JC (1989b) The uptake by crops of fresh and residual phosphatic fertilizers by simultaneous measurements with P-32 and P-33. Appl Radiat Isot 40:273–278
Morel C, Fardeau JC (1990a) Agronomical evaluation of phosphate fertilizer as a nutrient source of phosphorus for crops - isotopic procedure. Fert Res 24:115–122
Morel C, Fardeau JC (1990b) Uptake of phosphate from soils and fertilizers as affected by soil-p availability and solubility of phosphorus fertilizers. Plant Soil 121:217–224
Morel C, Fardeau JC (1991) Phosphorus bioavailability of fertilizers - a predictive laboratory method for its evaluation. Fert Res 28:1–9
Oberson A, Tagmann HU, Langmeier M, Dubois D, Mäder P, Frossard E (2010) Fresh and residual phosphorus uptake by ryegrass from soils with different fertilization histories. Plant Soil 334:391–407
Ohno T, Zibilske LM (1991) Determination of low concentrations of phosphorus in soil extracts using malachite green. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:892–895
Ott C, Rechberger H (2012) The European phosphorus balance. Resour Conserv Recycl 60:159–172
Parkinson JA, Allen SE (1975) A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 6:1–11
Peplinski B, Adam C, Michaelis M, Kley G, Emmerling F, Simon FG (2009) Reaction sequences in the thermo-chemical treatment of sewage sludge ashes revealed by X-ray powder diffraction - a contribution to the European project SUSAN. Z Kristallogr:459–464
Pypers P, Van Loon L, Diels J, Abaidoo R, Smolders E, Merckx R (2006) Plant-available P for maize and cowpea in P-deficient soils from the Nigerian Northern Guinea Savanna - Comparison of E- and L-values. Plant Soil 283:251–264
Rajan SSS, Watkinson JH, Sinclair AG (1996) Phosphate rocks for direct application to soils. Adv Agron 57:77–159
Renner R (2000) Sewage sludge: pros & cons. Environ Sci Technol 34:430A–435A
Richardson A, Lynch J, Ryan P, Delhaize E, Smith F, Smith S, Harvey P, Ryan M, Veneklaas E, Lambers H, Oberson A, Culvenor R, Simpson R (2011) Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture. Plant Soil 349:121–156
Sartorius C, von Horn J, Tettenborn F (2012) Phosphorus recovery from wastewater - expert survey on present use and future potential. Water Environ Res 84:313–322
Saunders WMH, Williams EG (1955) Observations on the determination of total organic phosphorus in soils. J Soil Sci 6:254–267
Schipanski ME, Bennett EM (2012) The influence of agricultural trade and livestock production on the global phosphorus cycle. Ecosystems 15:256–268
Sibbesen E (1983) Phosphate soil tests and their suitability to assess the phosphate status of soil. J Sci Food Agric 34:1368–1374
Sinaj S, Traore O, Frossard E (2002) Effect of compost and soil properties on the availability of compost phosphate for white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 62:89–102
Smit AL, Bindraban PS, Schröder JJ, Conijn JG, van der Meer HG (2009) Phosphorus in agriculture: global resources, trends and developments : report to the Steering Committee Technology Assessment of the Ministery of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality, The Netherlands. Report to the Steering Committee Technology Assessment of the Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality. Plant Research International, Wageningen University, Wageningen
Tiessen H, Ballester MV, Salcedo I (2011) Phosphorus and global change. In: Bünemann E, Oberson A, Frossard E (eds) Phosphorus in action: biological processes in soil phosphorus cycling, vol 100, Soil Biology. Springer, Berlin, pp 459–471
Tiessen H, Moir J (2007) Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In: Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd edn. CRC Press
Truong B, Pichot J. (1976) Influence du phosphore des graines de la plante test sur la determination du phosphore isotopiquement diluable. Agronomie Tropicale 31:379–386
Vogel C, Adam C (2011) Heavy metal removal from sewage sludge ash by thermochemical treatment with gaseous hydrochloric acid. Environ Sci Technol 45:7445–7450
Vogel C, Kohl A, Adam C (2011) Spectroscopic investigation in the mid- and far-infrared regions of phosphorus fertilizers derived from thermochemically treated sewage sludge ash. Appl Spectrosc 65:265–271
Whitehead DC (2000) Nutrient elements in grassland: soil-plant-animal relationships. Cabi, New York
Zapata F, Axmann H (1995) P-32 isotopic techniques for evaluating the agronomic effectiveness of rock phosphate materials. Fert Res 41:189–195
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Recycling, Entsorgung, Abwasser Lucerne (REAL) for providing the raw ashes and J. Casparin, P. Herk and H. Mattenberger (ASH DEC Umwelt AG) for the technical guidance during the preparation of thermo-chemically treated SSA. We thank T. Flura (ETH Zurich) for assistance in analytics and U. Eggenberger and C. Lemp (University of Berne) for XRD analyses. We acknowledge F. Liebisch (ETH Zurich), the anonymous reviewers and Prof. N. J. Barrow (The University of Western Australia) for their helpful comments on our script. The project was funded by the Swiss Federal Commission for Technology and Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: N. Jim Barrow.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
(PDF 43.4 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(PDF 53.3 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
(PDF 56.2 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nanzer, S., Oberson, A., Berger, L. et al. The plant availability of phosphorus from thermo-chemically treated sewage sludge ashes as studied by 33P labeling techniques. Plant Soil 377, 439–456 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1968-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1968-6