Abstract
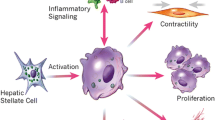
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are pericytes of liver in the space between parenchymal cells and sinusoidal endothelial cells of the hepatic lobule. HSCs comprise specialized functions such as vitamin A storage, hemodynamic functions, support of liver regeneration, and immunoregulation. In pathological conditions, HSCs transform to an activated myofibroblasts-like phenotype, start to proliferate, and de novo express several proinflammatory and profibrogenic genes. These processes are particularly important in the development of cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and hepatocellular cancer. This review highlights recent findings in understanding the biology of HSCs and discusses the physiological functions of HSCs and the role of activated HSCs in pathophysiology and disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α-SMA:
-
Alpha-smooth muscle actin
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- HSCs:
-
Hepatic stellate cells
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- MMPs:
-
Metalloproteinases
References
Ahern M, Hall P, Halliday LC, Olynyk J, Ramm G, Denk H (1996) Hepatic stellate cell nomenclature (letter). Hepatology 1:193
Amann T, Bataille F, Spruss T, Muhlbauer M, Gabele E, Scholmerich J, Kiefer P, Bosserhoff AK, Hellerbrand C (2009) Activated hepatic stellate cells promote tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci 4:646–653
Asahina K, Tsai SY, Li P, Ishii M, Maxson RE Jr, Sucov HM, Tsukamoto H (2009) Mesenchymal origin of hepatic stellate cells, submesothelial cells, and perivascular mesenchymal cells during mouse liver development. Hepatology 3:998–1011
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2:209–218
Blomhoff R, Blomhoff HK (2006) Overview of retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol 7:606–630
Cassiman D, Barlow A, Vander BS, Libbrecht L, Pachnis V (2006) Hepatic stellate cells do not derive from the neural crest. J Hepatol 6:1098–1104
Chang J, Hisamatsu T, Shimamura K, Yoneno K, Adachi M, Naruse H, Igarashi T, Higuchi H, Matsuoka K, Kitazume MT, Ando S, Kamada N, Kanai T, Hibi T (2012) Activated hepatic stellate cells mediate the differentiation of macrophages. Hepatol Res. doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01111.x
Chen L, Zhang W, Zhou QD, Yang HQ, Liang HF, Zhang BX, Long X, Chen XP (2012) HSCs play a distinct role in different phases of oval cell-mediated liver regeneration. Cell Biochem Funct 7:588–596
Fimmel CJ, Brown KE, O'Neill R, Kladney RD (1996) Complement C4 protein expression by rat hepatic stellate cells. J Immunol 6:2601–2609
Friedman SL (2008) Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 1:125–172
Gabele E, Muhlbauer M, Dorn C, Weiss TS, Froh M, Schnabl B, Wiest R, Scholmerich J, Obermeier F, Hellerbrand C (2008) Role of TLR9 in hepatic stellate cells and experimental liver fibrosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2:271–276
Geerts A (2001) History, heterogeneity, developmental biology, and functions of quiescent hepatic stellate cells. Semin Liver Dis 3:311–335
Ichikawa S, Mucida D, Tyznik AJ, Kronenberg M, Cheroutre H (2011) Hepatic stellate cells function as regulatory bystanders. J Immunol 10:5549–5555
Ito T, Nemoto M (1952) Kupfer’s cells and fat storing cells in the capillary wall of human liver. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 4:243–258
Marra F (2002) Chemokines in liver inflammation and fibrosis. Front Biosci 7:1899–1914
Mormone E, George J, Nieto N (2011) Molecular pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis and current therapeutic approaches. Chem Biol Interact 3:225–231
Muhlbauer M, Fleck M, Schutz C, Weiss T, Froh M, Blank C, Scholmerich J, Hellerbrand C (2006) PD-L1 is induced in hepatocytes by viral infection and by interferon-alpha and -gamma and mediates T cell apoptosis. J Hepatol 4:520–528
Paik YH, Schwabe RF, Bataller R, Russo MP, Jobin C, Brenner DA (2003) Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 5:1043–1055
Reynaert H, Urbain D, Geerts A (2008) Regulation of sinusoidal perfusion in portal hypertension. Anat Red 6:693–698
Rocky DC (1995) Characterization of endothelin receptors mediating rat hepatic stellate cell contraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2:725–731
Su YH, Shu KH, Hu C, Cheng CH, Wu MJ, Yu TM, Chuang YW, Huang ST, Chen CH (2012) Hepatic stellate cells attenuate the immune response in renal transplant recipients with chronic hepatitis. Transplant Proc 3:725–729
Tacke F, Weiskirchen R (2012) Update on hepatic stellate cells: pathogenic role in liver fibrosis and novel isolation techniques. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:67–80
Thabut D, Shah V (2010) Intrahepatic angiogenesis and sinusoidal remodeling in chronic liver disease: new targets for the treatment of portal hypertension? J Hepatol 5:976–980
Ueno T, Bioulac-Sage P, Balabaud C, Rosenbaum J (2004) Innervation of the sinusoidal wall: regulation of the sinusoidal diameter. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 1:868–873
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hellerbrand, C. Hepatic stellate cells—the pericytes in the liver. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 465, 775–778 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1209-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1209-5