Abstract
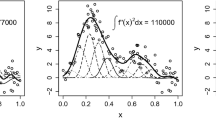
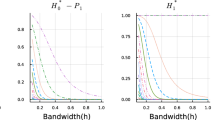
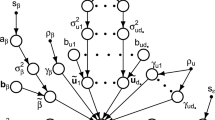
We consider the problem of estimating an additive regression function in an inverse regression model with a convolution type operator. A smooth backfitting procedure is developed and asymptotic normality of the resulting estimator is established. Compared to other methods for the estimation in additive models the new approach neither requires observations on a regular grid nor the estimation of the joint density of the predictor. It is also demonstrated by means of a simulation study that the backfitting estimator outperforms the marginal integration method at least by a factor of two with respect to the integrated mean squared error criterion. The methodology is illustrated by a problem of live cell imaging in fluorescence microscopy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertero, M., Boccacci, P., Desiderà, G., Vicidomini, G. (2009). Image deblurring with Poisson data: From cells to galaxies. Inverse Problems, 25(12), 123006.
Bissantz, N., Hohage, T., Munk, A., Ruymgaart, F. (2007). Convergence rates of general regularization methods for statistical inverse problems. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 45, 2610–2636.
Brillinger, D. R. (2001). Time series data analysis and theory. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), Philadelphia, PA.
Carroll, R. J., Härdle, W., Mammen, E. (2002). Estimation in an additive model when the parameters are linked parametrically. Econometric Theory, 18(4), 886–912.
Cavalier, L. (2008). Nonparametric statistical inverse problems. Inverse Problems, 24(3), 034004.
Diggle, P. J., Hall, P. (1993). A Fourier approach to nonparametric deconvolution of a density estimate. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, 55, 523–531.
Engl, H. W., Hanke, M., Neubauer, A. (1996). Regularization of inverse problems, volume 375 of mathematics and its applications. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers Group.
Fan, J. (1991). On the optimal rates of convergence for nonparametric deconvolution problems. Annals of Statistics, 19, 1257–1272.
Folland, G. B. (1984). Real Analysis—Modern Techniques and their Applications. New York: Wiley.
Giné, E., Guillou, A. (2002). Rates of strong uniform consistency for multivariate kernel density estimators. Annales de l’Institut Henri Poincaré (B) Probabilités et Statistiques, 38(6), 907–921.
Hengartner, N. W., Sperlich, S. (2005). Rate optimal estimation with the integration method in the presence of many covariates. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 95(2), 246–272.
Hildebrandt, T. (2013). Additive Modelle im inversen Regressionsproblem mit Faltungsoperator. PhD thesis, Fakultät für Mathematik, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Germany.
Hildebrandt, T., Bissantz, N., Dette, H. (2014). Additive inverse regression models with convolution-type operators. Electronic Journal of Statistics, 8, 1–40.
Kaipio, J., Somersalo, E. (2010). Statistical and computational inverse problems. Berlin: Springer.
Kammler, D. W. (2007). A first course in fourier analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Linton, O. B., Nielsen, J. P. (1995). A kernel method of estimating structured nonparametric regression based on marginal integration. Biometrika, 82(1), 93–100.
Mair, B. A., Ruymgaart, F. H. (1996). Statistical inverse estimation in Hilbert scales. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematic, 56, 1424–1444.
Mammen, E., Linton, O. B., Nielsen, J. (1999). The existence and asymptotic properties of a backfitting projection algorithm under weak conditions. Annals of Statistics, 27(5), 1443–1490.
Martinez-Miranda, M. D., Nielsen, J. P., Sperlich, S., Verrall, R. (2013). Continuous chain ladder: Reformulating and generalising a classical insurance problem. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(14), 5588–5603.
Martinez-Miranda, M. D., Nielsen, J. P., Verrall, R. (2012). Double chain ladder. Astin Bulletin, 42(1), 59–76.
Nielsen, J. P., Sperlich, S. (2005). Smooth backfitting in practice. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Serial B, 67(1), 43–61.
Saitoh, S. (1997). Integral transforms, reproducing kernels and their applications. Harlow: Longman.
Stefanski, L., Carroll, R. J. (1990). Deconvoluting kernel density estimators. Statistics, 21, 169–184.
van der Vaart, A. W. (1998). Asymptotic statistics, Cambridge series in statistical and probabilistic mathematics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Martina Stein and Alina Dette, who typed parts of this manuscript with considerable technical expertise. This work has been supported in part by the Collaborative Research Center “Statistical modeling of nonlinear dynamic processes” (SFB 823, Teilprojekt C1, C4) of the German Research Foundation (DFG). The authors are also grateful to two unknown referees. Their constructive comments on the first version of the paper led to a substantial improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Bissantz, N., Dette, H., Hildebrandt, T. et al. Smooth backfitting in additive inverse regression. Ann Inst Stat Math 68, 827–853 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-015-0517-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-015-0517-x