Abstract
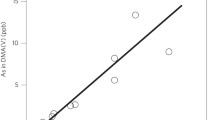
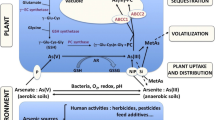
Methylation and demethylation of arsenic may change substantially the toxicity and mobility of arsenic in soils. Little is known about demethylation of organic arsenic species in organic soils. We incubated dimethylarsinic acid (DMA) and arsenobetaine (AsB) in soils and aqueous soil extracts from a forest floor and fen, in order to investigate demethylation processes. Incubations were conducted at 5°C in the dark under oxic or anoxic conditions. Arsenobetaine demethylated rapidly in all soil extracts with half-lives of 3.6–12 days, estimated from first order kinetic. Demethylation of DMA was relatively slow with half-lives of 187 and 46 days in the forest floor extracts and oxic fen extracts, respectively. In comparison, DMA was stable for 100 days in anoxic fen extracts. The apparent half-lives were much shorter in soils for DMA (1.3–12.6 days) and AsB (0.5–1.9 days) than in soil extracts, suggesting also irreversible AsB and DMA adsorption to soils beside demethylation. An unknown arsenic species and DMA were detected as metabolites of AsB demethylation. The results indicate rapid demethylation of AsB probably via the pathway AsB → Dimethylarsenoylacetate → DMA, followed up by slow demethylation of DMA → monomethylarsonic acid → inorganic As species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001) Trace elements in the terrestrial environment. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer.
Bhumbla, D. K., & Keefer, R. F. (1994). Arsenic mobilisation and bioavailability in soil. In J. O. Nriagu (Ed.), Arsenic in the environment, part I: Cycling and characterization (pp. 51–82). New York: Wiley.
Chiu, V. Q., & Hering, J. G. (2000). Arsenic adsorption and oxidation at manganite surfaces. 1. method for simultaneous determination of adsorbed and dissolved arsenic species. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 2029–2034.
Cullen, W. R., & Reimer, K. J. (1989). Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chemical Reviews, 89, 713–764.
Devesa, V., Loos, A., Súñer, M. A., Vélez, D., Feria, A., Martínez, A., et al. (2005). Transformation of organoarsenical species by the microflora of freshwater crayfish. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53, 10297–10305.
Francesconi, K. A., & Kuehnelt, D. (2004). Determination of arsenic species: A critical review of methods and applications, 2000–2003. Analyst, 129, 373–395.
Francesconi, K., Visoottiviseth, P., Sridokchan, W., & Gössler, W. (2002). Arsenic species in an arsenic hyperaccumulating fern, Pityrogramma calomelanos: A potential phytoremediator of arsenic-contaminated soils. Science of the Total Environment, 284, 27–35.
Gao, S., & Burau, R. G. (1997). Environmental factors affecting rates of arsenic evolution from and mineralization of arsenicals in soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 753–763.
Geiszinger, A., Gössler, W., & Kosmus, W. (2002). Organoarsenic compounds in plants and soil on top of an ore vein. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 16, 245–249.
Geiszinger, A., Gössler, W., Kühnelt, D., Francesconi, K., & Kosmus, W. (1998). Determination of arsenic compounds in earthworms. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 2238–2243.
Hanaoka, K., Nakamura, O., Ohno, H., Tagawa, S., & Kaise, T. (1995a). Degradation of arsenobetaine to inorganic arsenic by bacteria in seawater. Hydrobiologia, 316, 75–80.
Hanaoka, K., Tagawa, S., & Kaise, T. (1992). The degradation of arsenobetaine to inorganic arsenic by sedimentary microorganisms. Hydrobiologia, 1, 623–628.
Hanaoka, K., Uchida, K., Tagawa, S., & Kaise, T. (1995b). Uptake and degradation of arsenobetaine by the microorganisms occurring in sediments. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 9, 573–579.
Hanaoka, K., Ueno, K., Tagawa, S., & Kaise, T. (1989). Degradation of arsenobetaine by microorganisms associated with marine macro algae, Monostroma nitidum and Hizikia fusiforme. Comparative biochemistry and physiology B, Biochemistry & molecular biology, 94, 379–382.
Hanaoka, K., Yamamoto, H., Kawashima, K., Tagawa, S., & Kaise, T. (1988). Ubiquity of arsenobetaine in marine animals and degradation of arsenobetaine by sedimentary microorganisms. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2, 371–376.
Hasegawa, H. (1997). The behavior of trivalent and pentavalent methylarsenicals in Lake Biwa. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 11, 305–311.
Hatzinger, P. B., & Alexander, M. (1995). Effect of aging of chemicals in soil on their biodegradability and extractability. Environmental Science and Technology, 29, 537–545.
Helgesen, H., & Larsen, E. H. (1998). Bioavailability and speciation of arsenic in carrots grown in contaminated soil. Analyst, 123, 791–796.
Hollibaugh, J. T., Carini, S., Gürleyük, H., Jellison, R., Joye, S. B., LeCleir, G., et al. (2005). Arsenic speciation in Mono Lake, California: Response to seasonal stratification and anoxia. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69, 1925–1937.
Huang, J. H., & Matzner, E. (2006). Dynamics of organic and inorganic arsenic in the solution phase of an acidic fen in Germany. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70, 2023–2033.
Jenkins, R. O., Ritchie, A. W., Edmonds, J. S., Gössler, W., Molnat, N., Kühnelt, D., et al. (2003). Bacterial degradation of arsenobetaine via dimethylarsinoylacetate. Archives of Microbiology, 180, 142–150.
Kaise, T., Sakurai, T., Saitoh, T., Matsubara, C., Takada-Oikawa, N., & Hanaoka, K. (1998). Biotransformation of arsenobetaine to trimethylarsine oxide by marine microorganisms in a gill of clam Meretrix lusoria. Chemosphere, 37, 443–449.
Khokiattiwong, S., Gössler, W., Pedersen, S. N., Cox, R., & Francesconi, K. A. (2001). Dimethylarsinoylacetate from microbial demethylation of arsenobetaine in seawater. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 15, 481–489.
Lafferty, B. J,. & Loeppert, R. H. (2005). Methyl arsenic adsorption and desorption behavior on iron oxides. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 2120–2127.
Mandal, B. K., Ogra, Y., & Suzuki, K. T. (2001). Identification of dimethylarsinous and monomethylarsonous acids in human urine of the arsenic-affected areas in West Bengal, India. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 14, 371–378.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta, 58, 201–235.
Matschullat, J. (2000). Arsenic in the geosphere − a review. Science of the Total Environment, 249, 297–312.
Mukai, H., Ambe, Y., Muku, T., Takeshita, K., & Fukuma, T. (1986). Seasonal variation of methylarsenic compounds in airborne particulate matter. Nature, 324, 239–240.
Okina, M., Yoshida, K., Kuroda, K., Wanibuchi, H., Fukushima, S., & Endo, G. (2004). Determination of trivalent methylated arsenicals in rat urine by liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after solvent extraction. Journal of Chromatography B, 799, 209–215.
Pongratz, R. (1998). Arsenic speciation in environmental samples of contaminated soil. Science of the Total Environment, 224, 133–141.
Riis, V., Lorbeer, H., & Babel, W. (1998). Extraction of microorganisms from soil: Evaluation of the effeiciency by counting methods and activity measurements. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 30, 1573–1581.
Sadiq, M. (1997). Arsenic chemistry in soils: an overview of thermodynamic predictions and field observations. Water Soil Air Pollution, 93, 117–136.
Sierra-Alvarez, R., Yenal, U., Field, J. A., Kopplin, M., Gandolfi, A. J., & Garbarino, J. R. (2006). Anaerobic biotransformation of organoarsenical pesticides monomethylarsonic acid and dimethylarsinic acid. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54, 3959–3966.
Sohrin, Y., Matsui, M., Kawashima, M., Hojo, M., & Hasegawa, H. (1997). Arsenic biogeochemistry affected by Eutrophication in Lake Biwa, Japan. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 2712–2720.
Styblo, M., Del Razo, L. M., & Vega L. (2000). Comparative toxicity of trivalent and pentavalent inorganic and methylated arsenicals in rat and human cell. Archives of Toxicology, 74, 289–299.
Takamatsu, T., Aoki, H., & Yoshida, T. (1982). Determination of arsenate, arsenite, monomethylarsenate and dimethylarsinate in soil polluted with arsenic. Soil Science, 133, 239–246.
Tlustoš, P., Gössler, W., Száková, J., & Balík, J. (2002). Arsenic compounds in leaves and roots of radish grown in soil treated by arsenite, arsenate and dimethylarsinic acid. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 16, 216–220.
Turpeinen R, Pantsar-Kallio, M., Haggblom, M., & Kairesalo, T. (1999). Influence of microbes on the mobilization, toxicity and biomethylation of arsenic in soil. Science of the Total Environment, 236, 173–180.
Wilkin, R. T., Wallschläger, D., & Ford, R. G. (2003). Speciation of arsenic in sulfidic waters. Geochemical Transactions, 4, 1−7.
Woolson, E. A., Aharonson, N., & Iadevaia, R. (1982). Application of the high-performance liquid chromatography-flameless atomic absorption method to the study of alkyl arsenical herbicide metabolism in soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 30, 580–584.
Woolson, E. A., & Kearney, P. C. (1973). Persistence and reactions of 14C-cacodylic acid in soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 7, 47–50.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr Gunter Ilgen for analytical support and Uwe Hell for field work. Financial support came from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, JH., Scherr, F. & Matzner, E. Demethylation of Dimethylarsinic Acid and Arsenobetaine in Different Organic Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 182, 31–41 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9318-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9318-4