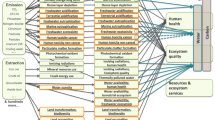
Abstract
This article analyses the benefits and shortcomings of the recently developed decision support systems (DSS) FLUMAGIS, Elbe-DSS, CatchMODS, and MedAction. The analysis elaborates on the following aspects: (i) application area/decision problem, (ii) stakeholder interaction/users involved, (iii) structure of DSS/model structure, (iv) usage of the DSS, and finally (v) most important shortcomings. On the basis of this analysis, we formulate four criteria that we consider essential for the successful use of DSS in landscape and river basin management. The criteria relate to (i) system quality, (ii) user support and user training, (iii) perceived usefulness and (iv) user satisfaction. We can show that the availability of tools and technologies for DSS in landscape and river basin management is good to excellent. However, our investigations indicate that several problems have to be tackled. First of all, data availability and homogenisation, uncertainty analysis and uncertainty propagation and problems with model integration require further attention. Furthermore, the appropriate and methodological stakeholder interaction and the definition of ‘what end-users really need and want’ have been documented as general shortcomings of all four examples of DSS. Thus, we propose an iterative development process that enables social learning of the different groups involved in the development process, because it is easier to design a DSS for a group of stakeholders who actively participate in an iterative process. We also identify two important lines of further development in DSS: the use of interactive visualization tools and the methodology of optimization to inform scenario elaboration and evaluate trade-offs among environmental measures and management alternatives.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkemade JRM, van Grinsven JJM, Wiertz J, Kros J (1998) Towards integrated national modelling with particular reference to the environmental effects of nutrients. Environmental Pollution 102:101–105
Argent RM, Perraud J-M, Rahman, JM, Grayson RB, Podger GM (2009) A new approach to water quality modelling and environmental decision support systems. Environmental Modelling and Software (article in press: doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2008.12.010)
Arnold JG, Srinivasan R, Muttiah R, Williams JR (1998) Large scale hydrologic modeling and assessment. Part 1: model development. Journal of the American Water Resources Association 31:73–89
Assmuth T, Bohle HW, Dirksen MT, Gück E, Krebs N, Thiel C, Zanke U (2002) Synthesebericht des BMBF zum Forschungsvorhaben Auswirkungen von Buhnen auf semiterrestrische Flächen. Research Report of the German Ministry of Education and Research FKZ 0339590. Accessed online March 15, 2009: http://elise.bafg.de/?179
Bach M, Frede HG (1998) Agricultural nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium balances in Germany—methodology and trends 1970 to 1995. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science 161:385–393
Bach M, Frede HG (2005) Assessment of agricultural nitrogen balances for municipalities—example Baden-Wuerttemberg (Germany). EWA online. Accessed online January 31, 2009: http://www.ewaonline.de/journal/2005_01.pdf
Behrendt H, Huber P, Opitz D, Scholl O, Scholz G, Uebe R (1999) Nährstoffbilanzierung der Flussgebiete Deutschlands. UBA-Texte 75/99, Umweltbundesamt, Berlin, Germany, 288 pp
Behrendt H, Bach M, Kunkel R, Opitz D, Pagenkopf WG., Scholz G, Wendland F (2003) Internationale Harmonisierung der Quantifizierung von Nährstoffeinträgen aus diffusen und punktuellen Quellen in die Oberflächengewässer Deutschlands. UBA-Texte 82/03, Umweltbundesamt, Berlin, Germany, 191 pp
Berlekamp J, Lautenbach S, Graf N, Reimer S, Matthies M (2007) Integration of MONERIS and GREAT-ER in the decision support system for the German Elbe river basin. Environmental Modelling and Software 22:239–247
Bishop ID, Stock C, Williams KJ (2008) Using virtual environments and agent models in multi-criteria decision-making. Land Use Policy 26:87–94
Bots PWG, van Twist MJW, van Duin JHR (1999) Designing a power tool for policy analysts: dynamic actor network analysis. In: Sprague RH, Nunamaker JF (eds) Proceedings of the 32nd Hawaii international conference on systems sciences—1999. IEEE Press, Los Alamitos, California, Volume 6:6029
Burke S, Mulligan M, Thornes, JB (1996) Regional estimation of groundwater recharge and the role of changing land use. In: Bromley J (ed) EFEDA-2: hydrology group final report, EU-DG12 (Contract EV5V-CT93-0282)
Burstein F, Holsapple CW (eds) (2008) Handbook on decision support systems, vol 1 (854 pp) and 2 (800 pp). Springer, Heidelberg, Berlin, NY
De Kok J-L, Kofalk S, Berlekamp J, Hahn B, Wind H (2008) From design to application of a decision-support system for integrated river-basin management. Water Resources Management (article in press: doi:10.1007/s11269-008-9352-7)
Diez E, McIntosh BS (2009) A review of the factors which influence the use and usefulness of information systems. Environmental Modelling and Software 24:588–602
Dockerty T, Lovett A, Appleton K, Bone A, Sünnenberg G (2006) Developing scenarios and visualizations to illustrate potential policy and climatic influences on future agricultural landscapes. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 114:103–120
Drewry JJ, Newham LTH, Croke BFW (2009) Suspended sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations and exports during storm-events to the Tuross estuary, Australia. Journal of Environmental Management 90:879–887
EC (2000) European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2000/60/EC establishing a framework for the Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Communities L327:1–72
EU (2008) Natura 2000 network. Accessed online March 28, 2009: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/nature/natura2000/index_en.htm
Federal Office for Building and Planning (2000) Regional Planning Report 2000 (in German), Accessed online March 2009: http://www.bbr.bund.de/cln_007/nn_22548/BBSR/DE/Fachthemen/Raumordnung/RaumentwicklungDeutschland/Raumordnungsberichte/ROB2000/ROB2000__pdf,templateId=raw,property=publicationFile.pdf/ROB2000_pdf.pdf
Feld CK, Rödiger S, Sommerhäuser M, Friedrich G (eds) (2005) Typologie, Bewertung, Management von Oberflächengewässern. Limnologie aktuell 11, E. Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung (Nägele u. Obermiller), Stuttgart, Germany, 243 pp
Fröhlich W (1998) Auswertung der mit dem ELBA-Programmsystem berechneten Wasserstandsvorhersagen vom Zeitraum August 1995 bis Dezember 1997 (Evaluation of the water level predictions calculated with the ELBA program system for the period August 1995–December 1997). German Federal Institute of Hydrology, Koblenz, Berlin, Germany
Fuchs E, Giebel H, Hettrich A, Huesing V, Rosenzweig S, Theis H-J (2003) Einsatz von ökologischen Modellen in der Wasser- und Schifffahrtsverwaltung, das integrierte Flussauenmodell INFORM.–BfG–Mitteilung Nr. 25. German Federal Institute of Hydrology, Koblenz, Germany, 212 pp
Gassman PW, Reyes M, Green CH, Arnold JG (2007) The soil and water assessment tool: historical development, applications, and future directions. Transactions of the ASABE 50:1211–1250
Gerstengarbe FW, Werner PC (1997) A method to estimate the statistical confidence of cluster separation. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 57:103–110
Gerstengarbe FW, Werner PC, Friedrich K (1999) Applying non-hierarchical cluster analysis algorithms to climate classification: some problems and their solution. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 64:143–150
Giupponi C (2007) Decision support systems for implementing the European water framework directive: The MULINO approach. Environmental Modelling and Software 22:248–258
Giupponi C, Mysiak J, Depietri Y, Tamaro M (2007) Decision support systems for water resources management: current state and guidelines for tool development. IWA Publishing, London
Glugla G, Fürtig G (1997) Dokumentation zur Anwendung des Rechenprogramms ABIMO. Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde, Berlin, 37 pp
Gourbesville P (2008) Integrated river basin management, ICT and DSS: challenges and needs. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth 33:312–321
Harremoës P, Gee D, MacGarvin M, Stirling A, Keys J, Wynne B, Guedes Vaz S (eds) (2001) Late lessons from early warnings: the precautionary principle 1896–2000. Environmental Issue Report 22, OPEC, Luxembourg, 210 pp
Harou JJ. Pulido-Velsquez M, Rosenberg DE, Medellin-Azuara, Lund JR, Howitt RE (2009) Hydro-economic models: concepts, design, applications, and future prospects. Journal of Hydrology. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.06.037
Hartmann J, Levy J, Okada N (2006) Managing surface water contamination in Nagoya, Japan: an integrated water basin management decision framework. Water Resources Management 20:411–430
Helms M, Büchele B, Merkel U, Ihringer J (2002) Statistical analysis of the flood situation and assessment of the impact of diking measures along the Elbe (Labe) river. Journal of Hydrology 267:94–114
Henrichsmeier W, Cypris C, Löhe W, Meudt M, Sander R, Von Sothen F, Isermeyer F, Schefski A, Schleef KH, Neander E, Fasterding F, Helmcke B, Neumann M, Nieberg H, Manegold D, Meier T (1996) Entwicklung eines gesamtdeutschen Agrarsektorenmodells RAUMIS 96, Forschungsbericht für das BML (94 HS 021), Bonn/Braunschweig-Völkenrode (in German)
Hettrich A, Rosenzweig S (2001) Erstellung multivariater statistischer Modelle und deren Anwendung zur Prognose der Ökologischen Ausstattung eines Raumes. Bundesanstalt für Gewässerkunde, BfG-Bericht Nr. 1332, Koblenz, Germany, 52 pp
Hewett CJM, Quinn PF, Heathwaite AL, Doyle A, Burke S, Whitehead PG, Lerner DN (2009) A multi-scale framework for strategic management of diffuse pollution. Environmental Modelling and Software 24:74–85
Hirschfeld J, Dehnhardt A, Dietrich J (2005) Socioeconomic analysis within an interdisciplinary spatial decision support system for an integrated management of the Werra River Basin. Limnologica 35:234–244
Højberg AL, Refsgaard JC, van Geer F, Jørgensen LF, Zsuffa I (2007) Use of models to support the monitoring requirements in the water framework directive. Water Resources Management 21:1649–1672
Holzkämper A, Seppelt R (2007) Evaluating cost-effectiveness of conservation management actions in an agricultural landscape on a regional scale. Biological Conservation 136:117–127
Holzkämper A, Lausch A, Seppelt R (2006) Optimizing landscape configuration to enhance habitat suitability for species with contrasting habitat requirements. Ecological Modelling 198:277–292
Huang Y (2005) Appropriate modeling for integrated flood risk assessment. Dissertation, University of Twente, Twente, The Netherlands, 176 pp. Accessed online March 21, 2009: http://doc.utwente.nl/50855/1/thesis_Huang.pdf
Hurkens J, Hahn B, van Delden H (2008) Using the GEONAMICA software environment for integrated dynamic spatial modelling. In: Proceedings of the international congress on environmental modelling and software, July 7–10, 2008, Barcelona, Spain, pp 751–758
Hydrotec (2001) Niederschlags-Abfluss-Modell NASIM - Programmdokumentation. Hydrotec, Aachen, 554 pp
Jakeman AJ, Littlewood IG, Whitehead PG (1990) Computation of the instantaneous unit hydrograph and identifiable component flows with application to two small upland catchments. Journal of Hydrology 117:275–300
Jessel B, Jacobs J (2005) Land use scenario development and stakeholder involvement as tools for watershed management within the Havel River Basin. Limnologica 35:220–233
Kleinhanss W, Osterburg B, Manegold D, Goertz D, Salamon P, Seifert K (1999) Modellgestützte Folgenabschätzung zu den Auswirkungen der Agenda 2000 auf die deutsche Landwirtschaft. Arbeitsbericht 1/99. Bundesforschungsanstalt für Landwirtschaft. Institut für Betriebswirtschaft, Agrarstruktur und ländliche Räume, Braunschweig
Kok K, van Delden H (2009) Combining two approaches of integrated scenario development to combat desertification in the Guadalentin watershed, Spain. Environment and Planning B 36:49–66
Koormann F, Rominger J, Schowanek D, Wagner J-O, Schröder R, Wind T, Silvani M, Whelan MJ (2006) Modeling the fate of down-the-drain chemicals in rivers: an improved software for GREAT-ER. Environmental Modelling and Software 21:925–936
Kosmas C, Kirkby M, Geeson N (1999) The Medalus project—Mediterranean desertification and land use. Manual on key indicators of desertification and mapping environmentally sensitive areas to desertification. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg, 88 pp. Accessed online at Mach 22, 2008: http://www.unep.org/dgef/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket=Kl0BNEh–gM%3D&tabid=1706&language=en-US
Krysanova V, Bronstert A, Muller-Wohlfeil DI (1999) Modelling river discharge for large drainage basins: from lumped to distributed approach. Hydrological Sciences Journal–Journal Des Sciences Hydrologiques 44:313–331
Langley A, Mintzberg H, Pitcher P, Posada E, Saint-Macary J (1995) Open up decision making: the view from the black stool. Organization Science 6:260–279
Lautenbach S, Berlekamp J, Graf N, Seppelt R, Matthies M (2009) Scenario analysis and management options for sustainable river basin management: application of the Elbe-DSS. Environmental Modelling and Software 24:26–43
Legris P, Ingham J, Collerette P (2003) Why do people use information technology? A critical review of the technology acceptance model. Information and Management 40:191–204
Matthies M, Berlekamp J, Koormann F, Wagner JO (2001) Geo-referenced regional simulation and aquatic exposure assessment. Water Science and Technology 43:231–238
Matthies M, Berlekamp J, Lautenbach S, Graf N, Reimer S (2006) System analysis of water quality management for the Elbe river basin. Environmental Modelling and Software 21:1309–1318
Matthies M, Giupponi C, Ostendorf B (2007) Environmental decision support systems: current issues, methods and tools. Environmental Modelling and Software 22:123–127
McIntosh BS, Jeffrey P, Lemon M, Winder N (2005) On the design of computerbased models for integrated environmental science. Journal of Environmental Management 35:741–752
Mödinger J, Kobus H, Schnitzler S, Lehn H (2004) Ansätze für eine nachhaltige Grundwasserbewirtschaftung und -nutzung im Rhein-Neckar-Raum bei konkurrierenden Interessen. Wasser Wirtschaft 94:40–45
ModMED (1998) ModMED. Modelling vegetation dynamics and degradation in mediterranean ecosystems, Final report, EU-DG12 (Contract ENV4-CT95-0139)
Möltgen J, Petry D (eds) (2004) Interdisziplinäre Methoden des Flussgebietsmanagements. Workshopbeiträge, 15./16. März 2004. IfGI prints 21. Münster: Institut für Geoinformatik, Universität Münster, Münster, 352 pp
Mulligan M (2004) MedAction: development, testing and application of the climate, hydrology and vegetation components of a Desertification policy support system. Final report for work undertaken as part of MedAction: Policies to combat desertification in the Northern Mediterranean region supported by the EC-DGXII under contract EVK2-2000-22032
Neitsch SL, Arnold JG, Kiniry JR, Williams JR, King KW (2002) Soil and water assessment tool. Theoretical documentation. Version 2000. GSWRL Report 02-01, BRC Report 2-05. Temple, Texas, USA, 506 pp
Newham LTH, Letcher RA, Jakeman AJ, Kobayashi T (2004) A framework for integrated hydrologic, sediment and nutrient export modelling for catchment-scale management. Environmental Modelling and Software 19:1029–1038
Newham LTH, Jakeman AJ, Letcher RA (2006) Stakeholder participation in modelling for integrated catchment assessment and management: an Australian case study. International Journal of River Basin Management 4:1–13
Newman S, Lynch T, Plummer AA (1999) Success and failure of decision support systems: learning as we go. In: Proceedings of the American Society of Animal Science. Accessed online February 25, 2009: http://www.asas.org/jas/symposia/proceedings/0936.pdf
NRC (2001) Assessing the TDML approach to water quality management. Committee to access the scientific basis of the total maximum daily load approach to water pollution reduction, Water Science and Technology Board, Division on Earth and Life Studies. National Research Council, Washington, DC
Otte-Witte K, Adam K, Meon G, Rathke K (2002) Hydraulisch-morphologische Charakeristika entlang der Elbe (Hydraulic–morphological characteristics along the Elbe river). In: Nestmann F, Buechele B (eds) Morphodynamik der Elbe. Schlussbericht des BMBF-Verbundprojektes mit Einzelbeitragen der Partner und Anlagen-CD, Institut fur Wasserwirtschaft und Kulturtechnik Universitat Karlsruhe, Karlsruhe, Germany
Oxley T, Allen P, Lemon M (1998) The integration of dynamic socio-economic and biophysical models: a model of slope dynamics in the Marina Baixa. IERC, Cranfield. Final report for the ERMES II Project EU-DG12 (ENV4-CT95-0181)
Oxley T, McIntosh B, Mulligan M, Winder N, Engelen G (2004) Integrated modelling and decision support tools: a Mediterranean example. Environmental Modelling and Software 19:999–1010
Paar P, Röhricht W, Schuler J (2008) Towards a planning support system for environmental management and agri-environmental measures—the Colorfields study. Journal of Environmental Management 89:234–244
Parker P et al (2002) Progress in integrated assessment and modelling. Environmental Modelling and Software 17:209–217
Prosser IP, Rustomji P, Young WJ, Moran C, Hughes A (2001) Constructing river basin sediment budgets for the national land and water resources audit. CSIRO Land and Water, Technical Report 15(1):34 pp. Canberra, Australia. Accessed online April 23, 2005: http://www.clw.csiro.au/publications/technical2001/tr15-01.pdf
Reynolds KM, Twery M, Lexer MJ, Vacik H, Ray D, Shao G, Borges JG (2008) Decision support systems in forest management. In: Burstein F, Holsapple CW (eds) Handbook on decision support systems, vol 2. Springer, Heidelberg, Berlin, NY, pp 499–533
RIKS (2008) Metronamica, a dynamic spatial land use model. RIKS, Maastricht
Rode M, Klauer B, Petry D, Volk M, Wenk G, Wagenschein D (2008) Integrated nutrient transport modelling with respect to the implementation of the European WFD: the Weisse Elster case study Germany. Water SA 34:490–496
Rutledge DT, Cameron M, Elliott S, Fenton T, Huser B, McBride G, McDonald G, O’Connor M, Phyn S, Poot J, Price R, Scrimgeour F, Small B, Tait A, Van Delden H, Wedderburn ME, Woods R (2009) Choosing regional futures: challenges and choices in building integrated models to support long-term regional planning in New Zealand. Regional Science Policy and Practice 1:85–108
Schneck A, Haakh F, Lang U (2004) Multikriterielle Optimierung der Grundwasserbewirtschaftung—dargestellt am Beispiel des Wassergewinnungsgebiets Donauried. Wasserwirtschaft 12:32–39
Seddon PB, Graeser V, Willcocks LP (2002) Measuring organisational IS effectiveness: an overview and update of senior management perspectives. Database for Advances in Information Systems 33:11–28
Seppelt R, Voinov A (2002) Optimization methodology for land use patterns using spatially explicit landscape models. Ecological Modelling 151:125–142
Seppelt R, Voinov A (2003) Optimization methodology for landuse patterns: evaluation based on multiscale habitat pattern comparison. Ecological Modelling 168:217–231
Seppelt R, Kühn I, Klotz S, Frank K, Schloter M, Auge A, Kabisch S, Görg C, Jax K (2009) Land use options – strategies and adaptation to global change. Gaia 18:77–80
Tress B, Tress G (2003) Scenario visualization for participatory landscape planning—a study from Denmark. Landscape and Urban Planning 64:161–178
Turban E, Aronson JE (1998) Decision support systems and intelligent systems. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 890 pp
Uran O, Janssen R (2003) Why are spatial decision support systems not used? Some experiences from the Netherlands. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems 27:511–526
USACE (1982) HEC-2: water surface profiles, user’s manual. CPD2A, Hydrologic Engineering Center. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Davis, CA
Vacik H, Lexer MJ (2001) Application of a spatial decision support system in managing the protection forests of Vienna for sustained yield of water resources. Forest Ecology and Management 143:65–76
Van Delden H (2000) A generic approach for the design of decision support systems for river basin management. University of Twente and INFRAM, The Netherlands (Project Report No. i312, Enschede)
Van Delden H, Luja P, Engelen G (2007) Integration of multi-scale dynamic spatial models of socio-economic and physical processes for river basin management. Environmental Modelling and Software 22:223–238
Van Delden H, Kirkby MJ, Hahn BM (2009) Towards a modelling framework for integrated assessment in arid and semi-arid regions. In: Anderssen B et al (eds) 18th IMACS World Congress—MODSIM09 International Congress on Modelling and Simulation. Cairns, Australia. ISBN: 978-0-9758400-7-8
Van der Helm R (2003) Challenging futures studies to enhance EU’s participatory river basin management. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth 28:563–570
Van der Leeuw S (ed) (1998) Understanding the natural and anthropogenic causes of land degradation and desertification in the Mediterranean basin. The ARCHAEOMEDES project—volume synthesis, EU-DG12 (EV5V-CT91-0021)
Van der Sluijs JP (2007) Uncertainty and precaution in environmental management: insights from the UPEM conference. Environmental Modelling and Software 22:590–598
Van Kouwen F, Schot PP, Wassen MJ (2008) A framework for linking advanced simulation models with interactive cognitive maps. Environmental Modelling and Software 23:1133–1144
Verheij HJ (2002) Modification breach growth model in HIS-OM; WL | Delft Hydraulics, Q3299, November 2002 (in Dutch)
Voinov A, Brown Gaddis EJ (2008) Lessons for successful participatory watershed modelling: a perspective from modelling practitioners. Ecological Modelling 216:197–207
Volk M, Hirschfeld J, Schmidt G, Bohn C, Dehnhardt A, Liersch S, Lymburner L (2007) A SDSS-based ecological-economic modelling approach for integrated river basin management on different scale levels—the project FLUMAGIS. Water Resources Management 21:2049–2061
Volk M, Hirschfeld J, Dehnhardt A, Schmidt G, Bohn C, Liersch S, Gassman PW (2008) Integrated ecological-economic modelling of water pollution abatement management options in the upper Ems river. Ecological Economics 66:66–76
Volk M, Liersch S, Schmidt G (2009) Towards the implementation of the European Water Framework Directive? Lessons learned from water quality simulations in an agricultural watershed. Land Use Policy 26:580–588
Walker DH (2002) Decision support, learning and rural resource management. Agricultural Systems 73:113–127
Ward FA, Lynch TP (1996) Integrated river basin optimization: modelling economic and hydrologic interdependence. Water Resources Bulletin 32:1127–1138
White R, Engelen G (1997) Cellular automata as the basis of integrated dynamic regional modelling. Environment and Planning B 24:235–246
Whittaker G, Confesor R Jr, Griffith SM, Färe R, Grosskopf S, Steiner JJ, Mueller-Warrant GW, Banowetz GM (2009) A hybrid genetic algorithm for multiobjective problems with activity analysis-based local search. European Journal of Operational Research 193:195–203
Wolfslehner B, Vacik H (2008) Evaluating sustainable forest management strategies with the analytic network process in a pressure-state-response framework. Journal of Environmental Management 88:1–10
Zapatero EG (1996) A quality assessment instrument for multi-criteria decision support software. Benchmarking for Quality Management & Technology 3:17–27
Zhu X, Healey RG et al (1998) A knowledge-based systems approach to design of spatial decision support systems for environmental management. Environmental Management 22:35–48
Acknowledgments
The work was partly funded by the Helmholtz Programme “Terrestrial Environmental Research” (Seppelt and others 2009). The projects FLUMAGIS (project ID FKZ 03300226) and Elbe-DSS (project ID FKZ 0339542A) were funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Science (BMBF) in Germany. The research on CatchMods has been assisted by the New South Wales Government (Australia) through a grant from its Environmental Trust. The authors are thankful for the cooperation and assistance of staff from the NSW Environmental Protection Authority. The research project MedAction was supported by the European Commission under contract EVK2-2000-22032: www.riks.nl/projects/medaction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volk, M., Lautenbach, S., van Delden, H. et al. How Can We Make Progress with Decision Support Systems in Landscape and River Basin Management? Lessons Learned from a Comparative Analysis of Four Different Decision Support Systems. Environmental Management 46, 834–849 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-009-9417-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-009-9417-2