Abstract
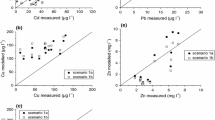
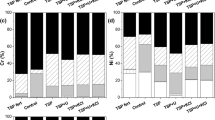
The applicability of laboratory tests for the prediction of soil solution composition and concentrations of inorganic contaminants is still under debate. Therefore, we carried out two batch-leaching tests differing in their liquid/solid ratios and column experiments (saturated flow, two flow velocities, four flow interruptions ranging from 4 h to 21 days) with a contaminated humic horizon (total contents: As, 196 mg kg−1; Cd, 4 mg kg−1; Cr, 202 mg kg−1; Cu, 227 mg kg−1; Ni, 64 mg kg−1; Pb, 308 mg kg−1; Zn, 1,176 mg kg−1) from a Mollic Fluvisol near the rivers Elbe and Saale (Germany) and compared the aqueous contaminant concentrations with those of soil solutions obtained in situ with ceramic suction cups on a monthly basis between 2002 and 2006. Contaminant release in the field slightly depended on the water regime, pH, and redox potential and was characterized by partially high concentrations (e.g., As, 47 µg l−1; Cd, 136 µg l−1; Ni, 328 µg l−1; Zn, 8.68 mg l−1), which exceeded the German inspection values. Metal concentrations obtained in batch-leaching tests partially fitted to those determined in the soil solution and to those from the column experiments even irrespective of the varying liquid/solid ratios. The column experiments yielded realistic concentrations of Cr, Cu, Ni, and Pb and their ranges. Furthermore, they provided an insight into release kinetics and release processes as well as into potential contaminant release due to enforced reducing conditions. As column experiments allow a larger temporal sampling resolution and enable quickly to manipulate experimental conditions, they are a useful complement of soil solution monitoring.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ad-hoc AG Boden. (2005). Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung (KA 5). Stuttgart: E. Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung.
Antelo, J., Avena, M., Fiol, S., Lopez, R., & Arce, F. (2005). Effects of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption of phosphate and arsenate at the goethite–water interface. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 285, 476–486.
BBodSchV (1999). Verordnung zur Durchführung des Bundes-Bodenschutzgesetzes (Bundes-Bodenschutz- und Altlastenverordnung, BBodSchV vom 16.7.1999), BGBl, I. 1554–1582.
Berger, W., Scheuering, I., & Peiffer, S. (2006). Emissionsabschätzung aus kontaminierten Materialien—was können Labormethoden hierzu leisten? altlasten spektrum, 15, 154–161.
Brümmer, G. W. (1974). Redoxpotentiale und Redoxprozesse von Mangan-, Eisen- und Schwefelverbindungen in hydromorphen Böden und Sedimenten. Geoderma, 12, 207–222.
Brusseau, M. L., Rao, P. S. C., Jessup, R. E., & Davidson, J. M. (1989). Flow interruption: A method for investigating sorption nonequilibrium. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 4, 223–240.
Cancès, B., Juliot, F., Morin, G., Laperche, V., Alvarez, L., Proux, O., et al. (2005). XAS evidence of As(V) association with iron oxyhydroxides in a contaminated soil at a former arsenical pesticide processing plant. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 9398–9405.
Davranche, M., & Bollinger, J.-C. (2000). Heavy metals desorption from synthesized and natural iron and manganese oxyhydroxides: Effect of reductive conditions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 227, 531–539.
Delay, M., Lager, T., Schulz, H. D., & Frimmel, F. H. (2007). Comparison of leaching tests to determine and quantify the release of inorganic contaminants in demolition waste. Waste Management, 27, 248–255.
Devai, I., Patrick, W. H., Jr., Neue, H.-U., DeLaune, R. D., Kongchum, M., & Rinklebe, J. (2005). Methyl mercury and heavy metal content in soils of rivers Saale and Elbe (Germany). Analytical Letters, 38, 1037–1048.
Du Laing, G., Rinklebe, J., Vandecasteele, B., Meers, E., & Tack, F. M. G. (2009a). Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments. A review. The Science of the Total Environment, 407, 3972–3985.
Du Laing, G., Meers, E., Dewispelaere, M., Vandecasteele, B., Rinklebe, J., Tack, F. M. G., et al. (2009b). Heavy metal mobility in intertidal sediments of the Scheldt estuary: Field monitoring. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 2919–2930.
Du Laing, G., Chapagain, S. K., Dewispelaere, M., Meers, E., Kazama, F., Tack, F. M. G., et al. (2009c). Presence and mobility of arsenic in estuarine wetland soils of the Scheldt estuary (Belgium). Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 11, 873–881.
Erses, A. S., & Onay, T. T. (2003). In situ heavy metal attenuation in landfills under methanogenic conditions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 99, 159–175.
Fakih, M., Davranche, M., Dia, A., Nowack, B., Morin, G., Petitjean, P., et al. (2009). Environmental impact of As(V)-Fe oxyhydroxide reductive dissolution: an experimental insight. Chemical Geology, 259, 290–303.
Förstner, U., Heise, S., Schwartz, R., Westrich, B., & Ahlf, W. (2004). Historical contaminated sediments and soils at the river basin scale. Examples from the Elbe river catchment area. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 4, 247–260.
Gambrell, R. P. (1994). Trace and toxic metals in wetlands—A review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23, 883–891.
IUSS/ISRIC/FAO. (2006). World reference base for soil resources 2006. Rome: FAO.
Kalbe, U., Berger, W., Eckhardt, J., & Simon, F.-G. (2008). Evaluation of leaching and extraction procedures for soil and waste. Waste Management, 28, 1027–1038.
Kandpal, G., Srivastava, P. C., & Ram, B. (2005). Kinetics of desorption of heavy metals from polluted soils: Influence of soil type and metal source. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 161, 353–363.
Kowalik, C., Kraft, J., & Einax, J. W. (2003). The situation of the German Elbe tributaries—Development of the loads in the last 10 years. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 31, 334–345.
Krüger, F., & Gröngröft, A. (2003). The difficult assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils and plants in Elbe river floodplains. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 31, 436–443.
Lager, T., Delay, M., Karius, V., Hamer, K., Frimmel, F. H., & Schulz, H. D. (2006). Determination and quantification of the release of inorganic contaminants from municipal waste incineration ash. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 34, 73–85.
Mehra, O. P., & Jackson, M. L. (1960). Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite–citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. Clays and Clay Minerals, 7, 317–327.
Overesch, M., Rinklebe, J., Broll, G., & Neue, H.-U. (2007). Metals and arsenic in soils and corresponding vegetation at central Elbe River floodplains (Germany). Environmental Pollution, 145, 800–812.
Rennert, T., & Mansfeldt, T. (2004). Bewertung der potenziellen Grundwasserbelastung von deponierten Hochofengasschlämmen. Zeitschrift für Umweltchemie und Ökotoxikologie, 16, 151–154.
Rennert, T., & Mansfeldt, T. (2006). Release of trace metals, sulfate and complexed cyanide from soils contaminated with gas-purifier wastes. Environmental Pollution, 139, 86–94.
Rennert, T., & Rinklebe, J. (2009). Release of Ni and Zn from contaminated floodplain soils under saturated flow conditions. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, in press.
Rinklebe, J. (2004). Differenzierung von Auenböden der Mittleren Elbe und Quantifizierung des Einflusses von deren Bodenkennwerten auf die mikrobielle Biomasse und die Bodenenzymaktivitäten von ß-Glucosidase, Protease und alkalischer Phosphatase. PhD thesis, Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg, Germany.
Rinklebe, J., Stubbe, A., Staerk, H.-J., Wennrich, R., & Neue, H.-U. (2005). Factors controlling the dynamics of As, Cd, Zn and Pb in alluvial soils of the Elbe River (Germany). In W. G. Lyon, J. Hong & R. K. Reddy (Eds.), Proceedings of environmental science and technology (Vol. 2, pp. 265–271). New Orleans: American Science Press.
Rinklebe, J., Franke, C., & Neue, H.-U. (2007). Aggregation of floodplain soils as an instrument for predicting concentrations of nutrients and pollutants. Geoderma, 141, 210–223.
Sauve, S., Hendershot, W., & Allen, H. E. (2000). Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 1125–1131.
Scheithauer, M. (2003). Aktuelle Ergebnisse des F&E-Vorhabens “Emissionsabschät-zung/Prüfwerte”. In R. Röder & C. Schertler Münchener Beiträge zur Sickerwasserprognose—Forschung und Praxis (vol. 56, pp. 111–128). München: Bayerisches Landesamt für Wasserwirtschaft.
Schröder, T. J., van Riemsdijk, W. H., van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M., & Vink, J. P. M. (2008). Monitoring and modeling of the solid-solution partitioning of metals and As in a river floodplain redox sequence. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 2350–2363.
Schwertmann, U. (1964). Differenzierung der Eisenoxide des Bodens durch Extraktion mit saurer Ammoniumoxalat-Lösung. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung, Düngung und Bodenkunde, 105, 194–202.
Schwertmann, U., Süsser, P., & Nätscher, L. (1987). Protonenpuffersubstanzen in Böden. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung und Bodenkunde, 150, 174–178.
Sukreeyapongse, O., Holm, P. E., Strobel, B. W., Panichsakpatana, S., Magid, J., & Hansen, H. C. B. (2002). pH-dependent release of cadmium, copper, and lead from natural and sludge-amended soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 1901–1909.
Toride, N., Leji, F. J., & van Genuchten, M Th. (1995). The CXTFIT code for estimating transport parameters from laboratory or field tracer experiments. Riverside: US Salinity Laboratory.
van der Sloot, H. A. (1996). Developments in evaluating environmental impact from utilization of bulk inert wastes using laboratory leaching tests and field verification. Waste Management, 16, 65–81.
van der Sloot, H. A., Comans, R. N. J., & Hjelmar, O. (1996). Similarities in the leaching behavior of trace contaminants from waste, stabilized waste, construction materials and soils. Science of the Total Environment, 178, 111–126.
Wehrer, M., & Totsche, K. U. (2003). Detection of non-equilibrium contaminant release in soil columns: Delineation of experimental conditions by numerical simulations. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 166, 475–483.
Wehrer, M., & Totsche, K. U. (2008). Effective rates of heavy metal release from alkaline wastes—Quantified by column outflow experiments and inverse simulations. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 97, 53–66.
Weigand, H., & Totsche, K. U. (1998). Flow and reactivity effects on dissolved organic matter transport in soil columns. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 62, 1268–1274.
Zeien, H., & Brümmer, G. W. (1989). Chemische Extraktion zur Bestimmung von Schwermetallbindungsformen in Böden. Mitteilungen der Deutschen Bodenkundlichen Gesellschaft, 59, 505–510.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the German Research Foundation (DFG; RE 2251), the European Fond for Regional Development (EFRE), and the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment of the Federal State Saxony-Anhalt (FKZ 76213/08/01). We would like to thank K. Greef, K. Kinze, Dr. M. Thönnessen, J. Steffen, Dr. R. Wennrich, and Dr. H.-J. Staerk for various analyses as well as H. Dittrich for technical assistance during the field monitoring.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rennert, T., Meißner, S., Rinklebe, J. et al. Dissolved Inorganic Contaminants in a Floodplain Soil: Comparison of In Situ Soil Solutions and Laboratory Methods. Water Air Soil Pollut 209, 489–500 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0217-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0217-3