Abstract
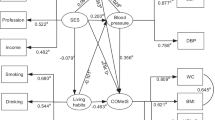
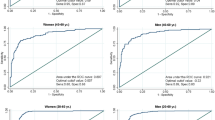
To assess the clustering of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors among Taiwanese adults, we evaluated 579 healthy participants who underwent health examinations between May and December 2007. Exploratory factor analysis was used to examine risk factor clustering. Smoking, alcohol intake, exercise habits, body mass index, waist circumference, total cholesterol, triglycerides, high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, fasting glucose, uric acid, serum hepatic enzymes, and mean arterial pressure were assessed. Separate factor analyses assessed total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Principal components analysis identified five factors for a model without low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and four factors for a model without total cholesterol. Four common factors in both models explained between 51.1 and 51.8% of variance in the original 14 factors. Metabolic factors, hematological factors (white blood cells and platelets), lifestyle factors (smoking and alcohol consumption), and exercise habits and fasting blood glucose explained about 20, 11, 10, 10% of total variance, respectively. In the model without low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, total cholesterol factor explained 8.83% of variance. This study confirmed clustering of established metabolic syndrome components and revealed additional associated cardiovascular disease risk factors, including lifestyle factors, exercise and total cholesterol, which should be targeted in prevention efforts.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
G.M. Reaven, Banting Lecture 1888. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37(12), 1595–1607 (1988)
K.G. Alberti, P.Z. Zimmet, Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications, Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet. Med. 15(7), 539–553 (1998)
B. Balkau, M.A. Charles, Comment on the provisional report from the WHO consultation. European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR). Diabet. Med. 16(5), 442–443 (1999)
J.B. Meigs, Invited commentary: insulin resistance syndrome? Syndrome X? Multiple metabolic syndrome? A syndrome at all? Factor analysis reveals patterns in the fabric of correlated metabolic risk factors. Am. J. Epidemiol. 152(10), 908–911 (2000)
P.A. Sakkinen, P. Wahl, M. Cushman, M.R. Lewis, R.P. Tracy, Clustering of procoagulation, inflammation, and fibrinolysis variables with metabolic factors in insulin resistance syndrome. Am. J. Epidemiol. 152(10), 897–907 (2000)
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 285(19), 2486–2497 (2001)
D. Einhorn, G.M. Reaven, R.H. Cobin, E. Ford, O.P. Ganda, Y. Handelsman, R. Hellman, P.S. Jellinger, D. Kendall, R.M. Krauss, N.D. Neufeld, S.M. Petak, H.W. Rodbard, J.A. Seibel, D.A. Smith, P.W. Wilson, American College of Endocrinology position statement on the insulin resistance syndrome. Endocr. Pract. 9(3), 237–252 (2003)
R. Kahn, J. Buse, E. Ferrannini, M. Stern, The metabolic syndrome: time for a critical appraisal: joint statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 28(9), 2289–2304 (2005)
S.M. Grundy, J.I. Cleeman, S.R. Daniels, K.A. Donato, R.H. Eckel, B.A. Franklin, D.I. Gordon, R.M. Krauss, P.J. Savage, S.C. Smith Jr, J.A. SPertus, F. Costa, American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lund and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 112, 2735–2752 (2005)
L.W. Johnson, R.S. Weinstock, The metabolic syndrome: concepts and controversy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 81(12), 1615–1620 (2006)
C. Tsai, S. Huang, K. Lin, The study of the metabolic syndrome and its relevant factors—data analysis of health examination. Chin. J. Fam. Med. 16, 84–94 (2006)
N. Nakanishi, K. Suzuki, K. Tatara, Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in middle-aged Japanese men. Diabetes Care 27(6), 1427–1432 (2004)
L.K. Niskanen, D.E. Laaksonen, K. Nyyssönen, G. Alfthan, H.M. Lakka, T.A. Lakka, J.T. Salonen, Uric acid level as a risk factor for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in middle-aged men: a prospective cohort study. Arch. Intern. Med. 164(14), 1546–1551 (2004)
K. Sudi, S. Gallistl, D. Payerl, R. Aigner, R. Möller, E. Tafeit, M.H. Borkenstein, Interrelationship between estimates of adiposity and body fat distribution with metabolic and hemostatic parameters in obese children. Metabolism 50(6), 681–687 (2001)
B.J. Shen, J.F. Todaro, R. Niaura, J.M. McCaffery, J. Zhang, A. Spiro 3rd, K.D. Ward, Are metabolic risk factors one unified syndrome? Modeling the structure of the metabolic syndrome X. Am. J. Epidemiol. 157(8), 701–711 (2003)
S.Y. Chuang, C.H. Chen, P. Chou, Hypertension and the insulin-related metabolic syndrome: factor analysis in 17, 539 Taiwanese. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 20, 229–236 (2004)
F. Leyva, I.F. Godsland, M. Worthington, C. Walton, J.C. Stevenson, Factors of the metabolic syndrome: baseline interrelationships in the first follow-up cohort of the HDDRISC Study (HDDRISC-1). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 18(2), 208–214 (1998)
C. Snehalatha, S. Sivasankari, K. Satyavani, V. Vijay, A. Ramachandran, Insulin resistance alone does not explain the clustering of cardiovascular risk factors in southern India. Diabet. Med. 17(2), 152–157 (2000)
T.L. Liou, M.W. Lin, L.C. Hsiao, T.T. Tsai, W.L. Chan, L.T. Ho, C.M. Hwu, Is hyperuricemia another facet of the metabolic syndrome? J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 69(3), 104–109 (2006)
K.M. Choi, J. Lee, K.B. Kim, D.R. Kim, S.K. Kim, D.H. Shin, N.H. Kim, I.B. Park, D.S. Choi, S.H. Baik, Factor analysis of the metabolic syndrome among elderly Koreans—the South-west Seoul Study. Diabet. Med. 20(2), 99–104 (2003)
S. Yusuf, S. Reddy, S. Ounpuu, S. Anand, Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: part II: variations in cardiovascular disease by specific ethnic groups and geographic regions and prevention strategies. Circulation 104(23), 2855–2864 (2001)
F. Hadaegh, H. Harati, A. Ghanbarian, F. Azizi, Association of total cholesterol versus other serum lipid parameters with the short-term prediction of cardiovascular outcomes: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 13(4), 571–577 (2006)
J. Ohrvik, P. Hedberg, T. Jonason, I. Lonnberg, G. Nilsson, Factor analysis of the individual components of the metabolic syndrome among elderly identifies two factors with different survival patterns—a population-based study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 7, 171–177 (2009)
A.J. Hanley, A.J. Karter, A. Festa, R. D’Agostino Jr., L.E. Wagenknecht, P. Savage, R.P. Tracy, M.F. Saad, S. Haffner, Factor analysis of metabolic syndrome using directly measured insulin sensitivity: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetes 51(8), 2642–2647 (2002)
C.Z. Wu, J.D. Lin, J.C. Li, F.C. Hsiao, S.W. Kuo, Yi Hung, C.H. Lu, C.T. He, D. Pei, Factor analysis of metabolic syndrome using direct measurement of insulin resistance in Chinese with different degrees of glucose tolerance. Indian J. Med. Res. 127(4), 336–343 (2008)
A. Bener, M. Zirie, M. Musallam, Y.S. Khader, A.O. Al-Hamaq, Prevalence of metabolic syndrome according to Adult Treatment Panel III and International Diabetes Federation criteria: a population-based study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 7, 221–229 (2009)
R.M. Mabry, M.M. Reeves, E.G. Eakin, N. Owen, Gender differences in prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in Gulf Cooperation Council Countries: a systematic review. Diabet. Med. 27, 593–597 (2010)
L.C. Hwang, C.H. Bai, C.J. Chen, K.L. Chien, Gender differences on the development of metabolic syndrome: a population-based study in Taiwan. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 22, 899–906 (2007)
Y.C. Chen, H.P. Wu, S.J. Hwang, I.C. Li, Exploring the components of metabolic syndrome with respect to gender difference and its relationship to health-promoting lifestyle behaviour: a study in Taiwanese urban communities. J. Clin. Nurs. 19, 3031–3041 (2010)
D.A. Lawlor, S. Ebrahim, M. May, G. Davey Smith, (Mis)use of factor analysis in the study of insulin resistance syndrome. Am. J. Epidemiol. 159(11), 1013–1018 (2004)
A. Gupta, V. Gupta, Metabolic syndrome: what are the risks for humans? Biosci. Trends 4, 204212 (2010)
R.K. Schindheim, M. Diamant, J.M. Dekker, M.E. Tushuizen, T. Teerlink, R.J. Heine, Alanine aminotransferase as a marker of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in relation to type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 22, 437–443 (2006)
R.L. Borges, A.B. Ribeiro, M.T. Zanella, M.C. Batista, Uric acid as a factor in the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 12, 113–119 (2010)
M. Alderman, K.J. Aiyer, Uric acid: role in cardiovascular disease and effects of Iosartan. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 20, 369–379 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Cheng Ching Hospital and the authors appreciate the expert assistance of all colleagues from the Health Management Center of Cheng Ching Hospital. Permission was granted for the acknowledgement of staff. Funding for this study was provided by Cheng Ching Hospital and no other funding support was received.
Disclosure
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, CH., Li, TC., Lin, CC. et al. Factor analysis of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult Taiwanese. Endocrine 40, 256–264 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9466-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9466-1