Abstract
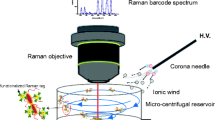
We present an immunoassay microarray flow-through system for the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) analysis of bacteria. The system has been constructed to support and automatize the nondestructive in situ analysis of different microorganisms in aqueous environment. After the immobilization of the desired antibodies to an activated PEG-coated surface, the chip is placed into the flow cell which is then flushed with the contaminated sample. Finally, colloidal metal nanoparticles are added and the cells are detected label-free by SERS. Here, we introduce the successful imaging of single microorganisms in the flow cell as well as the quantification of microorganisms in water by SERS mapping with a linear range between 4.3 × 103 to 4.3 × 105 cells/mL. The method has potential for routine application, e.g. for drinking water control.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seidel M, Niessner R (2008) Automated analytical microarrays: a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1521–1544
Kloth K, Rye-Johnsen M, Didier A, Dietrich R, Märtlbauer E, Niessner R, Seidel M (2009) A regenerable immunochip for the rapid determination of 13 different antibiotics in raw milk. Analyst 134:1433–1439
Karsunke XYZ, Niessner R, Seidel M (2009) Development of a multichannel flow-through chemiluminescence microarray chip for parallel calibration and detection of pathogenic bacteria. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1623–1630
Efrima S, Zeiri L (2009) Understanding SERS of bacteria. J Raman Spectrosc 40:277–288
Zhao Y, Jiang Y, Fang Y (2006) Quenching and enhancement of fluorescence of fullerene molecules on gold particle. Chemical Physics 323:169–172
Laserna JJ (1993) combining fingerprint capability with trace analytical detection: surface-enhanced Raman spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 283:607–622
Berthod A, Laserna JJ, Winefordner JD, (1987) Surface enhanced raman-spectrometry on silver hydrosols studied by flow-injection analysis applied spectroscopy 41:1137–1141
Wilson R, Monaghan P, Bowden SA, Parnell J, Cooper JM (2007) Surface-enhanced raman signatures of pigmentation of cyanobacteria from within geological samples in a spectroscopic-microfluidic flow cell. Anal Chem 79:7036–7041
Strehle KR, Cialla D, Rösch P, Henkel T, Köhler M, Popp J (2007) A reproducible surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy approach. online SERS measurements in a segmented microfluidic system. Anal Chem 79:1542–1547
Park T, Lee S, Seong GH, Choo J, Lee EK, Kim YS, Ji WH, Hwang SY, Gweon D-G, Lee S (2005) Highly sensitive signal detection of duplex dye-labelled DNA oligunucleotides in a PDMS microfluidic chip: confocal surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic study. Lab Chip 5:437–442
K-h Y, Lee S, Kyong JB, Choo J, Lee EK, Joo S-W, Lee S (2005) Ultra-sensitive trace analysis of cyanide water pollutant in a PDMS microfluidic channel using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 130:1009–1011
Hou D, Maheshwari S, Chang H-C (2007) Rapid bioparticle concentration and detection by combining a discharge driven vortex with surface enhanced Raman scattering. Biomicrofluidics 1:1–13
Guven B, Basaran-Akgul N, Temur E, Tamer U, Boyaci IH (2011) SERS-based sandwich immunoassay using antibody coated magnetic nanoparticles for Escherichia coli enumeration. Analyst 136:740–748
Chen L, Choo J (2008) Recent advances in surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection technology for microfluidic chips. Electrophoresis 29:1815–1828
Knauer M, Ivleva NP, Liu X, Niessner R, Haisch C (2010) SERS-based label-free microarray readout for the detection of microorganisms. Anal Chem 82:2766–2772
Leopold N, Lendl B (2003) A new method for fast preparation of highly surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) active silver colloids at room temperature by reduction of silver nitrate with hydroxylamine hydrochloride. J Phys Chem B 107:5723–5727
Knauer M, Ivleva NP, Niessner R, Haisch C (2010) Optimized surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) colloids for the characterization of microorganisms. Anal Sci 26:761–766
Chon H, Lim C, Ha S-M, Ahn Y, Lee EK, Chang S-I, Seong GH, Choo J (2010) On-chip immunoassay using surface-enhanced Raman scattering of hollow gold nanospheres. Anal Chem 82:5290–5295
Wilson R, Bowden SA, Parnell J, Cooper JM (2010) Signal enhancement of surface enhanced Raman scattering and surface enhanced resonance Raman scattering using in situ colloidal synthesis in microfluidics. Anal Chem 82:2119–2123
Kahraman M, Yazici MM, Sahin F, Culha M, (2008) Convective assembly of bacteria for surface-enhanced Raman scattering Langmuir 24:894–901
Laucks ML, Sengputa A, Junge K, Davis EJ, Swanson BD (2005) Comparison of psychro-active arctic marine bacteria and common mesophilic bacteria using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc 59:1222–1228
Wolter A, Niessner R, Seidel M (2008) Detection of Escheria coli O157:H7, Salmonella typhimurium and Legionella pneumophila in water using a flow-through chemiluminescence microarray readout system. Anal Chem 80:5854–5863
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank S. Wiesemann for technical support. A special thanks to M. Wagner for writing an excellent data evaluation program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the ANAKON special issue with guest editors P. Dittrich, D. Günther, G. Hopfgartner, and R. Zenobi.
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 568 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knauer, M., Ivleva, N.P., Niessner, R. et al. A flow-through microarray cell for the online SERS detection of antibody-captured E. coli bacteria. Anal Bioanal Chem 402, 2663–2667 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5398-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5398-0