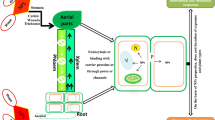
Abstract
Over the past decade, incorporation of nanomaterials into agricultural practices like nanofertilizers and nanopesticides has gained a lot of attention. Progress and application of fertilizers in nanoforms are one of the effective options for considerable improvement of the agricultural yield worldwide. Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) are considered as a biosafe material for biological species. Earlier studies have shown the potential of ZnO NPs in stimulation of seed germination and plant growth as well as disease suppression and plant protection by its antimicrobial activity. However, both positive and negative effects of ZnO NPs on plant growth and metabolism at various developmental periods have been documented. Uptake, translocation and accumulation of ZnO NPs by plants depend upon the features of NPs as well as the anatomy of the host plant. This review summarizes the applications of ZnO NPs as nanofertilizer in crop production and also attempts to examine and record the possible mechanism of antimicrobial activity of ZnO NPs. Biological synthesis of ZnO NPs and their uptake, translocation and biotransformation in plants via various routes have also been examined.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh A, Singh NB, Hussain I, Singh H, Singh SC (2015) Plant-nanoparticle interaction: an approach to improve agricultural practices and plant productivity. Int J Pharm Sci Invent 4(8):25–40
Khodakovskaya MV, Silva KD, Biris AS, Dervishi E, Villagarcia H (2012) Carbon nanotubes induce growth enhancement of tobacco cells. ACS Nano 6(3):2128–2135
Auld DS (2001) Zinc coordination sphere in biochemical zinc sites. Biometals 14:271–313
Rout GR, Das P (2003) Effect of metal toxicity on plant growth and metabolism. Agronomie 23:3–11
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2004) Zinc protects chloroplasts and associated photochemical functions in cadmium exposed Ceratophyllum demersum L., a fresh water macrophyte. Plant Sci 166:1321–1327
Hussain I, Singh NB, Singh A, Singh H, Singh SC (2016) Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol Lett 38(4):545–560
Singh A, Singh NB, Hussain I, Singh H, Yadav V, Singh SC (2016) Green synthesis of nano zinc oxide and evaluation of its impact on germination and metabolic activity of Solanum lycopersicum. J Biotechnol 233:84–94
Yadav A, Prasad V, Kathe AA, Raj S, Yadav D, Sundaramoorthy C, Vigneshwaran N (2006) Functional finishing in cotton fabrics using zinc oxide NPs. Bull Mater Sci 29:641–645
Singh NB, Amist N, Yadav K, Singh D, Pandey JK, Singh SC (2013) Zinc oxide nanoparticles as fertilizer for the germination, growth and metabolism of vegetable crops. J Nanoeng Nanomanufacturing 3:1–12
Lin D, Xing B (2008) Root uptake and phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 42:5580–5585
Xie Y, He Y, Irwin PLI, Jin T, Shi X (2011) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(7):2325–2331
Servin A, Elmer W, Mukherjee A, Torre-Roche RD, Hamdi H, White JC, Bindraban P, Dimkpa C (2015) A review of the use of engineered nanomaterials to suppress plant disease and enhance crop yield. J Nanoparticle Res 17:92
Hussain I, Singh NB, Singh A, Singh H, Singh SC, Yadav V (2017) Exogenous application of phytosynthesized nanoceria to alleviate ferulic acid stress in Solanum lycopersicum. Sci Hortic 214:158–164
Jeevanandam J, Chan YS, Danquah MK (2016) Biosynthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles. Chem Bio Eng Rev 3:55–67
Remedios C, Rosario F, Bastos V (2012) Environmental nanoparticles interactions with plants: morphological, physiological and genotoxic aspects. J Bot. doi:10.1155/2012/751686
Kumari M, Khan SS, Pakrashi S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2011) Cytogenetic and genotoxic effects of zinc oxide NPs on root cells of Allium cepa. J Hazards Mater 190:613–621
Marcano L, Carruyo I, Del-Campo A, Montiel X (2004) Cytotoxicity and mode of action of maleic hydrazide in root tips of Allium cepa L. Environ Res 94:221–226
Ahmed S, Annu Chaudhry SA, Ikram S (2017) A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: a prospect towards green chemistry. J Photochem Photobiol 166:272–284
Mittal AK, Chisti Y, Banerjee UC (2013) Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol Adv 31:346–356
Jayaseelana C, Rahumana AA, Kirthi AV, Marimuthua S, Santhosh KT, Bagavana A, Gaurav K, Karthik L, Rao KVB (2012) Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochim Acta Part A 90:78–84
Bhumi G, Savithramma N (2014) Biological synthesis of zinc oxide NPs from Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Leaf extract and validation for antibacterial activity. Int J Drug Dev Res 6(1):208–214
Clark J, Macquarrie D (2002) Handbook of green chemistry and technology. Blackwell Publishing Ltd., Oxford Press, Oxford
Gnanasangeetha D, Thambavani DS (2013) Biogenic production of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Acalypha indica. JCBPSC 4(1):238–246
Agarwal H, Venkat Kumar S, Rajeshkumar S (2017) A review on green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles–an eco-friendly approach. Resour Eff Technol. doi:10.1016/j.reffit.2017.03.002
Gunalan S, Sivaraj R, Venckatesh R (2011) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: structure and optical properties. Mater Res Bull 46:2560–2566
Ramesh P, Rajendran A, Meenakshisundaram M (2014) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract cassia auriculata. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 1:41–45
Bala N, Saha S, Chakraborty M, Mati M, Das S, Basu R, Nandy P (2015) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: effect of temperature on synthesis, antibacterial activity and anti-diabetic. RSC Adv 5:4993
Singh RP, Shukla VK, Yadav RS, Sharma PK, Singh PK, Pandey AC (2011) Biological approach of zinc oxide nanoparticles formation and its characterization. Adv Mat Lett 2(4):313–317
Tarafdar JC, Raliya R, Mahawar H, Rathore I (2014) Development of zinc nanofertilizer to enhance crop production in pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum). Agric Res 3(3):257–262
Raliya R, Tarafdar JC (2014) Biosynthesis and characterization of zinc, magnesium and titanium nanoparticles: an eco-friendly approach. Int Nano Lett 4:93
Senthilkumar SR, Sivakumar T (2014) Green tea (Camellia sinensis) mediated synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles and studies on their antimicrobial activities. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 6(6):461–465
Devi RS, Gayathri R (2014) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by using Hibiscus rosa-sinensis. Int J Curr Eng Technol 4(4):2444–2446
Samata NA, Nor RM (2013) Sol–gel synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Citrus aurantifolia extracts. Ceram Int 39:545–548
Banumathi B, Malaikozhundan B, Vaseeharan B (2016) In vitro acaricidal activity of ethnoveterinary plants and green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet Parasitol 216:93–100
Vishwakarma K (2011) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Abrus precatorius seeds extract and their characterization. PhD thesis, National institute of technology Rourkela
Sarkar J, Ghosh M, Mukherjee A, Chattopadhyay D, Acharya K (2014) Biosynthesis and safety evaluation of ZnO nanoparticles. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37:165–171
Fu L, Fu Z (2015) Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract-assisted biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int 41:2492–2496
Bhuyan T, Mishra K, Khanuja M, Prasad R, Varma A (2015) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater Sci Semicond Process 32:55–61
Yedurkar S, Maurya C, Mahanwar P (2016) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ixora coccinea leaf extract-A green approach. Open J Synth Theory Appl 5:1–14
Balusamy B, Kandhasamy YG, Senthamizhan A, Chandrasekaran G, Subramanian MS, Tirukalikundram K (2012) Characterization and bacterial toxicity of lanthanum oxide bulk and nanoparticles. J Rare Earth 30:1298–1302
Narendhran S, Shivraj R (2016) Biogenic ZnO NPs synthesised using L. aculeate leaf extract and there antifungal activity against plant fungal pathogens. Bull Mater Sci 39(1):1–5
Nagarajan S, Kuppusamy A (2013) Extracellular synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle using seaweeds of gulf of Mannar, India. J Nanobiotechnol 11:39
Rajiv P, Rajeshwari S, Venckatesh R (2013) Bio-fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Parthenium hysterophorus L. and its size-dependent antifungal activity against plant fungal pathogens. Spectrochim Acta Part A 112:384–387
Yu H, Ming H, Gong J, Li H, Huang H, Pan K, Liu Y, Kang Z, Wei J, Wang D (2013) Facile synthesis of Au/ZnO nanoparticles and their enhanced photocatalytic activity for hydroxylation of benzene. Bull Mater Sci 36:367–372
Wang P, Menzies NW, Lombi E, McKenna BA, Johannessen B, Glover CJ, Kappen P, Kopittke PM (2013) Fate of ZnO nanoparticles in soils and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Environ Sci Technol 47:13822–13830
Handy RD, Owen R, Valsami-Jones E (2008) The ecotoxicology of nanoparticles and nanomaterials: current status, knowledge gaps, challenges, and future needs. Ecotoxicology 17(5):315–325
Biswas P, Wu CY (2005) Critical review: nanoparticles and the environment. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 55(6):708–746
Nair R, Varghese SH, Nair BG, Maekawa T, Yoshida Y, Kumar DS (2010) Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci 179:154–163
Klaine SJ, Alvarez PJ, Batley GE et al (2008) Nanomaterials in the environment: behaviour, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(9):1825–1851
Lopez-Moreno ML, De La Rosa G, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Castillo-Michel H, Botez CE, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2010) Evidence of the differential biotransformation and genotoxicity of ZnO and CeO2 NPs on soybean (Glycine max) plants. Environ Sci Technol 44:7315–7320
Scheckel KG, Luxton TP, El Badawy AM, Impellitteri CA, Tolaymat TM (2010) Synchrotron speciation of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles aged in a kaolin suspension. Environ Sci Technol 44(4):1307–1312
Reed RB, Ladner DA, Higgins CP, Westerhoff P, Ranville JF (2012) Solubility of nano-zinc oxide in environmentally and biologically important matrices. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(1):93–99
Salt DE, Prince RC, Baker AJM, Raskin I, Pickering IJ (1999) Zinc ligands 471 in the metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspica erulescens as determined using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 33(5):713–717
Jitao LV, Zhang S, Luo L, Zhang J, Yang K, Christied P (2015) Accumulation, speciation and uptake pathway of ZnO nanoparticles in maize. Environ Sci Nano 2:68
Zhao LJ, Peralta-Videa JR, Ren MH, Varela-Ramirez A, Hernandez-Viezcas CQ, Li JA, Aguilera RJ, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2012) Transport of zinc in a sandy loam soil treated with ZnO NPs and uptake by corn plants: Electron microprobe and confocal microscopy studies. Chem Eng J 184:1–8
Alloway B, Graham R, Stacey S (2008) Micronutrient deficiencies in Australian field crops: In Micronutrient deficiencies in global crop production. Springer Netherlands, pp 63–92
Liu R, Lal R (2015) Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci Total Environ 514:131–139
Milani N, McLaughlin MJ, Stacey SP, Kirby JK, Hettiarachchi GM, Beak DG, Cornelis G (2012) Dissolution kinetics of macronutrient fertilizers coated with manufactured zinc oxide nanoparticles. J Agric Food Chem 60(16):3991–3998
Raliya R, Nair R, Chavalmane S, Wangab WN, Biswas P (2015) Mechanistic evaluation of translocation and physiological impact of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles on the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plant. Metallomics 7:1584–1594
Watson JL, Fang T, Dimpka CO, Britt DW, McLean JE, Jacobson A, Anderson AJ (2015) The phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles on wheat varies with soil properties. Biometals 28(1):101–112
Raliya R, Tarafdar JC (2013) ZnO nanoparticle biosynthesis and its effect on phosphorous-mobilizing enzyme secretion and gum contents in cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.). Agric Res 2:48–57
Prasad TNVKV, Sudhakar P, Sreenivasulu Y, Latha P, Munaswamy V, Raja Reddy K, Sreeprasad TS, Sajanlal PR, Pradeep T (2012) Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. J Plant Nutr 35(6):905–927
Ates M, Daniels J, Arslan Z, Farah IO, Rivera HF (2013) Comparative evaluation of impact of Zn and ZnO nanoparticles on brine shrimp (Artemia salina) larvae: effects of particle size and solubility on toxicity. Environ sci Processes Impacts 1:10. doi:10.1039/c2em30540b
Peng C, Zhang W, Gao H, Li Y, Tong X, Li K, Zhu X, Wang Y, Chen Y (2017) Behavior and potential impacts of metal-based engineered nanoparticles in aquatic environments. Nanomaterials 7(1):21
Misra SK, Nuseibeh S, Dybowska A, Berhanu D, Tetley TD, Valsami-Jones E (2014) Comparative study using spheres, rods and spindle-shaped nanoplatelets on dispersion stability, dissolution and toxicity of CuO nanomaterials. Nanotoxicology 8:422–432
Zhao LJ, Peralta-Videa JR, Rico CM, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Sun Y, Niu G, Servin A, Nunez JE, Duarte-Gardea M, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2014) CeO2 and ZnO nanoparticles change the nutritional quality of cucumber (Cucumis sativus). J Agric Food Chem 62:2752–2759
Pradhan S, Patra P, Das S, Chandra S, Mitra S, Dey KK, Akbar S, Palit P, Goswami A (2013) Photochemical modulation of biosafe manganese nanoparticles on vigna radiata: a detailed molecular, biochemical and biophysical study. Environ Sci Technol 47(22):13122–13131
Mahajan P, Dhoke SK, Khanna AS, Tarafdar JC (2011) Effect of nano-ZnO on growth of mung bean (Vigna radiata) and chickpea (Cicer arietinum) seedlings using plant agar method. Appl Biol Res 13:54–61
Lin D, Xing B (2007) Phytotoxicity of nanoparticles: inhibition of seed germination and root growth. Environ Pollut 150:243–250
Burman U, Saini M, Kumar P (2013) Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth and antioxidant system of chickpea seedlings. Toxicol Environ Chem 95(4):605–612
Dhoke SK, Mahajan P, Kamble R, Khanna A (2013) Effect of nanoparticles suspension on the growth of mung (Vigna radiata) seedlings by foliar spray method. Nanotechnol Dev 3(1):e1
Taheri M, Qarache HA, Qarache AA, Yoosefi M (2015) The effects of zinc-oxide nanoparticles on growth parameters of corn (SC704). STEM Fellowsh J 1(2):17–20
Latef AAHA, Alhmad MFA, Abdelfattah KE (2017) The possible roles of priming with ZnO nanoparticles in mitigation of salinity stress in lupine (Lupinus termis) plants. J Plant Growth Regul 36(1):60–70
Lawre S, Raskar S (2014) Influence of zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth, flowering and seed productivity in onion. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3(7):874–881
Zafar H, Ali A, Ali JS, Haq IU, Zia M (2016) Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on Brassica nigra seedlings and stem explants: growth dynamics and antioxidative response. Front Plant Sci 7:535. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00535
Vigneshwaran N, Kathe AA, Varadarajan PV, Nachane RP, Balasubramanya RH (2007) Silverprotein (coreshell) NP production using spent mushroom substrate. Langmuir 23:7113–7117
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Haida N, Kaus M, Ann Ling Chuo, Bakhori SKM, Hasan H, Mohamad D (2015) Review on Zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-micro Lett 7(3):219–242
Dimkpa CO, Mclean JE, Latta DE, Manangon E, Britt DW, Johnson WP, Boyanov MI, Anderson AJ (2012) CuO and ZnO nanoparticles: phytotoxicity, metal speciation, and induction of oxidative stress in sand-grown wheat. J Nanoparticle Res 14:112
Kumar SS, Venkateswarlu P, Rao VR, Rao GN (2013) Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int Nano Lett 3:1–6
Kaur P, Thakur R, Kumar S, Dilbaghi N (2011) Interaction of ZnO nanoparticles with food borne pathogens Escherichia coli DH5α and Staphylococcus aureus 5021 and their bactericidal efficacy, In International conference on advances in condensed and nano materials (ICACNM-2011): AIP proceedings, Chandigarh, India pp 153
Narayanan P, Wilson WS, Abraham AT, Sevanan M (2012) Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against human pathogens. BioNanoScience 2(4):329–335
Azeredo HD (2013) Antimicrobial nanostructures in food packaging. Trends Food Sci Technol 30(1):56–69
Soares NFF, Silva CAS, Santiago-Silva P, Espitia PJP, Goncalves MPJC, Lopez MJG, Miltz J, Cerqueira MA, Vicente AA, Teixeira J, Silva WA, Botrel DA (2009) Active and intelligent packaging for milk and milk products. In: Coimbra JSR, Teixeira JA (eds) Engineering aspects of milk and dairy products. CRC Press Taylor & Francis group, New York, pp 155–174. doi:10.1201/9781420090390-c8
Dobrucka R, Dugaszewska J (2016) Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles using Trifolium pratense flower Extract. Saudi J Biol Sci 23(4):517–523
Premanathan M, Karthikeyan K, Jeyasubramanian K, Manivannan G (2011) Nanomed: selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomedicine 7:184–192
Vani C, Sergin GK, Annamalai A (2011) A study on the effect of zinc oxide nanoparticle in staphylococcus aureus. Int J Pharma Bio Sci 2(4):326–335
Padmavathy N, Vijayaraghavan RR (2008) Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles-an antimicrobial study. Sci Technol Adv Mater 9:035004
Kairyte K, Kadys A, Luksiene Z (2013) Antimicrobial and antifungal activity of photoactivated ZnO nanoparticles in suspension. J Photochem Photobiol B 128:78–84
Sharma D, Rajput J, Kaith BS, Kaur M, Sharma S (2010) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and study of their antibacterial and antifungal properties. Thin Solid Films 519(3):1224–1229
Molina MA, Ramos JL, Espinosa-Urgel M (2006) A two-partner secretion system is involved in seed and root colonization and iron uptake by Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Environ Microbiol 8(4):639–647
Wani AH, Shah MA (2012) A unique and profound effect of MgO and ZnO nanoparticles on some plant pathogenic fungi. J appl Pharm Sci 2(3):40–44
Dimpka CO, McLean JE, Britt DW, Anderson AJ (2013) Antifungal activity of ZnO nanoparticles and their interactive effect with a biocontrol bacterium on growth antagonism of the plant pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Biometals 26(6):913–924
He L, Liu Y, Mustapa A, Lin M (2011) Antifungal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium expansum. Microbiol Res 166(3):207–215
Rispail N et al (2014) Quantum dot and superparamagnetic nanoparticle interaction with pathogenic fungi: internalization and toxicity profile. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(12):9100–9110
Mirhosseini M, Barzegari Firouzabadi F (2015) Reduction of Listeria monocytogenes and Bacillus cereus in Milk by Zinc oxide Nanoparticles. Iran J Pathol 10(2):97–104
Li Z, Yang R, Yu M, Bai F, Li C, Wang ZL (2008) Cellular level biocompatibility and biosafety of ZnO nanowires. J Phys Chem C 112(51):20114–20117
Han D, Tian Y, Zhang T, Ren G, Yang Z (2011) Nano-zinc oxide damages spatial cognition capability via over-enhanced long-term potentiation in hippocampus of Wistar rats. Int J Nanomedicine 6:1453–1461
Franklin NM, Rogers NJ, Apte SC, Batley GE, Gadd GE, Casey PS (2007) Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): the importance of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 41(24):8484–8490
Miao AJ, Zhang XY, Luo Z, Chen CS, Chin WC, Santschi PH, Quigg A (2010) Zinc oxide engineered nanoparticles: dissolution and toxicity to marine phytoplankton. Environ Toxicol Chem 29(12):2814–2822
Ma H, Williams PL, Diamond SA (2013) Ecotoxicity of manufactured ZnO nanoparticles–a review. Environ Pollut 172:76–85
Wang X, Yang X, Chen S, Li Q, Wang W, Hou C, Gao X, Wang L, Wang S (2016) Zinc oxide nanoparticles affect biomass accumulation and photosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Front plant Sci 6:1243
Cornelis G, Hund-Rinke K, Kuhlbusch T, vandenBrink N, Nickel C (2014) Fate and bioavailability of engineered nanoparticles in soils: a review. Crit Rev Env Sci Technol 44:2720–2764
de la Rosa G, Lopez-Moreno ML, De Haro D, Botez CE, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey J (2013) Effects of ZnO nanoparticles in alfalfa, tomato, and cucumber at the germination stage: root development and X-ray absorption spectroscopy studies. Pure Appl Chem 85(12):2161–2174
Kumari M, Khan SS, Pakrashi S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2011) Cytogenetic and genotoxic effects of zinc oxide NPs on root cells of Allium cepa. J Hazard Mater 190(1–3):613–621
Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Castillo-Michael H, Servin AD, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2011) Spectroscopic verification of zinc absorption and distribution in the desert plant Prosopisjuliflora velutina (velvet mesquite) treated with ZnO nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 170(1–3):346–352
Pokhrel LR, Dubey B (2013) Evaluation of developmental responses of two crop plants exposed to silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 452–453:321–332
Ghodake G, Seo YD, Lee DS (2011) Hazardous phytotoxic nature of cobalt and zinc oxide nanoparticles assessed using Allium cepa. J Hazards Mater 186:952–955
Stampoulis D, Sinha SK, White JC (2009) Assay-dependent phytotoxicity of nanoparticles to plants. Environ Sci Technol 43(24):9473–9479
Narendhran S, Rajiv P, Sivaraj R (2016) Toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles on germinating Sesamum indicum (Co-1) and their antibacterial activity. Bull Mater Sci 39(2):415–421
Lee S, Kim S, Kim S, Lee I (2013) Assessment of phytotoxicity of ZnO NPs on a medicinal plant Fagopyrum esculentum. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:848–854
Boonyanitipong P, Kumar P, Kositsup B, Baruah S, Dutta J (2011) Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on roots of rice Oryza Sativa L. In International conference on environment and bioscience IPCBEE. 21st edn. IACSIT Press, Singapore
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to the University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India, and University of Allahabad, India, for providing financial assistance to Ajey Singh.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest for this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Singh, N.B., Afzal, S. et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: a review of their biological synthesis, antimicrobial activity, uptake, translocation and biotransformation in plants. J Mater Sci 53, 185–201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1544-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1544-1