Abstract
The taxonomically complicated Crocus series Verni is characterized by high intra- and interspecific variability of karyotypes (2n = 8–23). With the aim to get more insights into complex karyotype evolution and to clarify the taxonomy of this group, we combined morphological (twelve characters), molecular (chloroplast DNA: trnL–trnF, ndhF; nuclear DNA: ITS, pCOSAt103) and karyological analyses. Samples of different populations of C. etruscus, C. ilvensis, C. kosaninii, C. tommasinianus, C. vernus sensu lato and C. longiflorus (series Longiflori) were analyzed. Quantitative karyotype parameters were calculated for all taxa involved based on the available literature. For the taxon traditionally known as C. vernus, the analyses suggest that it should be split in five species: C. heuffelianus, C. neapolitanus, C. neglectus sp. nov., C. siculus and C. vernus. The comparison of genome total haploid lengths suggests that in the evolution of the group polyploidization only played a role within the C. vernus species complex, where we also detected two hybridization events. In all other taxa, chromosome evolution is probably characterized by chromosome fusions and fissions, sometimes affecting the entire haploid chromosome set. Comparative cytogenetics of the group indicates that series Verni is subject to a peculiar type of unequal change in chromosome size, i.e., that not both chromosome arms gain or lose equally in DNA content. As a taxonomic consequence of our study, series Verni is newly circumscribed, now including the autumn-flowering C. longiflorus and excluding C. baytopiorum.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez I, Wendel JF (2003) Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29:417–434
Baldini RM (1990) Karyological observations on two Crocus species (Iridaceae) from Tuscany (Italy). Caryologia 43:341–345
Baldini RM (1993) Numeri cromosomici per la Flora Italiana: 1284–1289. Inform Bot Ital 24:189–195
Baldwin BG, Sanderson MJ, Porter JM, Wojciechowski MF, Campbell CS, Donoghue MJ (1995) The ITS region of nuclear ribosomal DNA: a valuable source of evidence on angiosperm phylogeny. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 82:247–277
Blattner FR (1999) Direct amplification of the entire ITS region from poorly preserved plant material using recombinant PCR. Biotechniques 29:1180–1186
Borzatti von Loewenstern A, Giordani T, Astuti G, Andreucci A, Peruzzi L (2013) Phylogenetic relationships of Italian Bellevalia species (Asparagaceae), inferred from morphology, karyology and molecular systematics. Pl Biosystems 147:776–787
Brighton CA (1976) Cytological problems in the genus Crocus (Iridaceae): I. Crocus vernus aggregate. Kew Bull 31:33–46
Brighton CA, Mathew B, Marchant CJ (1973) Chromosome counts in the genus Crocus (Iridaceae). Kew Bull 28:451–464
Carta A, Pierini B, Alessandrini A, Frignani F, Peruzzi L (2010) Contributo alla conoscenza della flora vascolare endemica di Toscana ed aree contermini. 1. Crocus etruscus Parl. (Iridaceae). Inform Bot Ital 42:47–52
Carta A, Probert R, Moretti M, Peruzzi L, Bedini G (2014) Seed dormancy and germination in three Crocus ser. Verni species (Iridaceae): implications for evolution of dormancy within the genus. Plant Biol. doi:10.1111/plb.12168
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol 9:1657–1660
Comes HP, Kadereit JW (1998) The effect of Quaternary climatic changes on plant distribution and evolution. Trends Plant Sci 3:432–438
Conti F, Abbate G, Alessandrini A, Blasi C (2005) An annotated checklist of the Italian vascular flora. Palombi Editori, Roma
de la Herrán R, Robles F, Cuñado N, Santos JN, Ruiz Rejón M, Garrido-Ramos RA, Ruiz Rejón C (2001) A heterochromatic satellite DNA is highly amplified in a single chromosome of Muscari (Hyacinthaceae). Chromosoma 110:197–202
Eickbush TH, Eickbush DG (2007) Finely orchestrated movements: evolution of ribosomal RNA genes. Genetics 175:477–485
Feliner GN (2011) Southern European glacial refugia: a tale of tales. Taxon 60:365–372
Foggi B, Viciani D, Baldini RM, Carta A, Guidi T (2014) A IUCN appraisal of the endemic plant of the Tuscan Archipelago (Tyrrhenian sea). Oryx: in press
Frello S, Heslop-Harrison JS (2000) Chromosomal variation in Crocus vernus Hill (Iridaceae) investigated by in situ hybridization of rDNA and a tandemly repeated sequence. Ann Bot 86:317–322
Frello S, Ørgaard M, Jacobsen N, Heslop-Harrison JS (2004) The genomic organization and evolutionary distribution of a tandemly repeated DNA sequence family in the genus Crocus (Iridaceae). Hereditas 141:81–88
Goldblatt P, Takei M (1997) Chromosome cytology of Iridaceae: patterns of variation, determination of base number, and modes of karyotype change. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 84:285–304
Harpke D, Meng S, Kerndorff H, Rutten T, Blattner FR (2013) Phylogeny of Crocus (Iridaceae) based on one chloroplast and two nuclear loci: ancient hybridization and chromosome number evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 66:617–627
Hewitt GM (2011) Quaternary phylogeography: the roots of hybrid zones. Genetica 139:617–638
Jakob SS, Blattner FR (2006) A chloroplast genealogy of Hordeum (Poaceae): long-term persisting haplotypes, incomplete lineage sorting, regional extinction, and the consequences for phylogenetic inference. Mol Biol Evol 23:1602–1612
Jakob SS, Ihlow A, Blattner FR (2007) Combined ecological niche modelling and molecular phylogeography revealed the evolutionary history of Hordeum marinum (Poaceae)—niche differentiation, loss of genetic diversity, and speciation in Mediterranean Quaternary refugia. Mol Ecol 16:1713–1727
Jang T-S, Emadzade K, Parker J, Temsch EM, Leitch AR, Speta F, Weiss-Schneeweiss H (2013) Chromosomal diversification and karyotype evolution of diploids in the cytologically diverse genus Prospero (Hyacinthaceae). BMC Evol Biol 13:136
Karasawa K (1943) Karyological studies in Crocus III. Jap J Bot 12:475–503
Kerndorff H (1993) Two new taxa in Turkish Crocus (Iridaceae). Herbertia 49:76–86
Kerndorff H, Pasche E (1994) Crocus mathewii: a new autumn-flowering Crocus from Turkey. New Plantsman 1:102–106
Kerndorff H, Pasche E (1997) Zwei bemerkenswerte Taxa des Crocus biflorus-Komplexes (Iridaceae) aus der Nordosttürkei. Linzer Biol Beitr 29:591–600
Kerndorff H, Pasche E (2003) Crocus biflorus in Anatolia. Plantsman 2:77–89
Kerndorff H, Pasche E (2004a) Two new taxa of the Crocus biflorus aggregate (Liliiflorae, Iridaceae) from Turkey. Linzer Biol Beitr 36:5–10
Kerndorff H, Pasche E (2004b) Crocus biflorus in Anatolia, Part Two. Plantsman 3:201–215
Kerndorff H, Pasche E (2006) Crocus biflorus in Anatolia, Part Three. Linzer Biol Beitr 38:165–187
Kerndorff H, Pasche E (2011) Two new taxa of Crocus (Liliiflorae, Iridaceae) from Turkey. Stapfia 95:2–5
Kerndorff H, Pasche E, Harpke D, Blattner FR (2011) Three new species of Crocus (Liliiflorae, Iridaceae) from Turkey. Stapfia 95:99–105
Kerndorff H, Pasche E, Harpke D, Blattner FR (2012) Seven new species of Crocus (Liliiflorae, Iridaceae) from Turkey. Stapfia 97:3–16
Kerndorff H, Pasche E, Harpke D, Blattner FR (2013a) A new species of Crocus (Liliiflorae, Iridaceae) from Turkey. Stapfia 99:141–144
Kerndorff H, Pasche E, Harpke D, Blattner FR (2013b) Fourteen new species of Crocus (Liliiflorae, Iridaceae) from West, South-west and South-Central Turkey. Stapfia 99:145–158
Kerndorff H, Pasche E, Harpke D, Blattner FR (2013c) Crocus biflorus Miller (Liliiflorae, Iridaceae) in Anatolia—Part IV. Stapfia 99:159–186
Kiefer C, Dobeš C, Sharbel TF, Koch MA (2009) Phylogeographic structure of the chloroplast DNA gene pool in North American Boechera: a genus and continental-wide perspective. Mol Phylogenet Evol 52:303–311
Leitch IJ, Bennett MD (2004) Genome downsizing in polyploid plants. Biol J Linn Soc 82:651–663
Leitch IJ, Hanson L, Lim KY, Kovarik A, Chase MW, Clarkson JJ, Leitch AR (2008) The ups and downs of genome size evolution in polyploid species of Nicotiana (Solanaceae). Ann Bot 101:805–814
Li W (1997) Molecular evolution. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Li M, Wunder J, Bissoli G, Scarponi E, Gazzani S, Barbaro E, Saedler H, Varotto C (2008) Development of COS genes as universally amplifiable markers for phylogenetic reconstructions of closely related plant species. Cladistics 24:1–19
Mathew B (1982) The Crocus: a revision of the genus Crocus (Iridaceae). Timber Press Inc, Portland
Mathew B, Petersen G, Seberg O (2009) A reassessment of Crocus based on molecular analysis. Plantsman 8:50–57
Micevska D (2000) Caryological analysis of the species of the genus Crocus. Master thesis, University of Skopje
Mihaly A, Kricfalusy V (1997) Population biology and ecology of Crocus heuffelianus Herb. (Iridaceae) in Ukraine. Linzer Biol Beitr 29:641–681
Mitic D (2001) Caryological analysis of some species of the genus Crocus L. Master thesis, University of Skopje
Olmstead RG, Sweere JA (1994) Combining data in phylogenetic systematics: an empirical approach using three molecular data sets in the Solanaceae. Syst Biol 43:467–481
Pasche E (1993) A new Crocus (Iridaceae) from Turkey. Herbertia 49:67–75
Pasche E, Kerndorff H (1999) A new natural hybrid in the genus Crocus (Iridaceae). New Plantsman 6:43–45
Peruzzi L (2013) “x” is not a bias, but a number with real biological significance. Pl Biosystems 147:1238–1241
Peruzzi L, Carta A (2011) Crocus ilvensis sp. nov. (section Crocus, Iridaceae), endemic to Elba Island (Tuscan Archipelago, Italy). Nordic J Bot 29:6–13
Peruzzi L, Eroğlu HE (2013) Karyotype asymmetry: again, how to measure and what to measure? Comp Cytogen 7:1–9
Peruzzi L, Leitch IJ, Caparelli KF (2009) Chromosome diversity and evolution in Liliaceae. Ann Bot 103:459–475
Peruzzi L, Bedini G, Andreucci A (2012) Homoploid hybrid speciation in Doronicum (Asteraceae)? Morphological, karyological and molecular evidences. Pl Biosystems 146:867–877
Peruzzi L, Carta A, Garbari F (2013) Lectotypification of the name Crocus sativus var. vernus L. (Iridaceae) and its consequences within the series Verni. Taxon 62:1037–1040
Petersen G, Seberg O, Thorsøe S, Jørgensen T, Mathew B (2008) A phylogeny of the genus Crocus (Iridaceae) based on sequence data from five plastid regions. Taxon 57:487–499
Peterson A, Harpke D, Peruzzi L, Tison J-M, John H, Peterson J (2010) Gagea bohemica (Liliaceae), a highly variable monotypic species within sect. Didymobulbos. Pl Biosystems 144:308–322
Peterson A, Levichev IG, Peterson J, Harpke D, Schnittler M (2011) New insights into the phylogeny and taxonomy of Chinese species of Gagea (Liliaceae)–speciation through hybridization. Org Div Evol 11:387–407
Pignatti S (1982) Flora d’Italia 1–3. Edagricole, Bologna
Podani J (1999) Extending Gower’s general coefficient of similarity to ordinal characters. Taxon 48:331–340
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Ranđelović N, Hill DA, Ranđelović V (1990) The genus Crocus L. in Serbia. The Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts. Monographs Volume DCI. Dept Nat Math Sci 66:1–52
Ranđelović N, Sekovski Ž, Dimeska G (2007) Systematic, chorological and genetic research into the genus Crocus L. in Macedonia. Collection of Papers Devoted to Academician Kiril Micevski 97–131
Ranđelović N, Ranđelović V, Hristovski N (2012) Crocus jablanicensis (Iridaceae), a new species from the Republic of Macedonia, Balkan peninsula. Ann Bot Fenn 49:99–102
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Rudall PJ, Owens SJ, Kenton AY (1984) Embryology and breeding systems in Crocus (Iridaceae): a study in causes of chromosome variation. Plant Syst Evol 148:119–134
Schneider I, Kerndorff H, Pasche E (2013) Chromosome numbers of Turkish Crocus (Liliiflorae, Iridaceae) and their geographical distribution. Feddes Repert 123:73–79
Šopova M, Sekovski Ž (1982) Chromosome atlas of some Macedonian angiospermus. Macedonian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Sec Biol Med Sci, Skopje 1–43
Tison J-M, Peterson A, Harpke D, Peruzzi L (2013) Reticulate evolution of the critical Mediterranean Gagea sect. Didymobulbos (Liliaceae), and its taxonomic implications. Plant Syst Evol 299:413–438
Yüzbaşıoğlu S, Varol Ö (2004) A new autumn-flowering Crocus from SW Turkey. Plantsman 3:104–106
Acknowledgments
We thank B. Kränzlin and P. Oswald for expert technical help in the lab, F. Bartolucci for logistic help in collecting material of C. neapolitanus in Abruzzo, G. Gestri and B. Pierini for collecting material of C. neglectus, L. Bernardo and D. Gargano for providing Crocus materials conserved in CLU, Thomas Huber and Dirk Schnabel for providing Crocus material of their living collection and for measuring morphological parameters for these specimen, H. Kerndorff for his comments on the manuscript, Z. Barina for providing images of Crocus heuffelianus in BP, G. Domina for useful advices about Tineo’s life and calligraphy. The Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia supported this research through Grant 173030 “Plant biodiversity of Serbia and the Balkans–assessment, sustainable use and protection” and the German Research Foundation (DFG) through Grant BL462/7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
606_2014_1074_MOESM1_ESM.tif
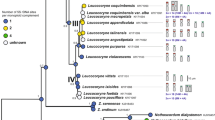
Phylogenetic tree of series Verni derived from a Bayesian analysis of combined sequences of the ITS, trnL–trnF and ndhF regions (24 sequences, 2026 characters). Posterior probabilities are given at the nodes (TIFF 12634 kb)
Appendix. Sources of the studied material with abbreviation for populations used in text and figures in the following order: Taxon: Acronym: Origin, herbar voucher. Order of GenBank accession numbers for voucher of outgroups: trnL–trnF, ndhF, ITS (ITS1 + 5.8SrDNA + ITS2), pCOSAt103;—denotes lacking sequence
Appendix. Sources of the studied material with abbreviation for populations used in text and figures in the following order: Taxon: Acronym: Origin, herbar voucher. Order of GenBank accession numbers for voucher of outgroups: trnL–trnF, ndhF, ITS (ITS1 + 5.8SrDNA + ITS2), pCOSAt103;—denotes lacking sequence
C. neglectus 2n = 16, PE: Italy, Monte Pelato (Livorno), Tuscany, PI s.n., PI: Italy, Monte Pisano (Lucca), PI s.n.; C. neapolitanus 2n = 8, A: Italy, Altopiano delle Rocche (L’Aquila), Abruzzo, PI s.n.; AII: Italy, Collarmele (L’Aquila), Abruzzo, PI s.n.; C. siculus 2n = 8, Sic: Italy, Nebrodi (Messina), Sicily, CLU 19778, 19779; C. vernus, 2n = 8, VER: Switzerland, Ticino, Airolo, San Gottardo area, 1100-1500 m a.s.l. (locus classicus), PI s.n.; C. ilvensis 2n = 8, Fi: Italy, Capanne, Filicaia (Elba Island), Tuscany, PI s.n.; C: Italy, Capanne, Colle Grottaggia (Elba Island), Tuscany, PI, s.n.; M: Italy, Capanne, Monte Maolo (Elba Island), Tuscany, PI s.n.; N: Italy, Capanne, Valle Nivera (Elba Island), Tuscany (locus classicus), PI s.n.; C. etruscus 2n = 8, S: Italy, Sassetta, Tuscany, PI s.n.; SS: Italy, Sassetta 2nd locality, Tuscany, PI s.n.; CA: Italy, Campiglia Marittima, Tuscany, PI s.n.; F: Italy, Salita del Filetto, Tuscany (locus classicus), PI s.n.; P: Italy, Punta Ala, Tuscany, PI s.n.; C. tommasinianus 2n = 16, E: Serbia, Krusevac, village Lazarevac, C Serbia BEOU 31678, E: Serbia, Soko Banja, village Resnik, E Serbia BEOU 31679; C. kosaninii, 2n = 14, R: Serbia, Mt Rujan, Planina, S Serbia, BEOU 31680, S: Serbia, Leskovac, village Strojkovce, SE Serbia, BEOU 31681; C. heuffelianus, 2n = 22?, W Serbia: Mt Zlatibor, Tornik peak, 1450 m a.s.l., BEOU 31682; C. longiflorus, 2n = 28, T: Italy, Tortora (Cosenza), 350 m, CLU 12508, G: Italy, Grotta della Manca (Cosenza), 1250 m a.s.l., CLU 13099, Ne: Italy, Nebrodi Range, Sicilia, 1050 m a.s.l., GAT 23048, EM: Italy, Luciano 680-1000 m a.s.l., EM1057, GAT 23049.
Outgroups: C. asumaniae B.Mathew and T.Baytop, cult., GAT 7207, -, -, HE801126,-; C. banaticus J.Gay, cult., GAT 7285, -, -, HE801147,-; C. baytopiorum B.Mathew, HKEP1014, Turkey, GAT 7187, -, -, HE663994,-; C. cambessedesii J.Gay, Spain, GAT 7211, -, -, a: HE801098 d: HE801104,.-; C. cartwrightianus Herb., Greece, B/DB 4304, -, -, HG518198; C. cartwrigthianus var. creticus Herb., Greece, MAIC 1991, -, -, HE801160, -; C. corsicus Vanucchi ex Maw, France, Corsica, GAT 7252; -, -,a: HE801091 b: HE801097, -; C. goulimyi Turrill, cult., GAT 7217, -, -, HE801130, b: HE663874 efgc: HE663876; C. hadriaticus Herb, Greece, ATH 1532, -, -, HE864270,-; C. imperati Ten., Italy, GAT 7221, -, -, HE801131,-; C. ligusticus Mariotti, Italy, GAT 7226, -, -, HE801167,-; C. malyi Vis., Croatia, HK293, GAT 7259, -, -, HE801170; C. mathewii Kernd. and Pasche, Turkey, GAT 7189, -, -, HE801089,-; C. moabiticus Bornm. and Dinsm. ex Bornm., Jordan, HKEP9942, -, -, HG518196,-; C. nudiflorus Sm. Spain, HKEP1231, -, -, HG518194,-; C. oreocreticus B.L.Burtt, Greece, MAIC 3674, -, -, HE801161; C. pallasii Goldb. subsp. pallasii, cult., GAT 7230, -, -, HG518197,-; C. pallasii Turkey, HKEP1033A, GAT 7175, -, -, HE664002,-; C. pelistericus Pulević, Greece, B 10 0355313, -, -, HE664020,-; C. sativus L., cult., GAT 7277, -, -, HE801144,-; C. scardicus Košanin, Macedonia, B 10 0112048, -, -, HE663961,-; C. scharojanii Rupr., Russia, Caucasus, 2570 m a.s.l., GAT 23083, HG518229, HG518260, -,-; C. serotinus Salisb. Spain, HKEP1124, -, -, HG518195,-; C. serotnius subsp. salzmannii B.Mathew, Morocco, GAT 7276, -, -, HE801125, a: HE663913 b: HE663914; C. thomasii Ten., Italy, CLU 13102, -, -, HE801118,-; Romulea bulbocodium (L.) Sebast. and Mauri, Turkey, HKEP1108, GAT 7481, -, -, HE664008,-; Romulea ramiflora Ten., Turkey, HKEP1115, GAT 7480, -, -, HE664012,-.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harpke, D., Carta, A., Tomović, G. et al. Phylogeny, karyotype evolution and taxonomy of Crocus series Verni (Iridaceae). Plant Syst Evol 301, 309–325 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-014-1074-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-014-1074-0