Abstract
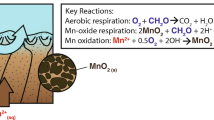
Seasonal manganese pollution has become an increasingly pressing water quality issue for water supply reservoirs in recent years. Manganese is a redox-sensitive element and is released from sediment under anoxic conditions near the sediment–water interface during summer and autumn, when water temperature stratification occurs. The reservoir water temperature and water dynamic conditions directly influence the formation of manganese pollution. Numerical models are useful tools to quantitatively evaluate manganese pollution and its influencing factors. This paper presents a reservoir manganese pollution model by adding a manganese biogeochemical module to a water quality model—CE-QUAL-W2. The model is applied to the Wangjuan reservoir (Qingdao, China), which experiences manganese pollution during summer and autumn. Field data are used to verify the model, and the results show that the model can reproduce the main features of the thermal stratification and manganese distribution. The model is used to evaluate the manganese pollution process and its four influencing factors, including air temperature, water level, wind speed, and wind directions, through different simulation scenarios. The results show that all four factors can influence manganese pollution. High air temperature, high water level, and low wind speed aggravate manganese pollution, while low air temperature, low water level, and high wind speed reduce manganese pollution. Wind that travels in the opposite direction of the flow aggravates manganese pollution, while wind in the same direction as the flow reduces manganese pollution. This study provides useful information to improve our understanding of seasonal manganese pollution in reservoirs, which is important for reservoir manganese pollution warnings and control.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abesser C, Robinson R, Robinson R (2010) Mobilisation of iron and manganese from sediments of a Scottish Upland reservoir. J Limnol. doi:10.4081/jlimnol.2010.42
Atkinson CA, Jolley DF, Simpson SL (2007) Effect of overlying water pH, dissolved oxygen, salinity and sediment disturbances on metal release and sequestration from metal contaminated marine sediments. Chemosphere 69:1428–1437. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.068
Baden SP, Eriksson SP, Weeks JM (1995) Uptake, accumulation and regulation of manganese during experimental hypoxia and normoxia by the decapod Nephrops norvegicus (L.). Mar Pollut Bull 31:93–102. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(94)00257-A
Bryant CL, Farmer JG, MacKenzie AB et al (1997) Manganese behavior in the sediments of diverse Scottish freshwater lochs. Limnol Oceanogr 42:918–929. doi:10.4319/lo.1997.42.5.0918
Bryant LD, Hsu-Kim H, Gantzer PA, Little JC (2011) Solving the problem at the source: controlling Mn release at the sediment-water interface via hypolimnetic oxygenation. Water Res 45:6381–6392. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.030
Castelletti A, Pianosi F, Soncini-Sessa R, Antenucci JP (2010) A multiobjective response surface approach for improved water quality planning in lakes and reservoirs. Water Resour Res 46:1–16. doi:10.1029/2009WR008389
Chen L, Zheng X, Wang T, Zhang J (2015) Influences of key factors on manganese release from soil of a reservoir shore. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11801–11812. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4443-5
Chung S, Gu R (1998) Two-dimensional simulations of contaminant currents in stratified reservoir. J Hydraul Eng 124:704–711. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1998)124:7(704)
Cole TM, Wells SA (2013) CE-QUAL-W2: a two-dimensional, laterally averaged, hydrodynamic and water quality model, version 3.71. Portland State University, Portland
Farmer JG, Lovell MA (1984) Massive diagenetic enhancement of manganese in Loch Lomond sediments. Environ Technol Lett 5:257–262. doi:10.1080/09593338409384274
Gantzer PA, Bryant LD, Little JC (2009) Controlling soluble iron and manganese in a water-supply reservoir using hypolimnetic oxygenation. Water Res 43:1285–1294. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.019
Graham MC, Gavin KG, Kirika A, Farmer JG (2012) Processes controlling manganese distributions and associations in organic-rich freshwater aquatic systems: the example of Loch Bradan, Scotland. Sci Total Environ 424:239–250. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.028
Groeger AW, Bass DA (2005) Empirical predictions of water temperatures in a subtropical reservoir. Arch Für Hydrobiol 162:267–285. doi:10.1127/0003-9136/2005/0162-0267
Hamilton-Taylor J, Davison W, Morfett K (1996) The biogeochemical cycling of Zn, Cu, Fe, Mn and dissolved organic C in a seasonally anoxic lake. Limnol Oceanogr 41:408–418
Johnson CA, Ulrich M, Sigg L, Imboden DM (1991) A mathematical model of the manganese cycle in a seasonally anoxic lake. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1415–1426
Kohl PM, Medlar SJ (2006) Occurrence of manganese in drinking water and manganese control. AWWA and USEPA. IWA Publishing, Philadelphia
Kristiansen KD, Kristensen E, Jensen EMH (2002) The influence of water column hypoxia on the behaviour of manganese and iron in sandy coastal marine sediment. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 55:645–654. doi:10.1006/ecss.2001.0934
Löfgren S, Boström B (1989) Interstitial water concentrations of phosphorus, iron and manganese in a shallow, eutrophic swedish lake—implications for phosphorus cycling. Water Res 23:1115–1125. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(89)90155-3
Lopes FA, Michard G, Poulin M et al (2010) Biogeochemical modelling of a seasonally anoxic lake: calibration of successive and competitive pathways and processes in Lake Aydat, France. Aquat Geochem 16:587–610. doi:10.1007/s10498-010-9095-y
Miao S, DeLaune RD, Jugsujinda A (2006) Influence of sediment redox conditions on release/solubility of metals and nutrients in a Louisiana Mississippi River deltaic plain freshwater lake. Sci Total Environ 371:334–343. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.07.027
Pakhomova SV, Hall POJ, Kononets MY et al (2007) Fluxes of iron and manganese across the sediment–water interface under various redox conditions. Mar Chem 107:319–331. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2007.06.001
Roitz JS, Flegal AR, Bruland KW (2002) The biogeochemical cycling of manganese in San Francisco Bay: temporal and spatial variations in surface water concentrations. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54:227–239. doi:10.1006/ecss.2000.0839
Sakata M (1985) Diagenetic remobilization of manganese, iron, copper and lead in anoxic sediment of a freshwater pond. Water Res 19:1033–1038. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(85)90373-2
Stauffer RE (1993) Effects of an early fall cold front on heat, phosphorus, silica, and manganese distributions in the hypolimnion of Lake Mendota, Wisconsin. J Hydrol 151:1–18. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(93)90245-5
Sundby B, Anderson LG, Hall POJ et al (1986) The effect of oxygen on release and uptake of cobalt, manganese, iron and phosphate at the sediment-water interface. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50:1281–1288. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(86)90411-4
World Health Organisation (2011) Guidelines for drinking. Water Quality, Geneva
Yagi A (1996) Manganese flux associated with dissolved and suspended manganese forms in Lake Fukami-ike. Water Res 30:1823–1832. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(96)00073-5
Yu SJ, Lee JY, Ha SR (2010) Effect of a seasonal diffuse pollution migration on natural organic matter behavior in a stratified dam reservoir. J Environ Sci 22:908–914. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60197-2
Zaw M, Chiswell B (1999) Iron and manganese dynamics in lake water. Water Res 33:1900–1910. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00360-1
Zhao L, Li Y, Zou R et al (2013) A three-dimensional water quality modeling approach for exploring the eutrophication responses to load reduction scenarios in Lake Yilong (China). Environ Pollut 177:13–21. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.01.047
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51409236), the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities of the Ministry of Education of China (201413060), the Opening Topic Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Simulation and Regulation of Water Cycle in River Basin (IWHR-SKL-201405), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014 M561966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H., Zheng, X., Chen, L. et al. Analysis of numerical simulations and influencing factors of seasonal manganese pollution in reservoirs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 14362–14372 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6380-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6380-3