Abstract
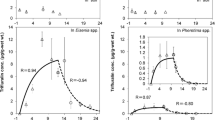
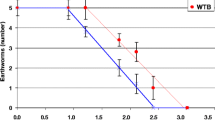
The uptake of chemicals in soil organisms, especially earthworms, has been studied many times. However, in Europe no internationally accepted standardised test guideline for the assessment of bioaccumulation in the soil ecosystem exists. Therefore, the German Federal Environmental Agency recently funded a project in which a standardisable test method for measuring bioaccumulation of chemicals using earthworms and enchytraeids is being developed. In this contribution, initial results with the new method are presented, using two model chemicals (the insecticide lindane and the fungicide hexachlorobenzene). Two enchytraeid species (Enchytraeus luxuriosus and Enchytraeus albidus) were selected as test organisms due to their easy handling and their important ecological role in the soil compartment. Artificial soil and a natural standard soil were used as test substrates. Test concentrations were based on previous results of acute and reproduction toxicity tests performed with the same species. Uptake as well as the elimination of the test substances were examined under standardised conditions in a closed test system. The first results show that both chemicals were accumulated considerably by both enchytraeid species. The bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) of lindane and hexachlorobenzene found for enchytraeids are significantly higher compared to those for lumbricid earthworms. Evaluation of the preliminary data suggests that the smaller species E. luxuriosus accumulated the two chemicals to a greater extent than E. albidus. In most cases, both chemicals were eliminated completely. The use of this new test method appears suitable for the ecotoxicological risk assessment of bioaccumulative chemicals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amorim, M., 2000. Chronic and toxicokinetic behavior of lindane (γ-HCH) in the enchytraeid Enchytraeus albidus. For the Degree of Master of Science in Ecology. Universidade de Coimbra, Faculdade de Ciencias e Tecnologia, Departamento de Zoologia. Coimbra, Portugal, 2000: 82 pp.
ASTM, 2000a. Standard Guide for Determination of the Bioaccumulation of Sediment-Associated Contaminants by Benthic Invertebrates. American Society for Testing and Materials, E 1688-00a: 54 pp.
ASTM, 2000b. Standard Guide for conducting laboratory soil toxicity or bioaccumulation tests with the lumbricid earthworm Eisenia fetida and the enchytraeid potworm Enchytraeus albidus. E 1676–97, draft version, July 17, 2000: 37 pp.
Augustsson, A. & S. Rundgren, 1998. The enchytraeid Cognettia sphagnetorum in risk assessment: advantages and disadvantages. Ambio 27: 62–69.
BBA, 1986. Richtlinien für die amtliche Prüfung von Pflanzenschutzmitteln. Teil IV, 4-1: Verbleib von Pflanzenschutzmitteln im Boden-Abbau, Umwandlung und Metabolismus. ACO Druck, Braunschweig: 35 pp.
Beyer, W. N., 1996. Accumulation of Chlorinated Benzenes in Earthworms. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 57: 729–736.
Belfroid, A., M. Sikkenk, W. Seinen, C. Van Gestel & J. Hermens, 1994. The toxicokinetic behaviour of chlorobenzenes in earthworms (Eisenia andrei): experiments in soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 13: 93–99.
Bengtsson, G. & S. Rundgren, 1982. Population density and species number of enchytraeids in coniferous forest soils polluted by a brass mill. Pedobiologia 24: 211–218.
Connell, D. W. & R. D. Markwell, 1990. Bioaccumulation in the soil to earthworm system. Chemosphere 20: 91–100.
De Boer, J., F. Smedes, D. Wells & A. Allan, 1999. Report on the QUASH interlaboratory study on the determination of totallipid in fish and shellfish. Round 1 SBT-2. Exercise 1000. EU, Standards, Measurement and Testing Programme: 20 pp.
De Bruijn, J., F. Busser, W. Seinen & J. Hermens, 1989. Determination of octanol/water partition coefficients for hydrophobic organic chemicals with the 'slow-stirring’ method. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 8: 499–512.
Didden, W. A. M., 1993. Ecology of terrestrial enchytraeidae. Pedobiologia 37: 2–29.
Didden, W. A. M. & J. Römbke, 2001. Enchytraeids as test organisms for chemical stress in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecotox. Environ. Safety 50: 25–43.
Ebing, W., J. Pflugmacher & A. Haque, 1984. Der Regenwurm als Schlüsselorganismus zur Messung der Bodenbelastung mit organischen Fremdchemikalien. Berichte über Landwirtschaft 62: 222–255.
Edwards, C. A., 1984. Report of the second stage in development of a standardized laboratory method for assessing the toxicity of chemical substances to earthworms. In Commission of the European Communities (ed.), Environment and the Quality of Life. Report EUR 9360 EN. ECSC-EEC-EAEC, Brussels, Luxembourg: 99 pp.
Egeler, Ph., J. Römbke, M. Meller, Th. Knacker, C. Franke, G. Studinger & R. Nagel, 1997. Bioaccumulation of lindane and hexachlorobenzene by tubificid sludgeworms (Oligochaeta) under standardised laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 35: 835–852.
Egeler, Ph., J. Römbke, M. Meller, Th. Knacker & R. Nagel, 1999. Bioaccumulation test with tubificid sludgeworms in artificial media-development of a standardisable method. Hydrobiologia 406: 271–280.
Fitzgerald, D. G., K. A. Warner, R. P. Lanno & D. G. Dixon, 1996. Assessing the effects of modifying factors of pentachlorophenol toxicity to earthworms: Application of body residues. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15: 2299–2304.
Franke, C., G. Studinger, G. Berger, S. Böhling, U. Bruckmann, D. Cohors-Fresenborg & U. Jöhnke, 1994. The assessment of bioaccumulation. Chemosphere 29: 1501–1514.
Füll, C., 1996. Bioakkumulation und Metabolismus von γ – 1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexachlorcyclohexan (Lindan) und 2,4-(2,4-Dichlorphenoxy)-Propionsäure (Dichlorprop) beim Regenwurm Lumbricus rubellus (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae). PhD-Thesis, Johannes Gutenberg-University, Mainz: 156 pp.
Högger, Ch. & H. U. Ammon, 1994. Testing the toxicity of pesticides to earthworms in laboratory and field tests. IOBC WPRS Bull. 17: 157–178.
ISO (International Organisation for Standardization), 2000. Soil Quality – Effects of Pollutants on Enchytraeidae (Enchytraeus sp.) Determinations of Effects on Reproduction (Enchytraeid reproduction test (ERT). Draft ISO / WD 16387: 31 pp.
Khalil, A. M., 1990. Aufnahme und Metabolismus von 14CHexachlorbenzol und 14C-Pentachlornitrobenzol in Regenwürmern. Ph.D.-Thesis, University Munich: 137 pp.
Kramarz, P. & R. Laskowski, 1999. Toxicity and possible foodchain effects of copper, dimethoate and a detergent (LAS) on a centipede (Lithobius mutabilis) and its prey (Musca domestica). Appl. Soil Ecol. 13: 177–185.
Løkke, H. & C. A. M. Van Gestel, 1998. Handbook of soil invertebrate toxicity tests. Ecological & Environmental Toxicology Series. Wiley & Sons, New York: 281 pp.
Nendza, M., 1991. QSARs of bioaccumulation: Validity assessment of log Pow/log BCF correlations. In Nagel, R. & R. Loskill (eds), Bioaccumulation in aquatic systems. Contributions to the assessment. Proceedings of an international workshop, Berlin 1990. VCH, Weinheim: 43–66.
OECD, 1984. Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals No. 207. Earthworm, Acute Toxicity Test. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), Paris: 9 pp.
OECD, 1992. Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals No. 203. Fish, Acute Toxicity Test. OECD, Paris: 9 pp.
OECD, 1996. Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals No. 305. Bioconcentration: Flow-through Fish Test. OECD, Paris: 9 pp.
OECD, 2000. Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals 220 (Proposal for a new Guideline) Enchytraeidae Reproduction Test. OECD, Paris: 24 pp.
Oliver, B. G., 1987. Biouptake of chlorinated hydrocarbons from laboratory-spiked and field sediments by oligochaete worms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21: 785–790.
Pirhonen, R. & V. Huhta, 1984. Petroleum fractions in soil: Effects on populations of Nematoda, Enchytraeidae and Microarthropoda. Soil Biol. Biochem. 16: 347–350.
Rippen, G., 1999. Handbuch der Umweltchemikalien: Physikalischchemische und ökotoxikologische Daten ausgewählter chemischer Stoffe. Loose-leaf book, updated periodically. Ecomed Verlagsgesellschaft, Landsberg.
Römbke, J., 1992. Estimates of the Enchytraeidae (Oligochaeta, Annelida) contribution to energy flow in the soil system of an acid beech wood forest. Biol. Fert. Soil 11: 255–260.
Römbke, J. & A. Federschmidt, 1994. Effects of the fungicide Carbendazim on Enchytraeidae in laboratory and field tests. Newsletter on Enchytraeidae 4: 79–96.
Römbke, J. & T. Moser, 1999. Organisation and Performance of an International Ringtest for the Validation of the Enchytraeid Reproduction Test. UBA-Text 4/99: 150 pp. (+ annex: 249 pp.).
Romijn, C. F. A. M., R. Luttik & J. R. Canton, 1994. Presentation of a general algorithm to include effect assessment of secondary poisoning in the derivation of environmental quality criteria. Part 2. Terrestrial food chains. Ecotox. Environ. Safety 27: 107–127.
Schmelz, R. & R. Collado, 1999. Enchytraeus luxuriosus sp. nov., a new terrestrial oligochaete species (Enchytraeidae, Clitellata, Annelida). Carolinea 57: 93–100.
Spacie, A. & J. L. Hamelink, 1982. Alternative models for describing the bioconcentration of organics in fish. Environ. Ecotox. Chem. 1: 309–320.
Tracey, G. A. & D. J. Hansen, 1996. Use of biota-sediment accumulation factors to assess similarity of nonionic organic chemical exposure to benthically-coupled organisms of differing trophic mode. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 30: 467–475.
U.S. EPA, 1996. Ecological Test Guidelines OPPTS 850.1730 Fish BCF (Public Draft): 23 pp. U.S. EPA, 2000. Methods for measuring the toxicity and bioaccumulation of sediment-associated contaminants with freshwater invertebrates. 2nd edn. EPA 600/R-99/064, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Duluth, MN. March 2000: 192 pp.
Viswanathan, R., S. Ray, I. Scheunert & F. Korte, 1988. Investigations on accumulation and biotransformation by earthworms of lindane occurring as soil contaminant. In Abbou, R. (ed.), Hazardous Waste: Detection, Control, Treatment. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam: 759–765.
Zok, S., G. Görge, W. Kalsch & R. Nagel, 1991. Bioconcentration, metabolism and toxicity of substituted anilines in the zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Sci. Total. Environ. 109/110: 411–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruns, E., Egeler, P., Roembke, J. et al. Bioaccumulation of lindane and hexachlorobenzene by the oligochaetes Enchytraeus luxuriosus and Enchytraeus albidus (Enchytraeidae, Oligochaeta, Annelida). Hydrobiologia 463, 185–196 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013159810067
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013159810067