Abstract
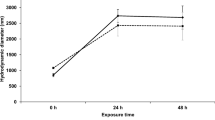
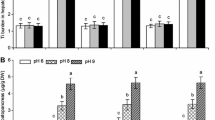
The impact of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (nano-TiO2) on the bioavailability of metals in aquatic filter-feeding organisms has rarely been investigated, especially in the presence of algae as a food source. In this study, we quantified the accumulation and subcellular distribution of arsenate (AsV) in Daphnia magna in the presence of nano-TiO2 and a green alga (Scenedesmus obliquus) food source. Results showed that S. obliquus significantly increased the accumulation of total arsenic (As) and titanium (Ti) in D. magna. The presence of this food source increased As in metal-sensitive fractions (MSF) and as biologically detoxified metals (BDM), while it decreased Ti levels in MSF but increased levels as BDM. The difference in the subcellular distribution of As and Ti demonstrates the dissociation of As from nano-TiO2 during digestion at subcellular partitioning irrespective of food availability. In turn, the presence of algae was shown to increase metal-based toxicity in D. magna due to the transfer of As from BMD to MSF. Furthermore, S. obliquus significantly increased the concentration of As and Ti in soluble fractions, indicating that As and nano-TiO2 ingested by D. magna could be transferred more readily to their predators in the presence of S. obliquus. Our study shows the potential of algae to increase the toxicity and biomagnification of AsV. Furthermore, it highlights food as an important factor in the toxicity assessment of nanomaterials and co-existing pollutants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balmès I, Corasaniti PS (1990) Clonal variation in general responses of Daphnia magna Straus to toxic stress. I. Chronic life-history effects. Funct Ecol 4:409–414
Barry M, Logan D, Ahokas J, Holdway D (1995) Effect of algal food concentration on toxicity of two agricultural pesticides to Daphnia carinata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 32:273–279
Brown D, Parsons T (1978) Relationship between cytoplasmic distribution of mercury and toxic effects to zooplankton and chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) exposed to mercury in a controlled ecosystem. J Fish Board Canada 35:880–884
Bundschuh M, Vogt R, Seitz F, Rosenfeldt RR, Schulz R (2016) Do titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce food depletion for filter feeding organisms? A case study with Daphnia magna. Environ Pollut 214:840–846
Deng R, Lin DH, Zhu LZ, Majumdar S, White JC, Gardea-Torresdey JL, Xing BS (2017) Nanoparticle interactions with co-existing contaminants: joint toxicity, bioaccumulation and risk. Nanotoxicology 11:591–612
Filippis LFD, Pallaghy CK (1976) The effect of sub-lethal concentrations of mercury and zinc on Chlorella I. Growth characteristics and uptake of metals. Z Pflanzenphysiol 78:197–207
Geller W, Müller H (1981) The filtration apparatus of Cladocera: filter mesh-sizes and their implications on food selectivity. Oecologia 49:316–321
Gong N, Shao K, Feng W, Lin Z, Liang C, Sun Y (2011) Biotoxicity of nickel oxide nanoparticles and bio-remediation by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere 83:510–516
Gophen M, Geller W (1984) Filter mesh size and food particle uptake by Daphnia. Oecologia 64:408–412
Guan XH, Du JS, Meng XG, Sun YK, Sun B, Hu QH (2012) Application of titanium dioxide in arsenic removal from water: a review. J Hazard Mater 215:1–16
Hartmann HJ, Kunkel DD (1991) Mechanisms of food selection in Daphnia. Hydrobiologia 225:129–154
Jenkins KD, Mason AZ (1988) Relationships between subcellular distributions of cadmium and perturbations in reproduction in the polychaete Neanthes arenaceodentata. Aquat Toxicol 12:229–244
Ji J, Long ZF, Lin DH (2011) Toxicity of oxide nanoparticles to the green algae Chlorella sp. Chem Eng J 170:525–530
Klerks P, Bartholomew P (1991) Cadmium accumulation and detoxification in a Cd-resistant population of the oligochaete Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri. Aquat Toxicol 19:97–112
Li M, Luo Z, Yan Y, Wang Z, Chi Q, Yan C, Xing B (2016) Arsenate accumulation, distribution, and toxicity associated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 50:9636–9643
Lin DH, Ji J, Long ZF, Yang K, Wu FC (2012) The influence of dissolved and surface-bound humic acid on the toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to Chlorella sp. Water Res 46:4477–4487
Luo Z, Wang Z, Yan Y, Li J, Yan C, Xing B (2018) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles enhance inorganic arsenic bioavailability and methylation in two freshwater algae species. Environ Pollut 238:631–637
Ma S, Zhou KJ, Yang K, Lin DH (2015) Heteroagglomeration of oxide nanoparticles with algal cells: effects of particle type, ionic strength and pH. Environ Sci Technol 49:932–939
Maeda S, Mizoguchi M, Ohki A, Inanaga J, Takeshita T (1990) Bioaccumulation of zinc and cadmium in freshwater alga. Part II Assoc Mode Metals Cell tissue Innov 21:965–973
Mangas-Ramírez E, Sarma S, Nandini S (2001) Acute and chronic toxicity of ammonium chloride to the cladoceran Daphnia pulex Leydig in relation to algal food density. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 67:834–840
Mason A, Jenkins K (1995) Metal detoxification in aquatic organisms. Metal Speciation Bioavailability Aquat Syst 3:479–578
Matzku S, Broda E (1970) Die Zinkaufnahme in das Innere von Chlorella. Planta 92:29–40
Metzler DM, Li M, Erdem A, Huang CP (2011) Responses of algae to photocatalytic nano-TiO 2 particles with an emphasis on the effect of particle size. Chem Eng J 170:538–546
Pena ME, Korfiatis GP, Patel M, Lippincott L, Meng XG (2005) Adsorption of As(V) and As(III) by nanocrystalline titanium dioxide. Water Res 39:2327–2337
Reinfelder JR, Fisher NS (1994) The assimilation of elements ingested by marine planktonic bivalve larvae. Limnol Oceanogr 39:12–20
Roesijadi G (1981) The significance of low molecular weight, metallothionein-like proteins in marine invertebrates: current status. Mar Environ Res 4:167–179
Rosenfeldt RR, Seitz F, Schulz R, Bundschuh M (2014) Heavy metal uptake and toxicity in the presence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a factorial approach using Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 48:6965–6972
Rosenkranz P, Chaudhry Q, Stone V, Fernandes TF (2009) A comparison of nanoparticle and fine particle uptake by Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:2142–2149
Seitz F, Bundschuh M, Rosenfeldt RR, Schulz R (2013) Nanoparticle toxicity in Daphnia magna reproduction studies: the importance of test design. Aquat Toxicol 126:163–168
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Ting YP, Lawson F, Prince IG (1989) Uptake of cadmium and zinc by the alga Chlorella vulgaris: part 1. Individual ion species. Biotechnol Bioeng 34:990–999
Wallace WG, Lopez GR (1997) Bioavailability of biologically sequestered cadmium and the implications of metal detoxification. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 147:149–157
Wallace WG, Luoma SN (2003) Subcellular compartmentalization of Cd and Zn in two bivalves. II. Significance of trophically available metal (TAM). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 257:125–137
Wallace WG, Lopez GR, Levinton JS (1998) Cadmium resistance in an oligochaete and its effect on cadmium trophic transfer to an omnivorous shrimp. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 172:225–237
Wallace V, Bamber J, Crawford D, Ott R, Mortimer P (2000a) Classification of reflectance spectra from pigmented skin lesions, a comparison of multivariate discriminant analysis and artificial neural networks. Phys Med Biol 45:2859–2871
Wallace WG, Brouwer TMH, Brouwer M, Lopez GR (2000b) Alterations in prey capture and induction of metallothioneins in grass shrimp fed cadmium-contaminated prey. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:962–971
Wallace WG, Lee B-G, Luoma SN (2003) Subcellular compartmentalization of Cd and Zn in two bivalves. I. Significance of metal-sensitive fractions (MSF) and biologically detoxified metal (BDM). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 249:183–197
Wang WX, Guan R (2010) Subcellular distribution of zinc in Daphnia magna and implication for toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:1841–1848
Wang ZH, Luo ZX, Yan CZ (2013) Accumulation, transformation, and release of inorganic arsenic by the freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:7286–7295
Wang ZH, Luo ZX, Yan CZ, Che FF, Yan YM (2014) Arsenic uptake and depuration kinetics in Microcystis aeruginosa under different phosphate regimes. J Hazard Mater 276:393–399
Wang ZH, Luo ZX, Yan CZ, Xing BS (2017) Impacts of environmental factors on arsenate biotransformation and release in Microcystis aeruginosa using the Taguchi experimental design approach. Water Res 118:167–176
Weltens R, Goossens R, Van Puymbroeck S (2000) Ecotoxicity of contaminated suspended solids for filter feeders (Daphnia magna). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:315–323
Zhang S, Deng R, Lin DH, Wu FC (2017) Distinct toxic interactions of TiO2 nanoparticles with four coexisting organochlorine contaminants on algae. Nanotoxicology 11:1115–1126
Funding
This study was jointly funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (41401552 and 41271484), the Nature Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China (2016J01691 and 2017Y0081), and the Science and Technology project of Xiamen, China (3502Z20172026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Cinta Porte
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Z., Li, M., Wang, Z. et al. Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the accumulation and distribution of arsenate in Daphnia magna in the presence of an algal food. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 20911–20919 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2265-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2265-y