Abstract
Aims
The objective of this study was to compare the perioperative, short-term, and long-term outcomes of stapled hemorrhoidectomy with Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy.
Materials and methods
The present meta-analysis pooled the effects of outcomes of a total 926 patients treated with stapled or Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy in five out of 122 screened for retrieval randomized controlled trials using the fixed-effects or a random-effects model.
Results
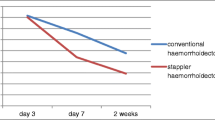
Stapled hemorroidectomy was equivalent to the Ferguson procedure in comparisons pertaining to the following outcomes: hospital stay, postoperative hemorrhage requiring intervention, early postoperative bleeding <4 weeks, late postoperative bleeding <8 weeks, and the presence of anal pathology at 1 year follow-up. Stapled hemorrhoidectomy was superior with impact to operative time, pain visual analogue scale score at 24 h, urinary retention, and wound healing.
Conclusions
There is convincingly apparent evidence about the safety and efficacy of stapled hemorrhoidectomy in the comparison with the well-established Ferguson procedure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johanson JF (2002) Evidence based approach to the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease. Evid Based Gastroenterol 3:26–31
Ferguson JA, Heaton JR (1959) Closed hemorrhoidectomy. Dis Colon Rectum 2(2):176–179 (Mar–Apr)
Longo A (1998) Treatment of hemorrhoidal disease by reduction of mucosa and hemorrhoidal prolapse with a circular suturing device: a new procedure. In: Proceedings of the 6th world congress of endoscopic surgery, Bologna, Italy. Monduzzi Publishing Co., pp 777–784
Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF (1999) Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses. Lancet 354:1896–1900
Mahid SS, Hornung CA, Minor KS, Turina M, Galandiuk S (2006) Systematic reviews and meta-analysis for the surgeon scientist. Br J Surg 93:1315–1324
Egger M, Smith GD, Altman DG (2001) Systematic reviews in health care: meta-analysis in Context, 2nd edn. BMJ Books, London
Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program] (2003) Version 4.2 for Windows. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration
Higgins JPT, Green S editors (2006) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.6 [updated September 2006]. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 4. Wiley, Chichester, UK
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary. Control Clin Trials 17:1–12
Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, Tugwell P, Klassen TP (1998) Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta-analyses? Lancet 352:609–613
Correa-Rovelo JM, Tellez O, Obregón L, Miranda-Gomez A, Moran S (2002) Stapled rectal mucosectomy vs. closed hemorrhoidectomy: a randomized, clinical trial. Dis Colon Rectum 45(10):1367–1374 (discussion 1374–1375 Oct)
Hetzer FH, Demartines N, Handschin AE, Clavien PA (2002) Stapled vs excision hemorrhoidectomy: long-term results of a prospective randomized trial. Arch Surg 137(3):337–340 (Mar)
Ho KS, Ho YH (2006) Prospective randomized trial comparing stapled hemorrhoidopexy versus closed Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy. Tech Coloproctol 10(3):193–197 (Oct)
Huang WS, Chin CC, Yeh CH, Lin PY, Wang JY (2007) Randomized comparison between stapled hemorrhoidopexy and Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy for grade III hemorrhoids in Taiwan: a prospective study. Int J Colorectal Dis 22(8):955–961 (Aug)
Senagore AJ, Singer M, Abcarian H, Fleshman J, Corman M, Wexner S, Nivatvongs S (2004) Procedure for Prolapse and Hemmorrhoids (PPH) Multicenter Study Group. A prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter trial comparing stapled hemorrhoidopexy and Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy: perioperative and one-year results. Dis Colon Rectum Nov;47(11):1824–1836. Erratum in: Dis Colon Rectum. 2005 Feb;48(2):400. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005 May;48(5):1099
Khalil KH, O’Bichere A, Sellu D (2000) Randomized clinical trial of sutured versus stapled closed haemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg 87:1352–1355
Lan P, Wu X, Zhou X, Wang J, Zhang L (2006) The safety and efficacy of stapled hemorrhoidectomy in the treatment of hemorrhoids: a systematic review and meta-analysis of ten randomized control trials. Int J Colorectal Dis 21(2):172–178 (Mar)
Sutherland LM, Burchard AK, Matsuda K, Sweeney JL, Bokey EL, Childs PA, Roberts AK, Waxman BP, Maddern GJ (2002) A systematic review of stapled hemorrhoidectomy. Arch Surg 137(12):1395–1406 (discussion 1407 Dec)
Nisar PJ, Acheson AG, Neal KR, Scholefield JH, Stapled (2004) Hemorrhoidopexy compared with conventional hemorrhoidectomy: systematic review of randomized, controlled trials. Dis Colon Rectum 47(11):1837–1845 (Nov)
Jayaraman S, Colquhoun PH, Malthaner RA (2007) Stapled hemorrhoidopexy is associated with a higher long-term recurrence rate of internal hemorrhoids compared with conventional excisional hemorrhoid surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 50(9):1297–1305 (Sep)
Tjandra JJ, Chan MK (2007) Systematic review on the procedure for prolapse and hemorrhoids (stapled hemorrhoidopexy). Dis Colon Rectum 50(6):878–892 (Jun)
Ortiz H, Marzo J, Armendariz P (2002) Randomized clinical trial of stapled haemorrhoidopexy versus conventional diathermy haemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg 89:1376–1381
Barone JB, Cummings KB (1994) Etiology of acute urinary retention following benign anorectal surgery. Am Surg 60:210–211
Toyonaga T, Matsushima M, Sogawa N, Jiang SF, Matsumura N, Shimojima Y, Tanaka Y, Suzuki K, Masuda J, Tanaka M (2006) Postoperative urinary retention after surgery for benign anorectal disease: potential risk factors and strategy for prevention. Int J Colorectal Dis 21(7):676–682 (Oct)
Patti R, Almasio PL, Muggeo VM, Buscemi S, Arcara M, Matranga S, Di Vita G (2005) Improvement of wound healing after hemorrhoidectomy: a double-blind, randomized study of botulinum toxin injection. Dis Colon Rectum 48(12):2173–2179 (Dec)
Mattana C, Coco G, Manno A, Verbo A, Rizzo G, Petito L, Sermoneta D (2007) Stapled hemorrhoidopexy and Milligan Morgan hemorrhoidopexy in the cure of fourth-degree hemorrhoids: long-term evaluation and clinical results. Dis Colon Rectum 50:1770–1775
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
George Sgourakis and Georgios C. Sotiropoulos contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sgourakis, G., Sotiropoulos, G.C., Dedemadi, G. et al. Stapled versus Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy: is there any evidence-based information?. Int J Colorectal Dis 23, 825–832 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-008-0502-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-008-0502-4