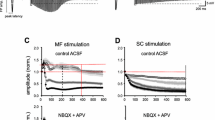
Current concepts hold that during learning in waking animals, new information is transmitted from the neocortex to the hippocampus, where it leaves a temporary trace in the form of a mosaic of modified synapses. During sleep, reactivation of the neuron population initially activated by the new stimulus has the result that this information is returned to the neocortex, ensuring consolidation of a permanent memory trace. Exchange of information between the neocortex and hippocampal formation is mediated mainly by the entorhinal cortex, whose internal connections, in principle, allow “messages” from the output of the hippocampal formation to return to its inputs. Our experiments in awake and sleeping rabbits demonstrated that waves of excitation can return to hippocampal field CA1 and the dentate gyrus via fibers of the perforant path, these waves having initially entered field CA1 via potentiated synapses of Schäffer collaterals; during sleep, re-entrant waves of excitation reach a maximum and have a high probability of evoking discharges of dentate gyrus neurons. Thus, the new stimulus, potentiating synaptic connections in the hippocampus and, probably, the entorhinal cortex during waking, create conditions for reactivation of the corresponding hippocampal neuron populations during sleep by waves of excitation returning via the entorhinal cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. A. Zosimovskii,V. A. Korshunov, and V. A. Markevich, “Conditions for the appearance in hippocampal field CA1 of a double response to application of single-pulse stimuli to Schäffer collaterals in freely moving rats,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 57, No. 2, 210–220 (2007).
R. Bartesaghi and T. Gessi, “Activation of perforant path neurons to field CA1 by hippocampal projections,” Hippocampus, 13, No. 2, 235–249 (2003).
G. Buzsaki, “Two-stage model of memory trace formation: a role for ‘noisy’ brain states,” Neurosci., 31, No. 3, 551–570 (1989).
M. Y. Cheong, S. H. Yun, I. Mook-Jung, I. Joo, K. Huh, and M.W. Jung, “Cholinergic modulation of synaptic physiology in deep layer entorhinal cortex of the rat,” J. Neurosci. Res., 66, No. 1, 117–121 (2001).
S. Craig and S. Commins, “Plastic and metaplastic changes in the CA1 and subicular projections to the entorhinal cortex,” Brain Res., 1147, 124–139 (2007).
C. D. Davis, F. L. Jones, and B. E. Derrick, “Novel environments enhance the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus,” J. Neurosci., 24, No. 29, 6497–6506 (2004).
S. Gais and J. Born, “Declarative memory consolidation: mechanisms acting during human sleep,” Learn. Mem., 11, No. 6, 679–685 (2004).
M. E. Hasselmo, “The role of acetylcholine in learning and memory,” Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 16, No. 6, 710–715 (2006).
M. E. Hasselmo and B. P. Fehlau, “Differences in time course of ACh and GABA modulation of excitatory synaptic potentials in slices of rat hippocampus,” J. Neurophysiol., 86, No. 4, 1792–1802 (2001).
M. E. Hasselmo and E. Schnell, “Laminar selectivity of the cholinergic suppression of synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal region CA1: computational modeling and brain slice physiology,” J. Neurosci., 14, No. 6, 3898–3914 (1994).
T. L. Ivanco and R. J. Racine, “Long-term potentiation in the reciprocal corticohippocampal and corticocortical pathways in the chronically implanted, freely moving rat,” Hippocampus, 10, No. 2, 143–152 (2000).
A. Kemp and D. Manahan-Vaughan, “Hippocampal long-term depression and long-term potentiation encode different aspects of novelty acquisition,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, No. 21, 8192–8197 (2004).
F. Kloosterman, T. Van Haeftten, and F. H. da Silva, “Two reentrant pathways in the hippocampal-entorhinal system,” Hippocampus, 14, No. 8, 1026–1039 (2004).
P. Lavenex and D. G. Amaral, “Hippocampal-neocortical interaction: a hierarchy of associativity,” Hippocampus, 10, 420–430 (2000).
M. G. Lee, O. K. Hassani, A. Alonso, and B. E. Jones, “Cholinergic basal forebrain neurons burst with theta during waking and paradoxical sleep,” J. Neurosci., 25, No. 17, 4365–4369 (2005).
I. Lee and R. P. Kesner, “Differential contributions of dorsal hippocampal subregions to memory acquisition and retrieval in contextual fear-conditioning,” Hippocampus, 14, No. 3, 301–310 (2004).
L. S. Leung, B. Shen, N. Rajakumar, and J. Ma, “Cholinergic activity enhances hippocampal long-term potentiation in CA1 during waking in rats,” J. Neurosci., 23, No. 28, 9297–9304 (2003).
F. Marrosu, C. Portas, M. S. Mascia, M. A. Casu, M. Fa, M. Giagheddu, A. Imperato, and G. L. Gessa, “Microdialysis measurement of cortical and hippocampal acetylcholine release during sleep-wake cycle in freely moving cats,” Brain Res., 671, No. 2, 329–332 (1995).
R. G. Morris, “Elements of a neurobiological theory of hippocampal function: the role of synaptic plasticity, synaptic tagging and schemas,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 23, No. 11, 2829–2846 (2006).
M. Remondes and E. M. Schuman, “Role for a cortical input to hippocampal area CA1 in the consolidation of a long-term memory,” Nature, 431, No. 7009, 699–703 (2004).
S. Ribeiro, D. Gervasoni, E. S. Soares,Y. Zhou, S.-C. Lin, J. Pantoja, M. Lavine, and M. A. L. Nicolelis, “Long-lasting novelty-induced neuronal reverberation during slow-wave sleep in multiple forebrain areas,” PLoS Biol., 2, No. 1, 0126–0137 (2004).
S. Ribeiro and M. A. L. Nicolelis, “Reverberation, storage, and postsynaptic propagation of memories during sleep,” Learn. Mem., 11, No. 6, 686–696 (2004).
M. Richter, T. Schilling, and W. Muller, “Muscarinic control of intracortical connections to layer II in rat entorhinal cortex slice,” Neurosci. Lett., 273, No. 3, 2002–202 (1999).
H. Wang, Y. Hu, and J. Z. Tsien, “Molecular and systems mechanisms of memory consolidation and storage,” Prog. Neurobiol., 79, No. 3, 123–135 (2006).
J. R. Whitlock, A. J. Heynen, M. G. Shuler, and M. F. Bear, “Learning induces long-term potentiation in the hippocampus,” Science, 313, No. 5790, 1093–1097 (2006).
G. M. Wittenberg, M. R. Sullivan, and J. Z. Tsien, “Synaptic reentry reinforcement based network model for long-term memory consolidation,” Hippocampus, 12, No. 5, 637–647 (2002).
M. P. Witter and E. I. Moser, “Spatial representation and the architecture of the entorhinal cortex,” Trends Neurosci., 29, No. 12, 671–678 (2006).
S. Yang, S. D. Lee, C. H. Chung, M. Y. Cheong, C. J. Lee, and M. W. Jung, “Long-term synaptic plasticity in deep layer-originated associational projections to superficial layers of rat entorhinal cortex,” Neurosci., 127, No. 4, 805–812 (2004).
S. H. Yun, M. Y. Cheong, I. Mook-Jung, K. Huh, C. Lee, and M. W. Jung, “Cholinergic modulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity in entorhinal cortex and hippocampus of the rat,” Neurosci., 97, No. 4, 671–676 (2000).
S. H. Yun, I. Mook-Jung, and M. W. Jung, “Variation in effective stimulus patterns for induction of long-term potentiation across different layers of rat entorhinal cortex,” J. Neurosci., 22, No. 5, Rc214, 105 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 59, No. 1, pp. 87–97, January–February, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zosimovskii, V.A., Korshunov, V.A. Return of Excitatory Waves from Field CA1 to the Hippocampal Formation Is Facilitated after Tetanization of Schäffer Collaterals during Sleep. Neurosci Behav Physi 40, 315–323 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9258-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9258-8