Abstract
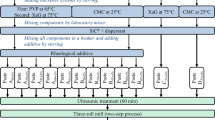
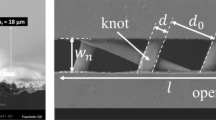
For printing the front side metallization of solar cells using the non-contact aerosol printer different silver inks with different rheological properties and silver components were tested. Both atomization methods of the aerosol printer are introduced and the optimized printing parameters are discussed. With the most suitable inks and printing parameters it was possible to achieve high aspect ratios within 2:1 up to 4:1 with small lateral resolutions. A particle-free ink and several particle-containing inks for example diluted screen printing pastes were tested as aerosol ink to evaluate the most feasible ink. According to these results it was possible to assess the most important properties for aerosol inks, which are necessary to obtain a good printability and well defined printed structures. High aspect ratios (AR) of 2:1 were achieved by aerosol printing with the pneumatic atomizer for the front side metallization grid of solar cells and efficiencies of 14–17 % were achieved.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hildebrandt S, Waltinger A, Eberstein M, Mosch S, Michaelis, Kinski I (2011) Seedlayer Deposition of a novel particle-free nickel ink. 26th European photovoltaic solar energy conference and exhibition. doi:10.4229/26thEUPVSEC2011-2BV.3.71
Hong CM, Wagner S (2000) Inkjet printed copper source/drain metallization for amorphous silicon thin-film transistors. IEEE Electr Device L 21(8):384–386. doi:10.1109/55.852958
Hong K-K, Cho S-B, You JS, Jeong J-W, Bea S-M, Huh J-Y (2009) Mechanism for the formation of Ag crystallites in the Ag thick-film contacts of crystalline Si solar cells. Sol Energ Mat Sol C 93:898–904. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2008.10.021
Hörteis M, Glunz SW (2008) Fine line printed silicon solar cells exceeding 20% efficiency. Prog Photovolt: Res Appl 16:555–560. doi:10.1002/pip.850
King BH, Barnes SM (2008) Aerosol jet printing system for high speed, non-contact, front side metallization helping improve efficiencies of silicon solar cells. 24th international conference on digital printing technologies, pp 918-922. ISBN: 9780892082797
Kress A (2001) Emitterverbund-Rückkontaktsolarzellen für die industrielle Fertigung, Dissertation, Universität Konstanz
Mette A, Schetter C, Wissen D, Lust S, Glunz SW, Willeke G (2006) Increasing the efficiency of screen-printed silicon solar cells by light induced silver plating. IEEE 4th world conference on photovoltaic energy conversion
Mette A, Richter PL, Hörteis M, Glunz SW (2007) Metal aerosol jet printing for solar cell metallization. Prog Photovolt Res Appl 15:621–627. doi:10.1002/pip.759
Obliers-Hommrich B, Fischer A, Willeck H, Eberhardt W, Kück H (2008) Single- and multi-layer conductive patterns fabricated using M3D technology. Multi-material micro manufacture conference. 4m-net.org. http://www.4m-net.org/files/papers/4M2008/03-05/03-05.PDF. Accessed 06 March 2014
Schubert G (2006) Thick film metallization of crystalline silicon solar cells. Dissertation, Universität Konstanz
Teng KF, Vest RW (1988) Metallization of solar cells with ink jet printing and silver metallo-organic inks. IEEE Trans Comp Hybrids 11(3):291–297. doi:10.1109/33.16656
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the SAB with Grant Number 12894/2154.

Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hildebrandt, S., Kinski, I., Mosch, S. et al. Non-contact printing: conductive track geometry affected by ink rheology and composition. Microsyst Technol 21, 1363–1369 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2275-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2275-8