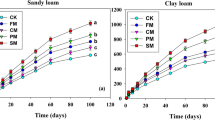
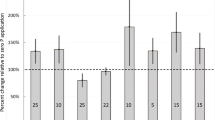
Abstract
Organic farming largely depends on animal manure as a source of phosphorus (P) and the recycling of animal manure globally is becoming increasingly important. In a pot experiment, using radioactive P labeling techniques, we studied ryegrass uptake of P applied with animal manure and water soluble mineral fertilizer to soils that had been cropped for 22 years according to organic or conventional farming practices. The soils differed in P status and microbial activity. Labeling soil-available P also allowed assessing the uptake from residual P that remained in the soils because of their different fertilization histories. On each soil, recovery of fresh manure P in four harvests of ryegrass shoots was lower than recovery of mineral P. It ranged from 24% to 35% for manure P and from 37% to 43% for mineral P. Recovery of fresh manure P was affected by soil-available P contents. It was lower at a higher available P in a conventional soil. Different levels in microbial activity among soils were of lesser importance for the recovery of fresh manure P in plants. The recovery of residual P ranged from 9% to 15%. Residual P contained in organic cropped soils contributed less to P nutrition of ryegrass than the residual P contained in conventional cropped soils, probably due to their lower residual P contents being composed of stable P forms. The indirect isotope dilution technique is useful in assessing manure P uptake by plants, but attention must be given to added P interactions, i.e., the potential impact of organic amendments on P uptake from non-labeled soil and residual P.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrow N J (1980) Evaluation and utilization of residual phosphorus in soils. In: The role of phosphorus in agriculture. pp 333–359. ASA-CSSA-SSSA, Madison, Wisconsin
Bergmann W (1993) Ernährungsstörungen bei Kulturpflanzen. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena und Stuttgart
Besson JM, Niggli U (1991) DOK-Versuch: vergleichende Langzeit-Untersuchungen in den drei Anbausystemen biologisch-dynamisch, organisch-biologisch und konventionell: 1. Konzeption des DOK-Versuches: 1. und 2. Fruchtfolgeperiode. Schweiz Landw Forschung 31:79–109
Bühler S, Oberson A, Sinaj S, Friesen DK, Frossard E (2003) Isotope methods for assessing plant available phosphorus in acid tropical soils. Europ J Soil Sci 54:605–616
Cornish PS (2009) Phosphorus management on extensive organic and low-input farms. Crop & Pasture Science 60:105–115
Eghball B, Power JF (1999) Phosphorus- and nitrogen-based manure and compost applications: corn production and soil phosphorus. Soil Sci Soc Am J 63:895–901
Fardeau JC (1993) Le Phosphore assimilable du sol: sa représentation par un modèle fonctionnel a plusieurs compartiments. Agronomie 13:317–331
Fardeau JC (1996) Dynamics of phosphate in soils: an isotopic outlook. Fert Res 45:91–100
Fliessbach A, Oberholzer HR, Gunst L, Mäder P (2007) Soil organic matter and biological soil quality indicators after 21 years of organic and conventional farming. Agric Ecosyst Environ 118:273–284
Frossard E, Fardeau JC, Brossard M, Morel JL (1994) Soil isotopically exchangeable phosphorus: a comparison between E and L values. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:846–851
Frossard E, Sinaj S, Zhang LM, Morel JL (1996) Effect of soil and sludge properties on the fate of sludge phosphorus in soil-plant systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1248–1253
Frossard E, Julien P, Neyroud J-A, Sinaj S (2004) Phosphor in Böden—Standortbestimmung Schweiz. p. 174. Bundesamt für Umwelt, Wald und Landschaft, Bern
Gallet A, Flisch R, Ryser JP, Nösberger J, Frossard E, Sinaj S (2003) Uptake of residual phosphate and freshly applied diammonium phosphate by Lolium perenne and Trifolium repens. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 166:557–567
Guggenberger G, Christensen BT, Rubæk GH (2000) Isolation and characterization of labile organic phosphorus pools in soils from the Askov long-term field experiments. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163:151–155
Hooda PS, Truesdale VW, Edwards AC, Withers PJA, Aitken MN, Miller A, Rendell AR (2001) Manuring and fertilization effects on phosphorus accumulation in soils and potential environmental implications. Adv Environ Res 5:13–21
Hood R (2001) Evaluation of a new approach to the nitrogen-15 isotope dilution technique, to estimate crop N uptake from organic residues in the field. Biol Fertil Soils 34:156–161
Jenkinson DS, Fox RH, Rayner JH (1985) Interactions between fertilizer nitrogen and soil nitrogen—the so-called priming effect. J Soil Sci 36:425–444
Langmeier M, Frossard E, Kreuzer M, Mäder P, Dubois D, Oberson A (2002) Nitrogen fertilizer value of cattle manure applied on soils originating from organic and conventional farming systems. Agronomie 22:789–800
Leifeld J, Reiser R, Oberholzer HR (2009) Consequences of conventional versus organic farming on soil carbon: results from a 27-year field experiment. Agron J 101:1204–1218
Løes AK, Øgaard AF (2001) Long-term changes in extractable soil phosphorus (P) in organic dairy farming systems. Plant Soil 237:321–332
Mäder P, Fliessbach A, Dubois D, Gunst L, Fried P, Niggli U (2002) Soil fertility and biodiversity in organic farming. Science 296:1694–1697
McLaughlin MJ, Alston AM, Martin JK (1988) Phosphorus cycling in wheat-pasture rotations I The source of phosphorus taken up by wheat. Aust J Soil Res 26:323–331
Motavalli PP, Miles RJ (2002) Soil phosphorus fractions after 111 years of animal manure and fertilizer application. Biol Fertil Soils 36:35–42
Morel C, Fardeau JC (1989a) The uptake by crops of fresh and residual phosphatic fertilizers by simultaneous measurements with 32P and 33P. Appl Radiat Isot 40:273–278
Morel C, Fardeau JC (1989b) Native soil and fresh fertilizer phosphorus uptake as affected by rate of application and P fertilizers. Plant Soil 115:123–128
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Oberson A, Frossard E (2005) Phosphorus management for organic agriculture. In: Sims JT, Sharpley AN (eds) Phosphorus: agriculture and the environment. ASA, CSSA and SSSA, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, pp 761–779
Oberson A, Fardeau JC, Besson JM, Sticher H (1993) Soil phosphorus dynamics in cropping systems managed according to conventional and biological agricultural methods. Biol Fertil Soils 16:111–117
Oehl F, Oberson A, Probst M, Fliessbach A, Roth HR, Frossard E (2001) Kinetics of microbial phosphorus uptake in cultivated soils. Biol Fertil Soils 34:31–41
Oehl F, Oberson A, Tagmann HU, Besson JM, Dubois D, Mäder P, Roth HR, Frossard E (2002) Phosphorus budget and phosphorus availability in soils under organic and conventional farming. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 62:25–35
Oehl F, Frossard E, Fliessbach A, Dubois D, Oberson A (2004) Basal organic phosphorus mineralization in soils under different farming systems. Soil Biol Biochem 36:667–675
Saunders WMH, Williams EG (1955) Observations on the determination of total organic phosphorus in soils. J Soil Sci 6:247–267
Sinaj S, Traoré O, Frossard E (2002) Effect of compost and soil properties on the availability of compost phosphate for white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 62:89–102
Stewart WM, Hammond LL, van Kauwenbergh SJ (2005) Phosphorus as a natural resource. In Phosphorus: agriculture and the environment. Eds. JT Sims and AN Sharpley. pp 3–22. ASA, CSSA and SSSA. Madison, Wisconsin, USA
Toor GS, Hunger S, Peak JD, Sims JT, Sparks DL, Donald LS (2006) Advances in the characterization of phosphorus in organic wastes: environmental and agronomic applications. Adv Agron 89:1–72
Traoré O, Sinaj S, Frossard E, Van De Kerkhove JM (1999) Effect of composting time on phosphate exchangeability. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 55:123–131
Sharpley AN, Smith SJ, Stewart BA, Mathers AC (1984) Forms of phosphorus in soil receiving cattle feedlot waste. J Environ Qual 13:211–215
USDA 1999 Soil Taxonomy—A basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. United States Department of Agriculture
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Wichern F, Müller T, Joergensen RG, Buerkert A (2004) Effects of manure quality and application forms on soil C and N turnover of a subtropical oasis soil under laboratory conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 39:165–171
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge L. Gunst (ART) for providing data records on the field experiment. We warmly thank T. Flura and T. Rösch (ETH Zurich) for assistance in the analytical work and Catherine Palmer (ETH Zurich) for checking the English. We gratefully acknowledge Simone Nanzer (ETH Zurich) and two anonymous reviewers for her helpful comments on our script.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: N. Jim Barrow.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oberson, A., Tagmann, H.U., Langmeier, M. et al. Fresh and residual phosphorus uptake by ryegrass from soils with different fertilization histories. Plant Soil 334, 391–407 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0390-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0390-6