Abstract
Purpose
Application of olive mill wastewater (OMW) to soil may cause positive or negative effects. The present study aims at a better understanding of the fate of organic matter brought into soil by OMW application under different environmental conditions.
Materials and methods
Single OMW application to soil was conducted in spring, dry summer, summer with irrigation, and in winter. Two days and 18–24 months after the application, soil samples from two depths were analyzed for thermal soil organic matter (SOM) properties, total organic carbon, water-extractable dissolved soil organic carbon, and its specific ultraviolet absorbance at 254 nm.
Results and discussion
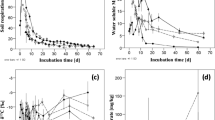
After winter and irrigated summer treatments, OMW was largely leached from the upper horizon within 2 days. Application in spring and summer dry initially increased the thermolabile fraction and the calorific value of SOM, however, in a different degree due to different transport, transformation, and immobilization mechanisms. At the long term, SOM content was still elevated after summer dry treatment. The reduction of the thermostable fraction in spring treatment indicates a priming effect of the labile OMW constituents.
Conclusions
Application in winter or with irrigation cannot be recommended for the investigated site. Under hot and dry conditions, SOM content increased most persistently due to stronger mineral-organic interactions. Favorable conditions for biodegradation during OMW application in spring reduced the effects on SOM quantity in the long term. However, a possible priming effect and the persistence of changes in thermal properties need to be further investigated for repeated applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho MJ, Hämäläinen JP, Tummavuori JL (1991) Catalytic effects of metals on peat combustion. Fuel 70:1143–1145
Baldock JA, Skjemstad JO (2000) Role of the soil matrix and minerals in protecting natural organic materials against biological attack. Org Geochem 31:697–710
Barbera AC, Maucieri C, Cavallaro V, Ioppolo A, Spagna G (2013) Effects of spreading olive mill wastewater on soil properties and crops: a review. Agr Water Manage 119:43–53
Belaid C, Khadraoui M, Mseddi S, Kallel M, Elleuch B, Fauvarque JF (2013) Electrochemical treatment of olive mill wastewater: treatment extent and effluent phenolic compounds monitoring using some uncommon analytical tools. J Environ Sci-China 25:220–230
Ben Brahim S, Gargouri B, Marrakchi F, Bouaziz M (2016) The effects of different irrigation treatments on olive oil quality and composition: a comparative study between treated and olive mill wastewater. J Agric Food Chem 64:1223–1230
Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y (2008) Mechanisms of real and apparent priming effects and their dependence on soil microbial biomass and community structure: critical review. Biol Fertil Soils 45:115–131
Brunetti G, Senesi N, Plaza C (2007) Effects of amendment with treated and untreated olive oil mill wastewaters on soil properties, soil humic substances and wheat yield. Geoderma 138:144–152
Buchmann C, Felten A, Peikert B, Muñoz K, Bandow N, Dag A, Schaumann GE (2015) Development of phytotoxicity and composition of a soil treated with olive mill wastewater (OMW): an incubation study. Plant Soil 386:99–112
Buurman P, Lagen BV, Piccolo A (2002) Increase in thermal stability of soil humic substances as a result of self-association. Org Geochem 33:367–381
Casa R, D’Annibale A, Pieruccetti F, Stazi SR, Giovannozzi Sermanni G, Lo Cascio B (2003) Reduction of the phenolic components in olive-mill wastewater by an enzymatic treatment and its impact on durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) germinability. Chemosphere 50:959–966
Cebulak S, Langier-Kuzniarowa A (1997) Application of oxyreactive thermal analysis to the examination of organic matter associated with rocks. J Therm Anal Calorim 50:175–190
Chaari L, Elloumi N, Gargouri K, Bourouina B, Michichi T, Kallel M (2014a) Evolution of several soil properties following amendment with olive mill wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 52:2180–2186
Chaari L, Elloumi N, Mseddi S, Gargouri K, Bourouina B, Mechichi T, Kallel M (2014b) Effects of olive mill wastewater on soil nutrients availability. Int J Interdiscip Multidiscip Stud 2:175–183
Chaari L, Ellouni N, Mseddi S, Gargouri K, Rouina BB, Mechchichi T, Kallel M (2015) Changes in soil macronutrients after a long-term application of olive mill wastewater. J Agr Chem Environ 04:12
Cox L, Celis R, Hermosin MC, Becker A, Cornejo J (1997) Porosity and herbicide leaching in soils amended with olive-mill wastewater. Agric Ecosyst Environ 65:151–161
Dell’Abate MT, Benedetti A, Sequi P (2000) Thermal methods of organic matter maturation monitoring during a composting process. J Therm Anal Calorim 61:389–396
Dell’Abate MT, Benedetti A, Brookes PC (2003) Hyphenated techniques of thermal analysis for characterisation of soil humic substances. J Sep Sci 26:433–440
Di Bene C, Pellegrino E, Debolini M, Silvestri N, Bonari E (2013) Short- and long-term effects of olive mill wastewater land spreading on soil chemical and biological properties. Soil Biol Biochem 56:21–30
Diamantis V, Pagorogon L, Gazani E, Doerr SH, Pliakas F, Ritsema CJ (2013) Use of olive mill wastewater (OMW) to decrease hydrophobicity in sandy soil. Ecol Eng 58:393–398
Doerr SH, Shakesby SH, Walsh RPD (2000) Soil water repellency: its causes, characteristics and hydro-geomorphological significance. Earth-Sci Rev 51:33–65
Feng W, Klaminder J, Boily J-F (2015) Thermal stability of goethite-bound natural organic matter is impacted by carbon loading. J Phys Chem A 119:12790–12796
Fernández J, Plante A, Leifeld J, Rasmussen C (2011) Methodological considerations for using thermal analysis in the characterization of soil organic matter. J Therm Anal Calorim 104:389–398
Fernandez JM, Peltre C, Craine JM, Plante AF (2012) Improved characterization of soil organic matter by thermal analysis using CO2/H2O evolved gas analysis. Environ Sci Technol 46:8921–8927
Gélinas Y, Prentice KM, Baldock JA, Hedges JI (2001) An improved thermal oxidation method for the quantification of soot/graphitic black carbon in sediments and soils. Environ Sci Technol 35:3519–3525
Gonzalez-Vila FJ, Verdejo T, Delrio JC, Martin F (1995) Accumulation of hydrophobic compounds in the soil lipidic and humic fractions as result of a long-term land treatment with olive oil mill effluents (alpechin). Chemosphere 31:3681–3686
Gregorich EG, Monreal CM, Carter MR, Angers DA, Ellert BH (1994) Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic matter quality in agricultural soils. Can J Soil Sci 74:367–385
Harvey OR, Kuo L-J, Zimmerman AR, Louchouarn P, Amonette JE, Herbert BE (2012) An index-based approach to assessing recalcitrance and soil carbon sequestration potential of engineered black carbons (biochars). Environ Sci Technol 46:1415–1421
Kallel M, Belaid C, Mechichi T, Ksibi M, Elleuch B (2009) Removal of organic load and phenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater by Fenton oxidation with zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 150:391–395
Kaloustian J, Pauli AM, Pastor J (2001) Kinetic study of the thermal decompositions of biopolymers extracted from various plants. J Therm Anal Calorimetry 63:7–20
Kurtz MP, Peikert B, Brühl C, Dag A, Zipori I, Shoqeir Hasan J, Schaumann GE (2015) Effects of olive mill wastewater on soil microarthropods and soil chemistry in two different cultivation scenarios in Israel and Palestinian territories. Agriculture 5:857
Leinweber P, Schulten HR (1992) Differential thermal-analysis, thermogravimetry and in-source pyrolysis-mass spectrometry studies on the formation of soil organic-matter. Thermochim Acta 200:151–167
Licursi D, Antonetti C, Bernardini J, Cinelli P, Coltelli MB, Lazzeri A, Martinelli M, Galletti AMR (2015) Characterization of the Arundo donax L. solid residue from hydrothermal conversion: comparison with technical lignins and application perspectives. Ind Crop Prod 76:1008–1024
Lopez-Capel E, Sohi SP, Gaunt JL, Manning DAC (2005) Use of thermogravimetry-differential scanning calorimetry to characterize modelable soil organic matter fractions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:136–140
Lopez-Pineiro A, Fernandez J, Nunes JMR, Garcia-Navarro A (2006) Response of soil and wheat crop to the application of two-phase olive mill waste to Mediterranean agricultural soils. Soil Sci 171:728–736
Lopez-Pineiro A, Fernandez J, Albarran A, Nunes JMR, Barreto C (2008) Effects of de-oiled two-phase olive mill waste on Mediterranean soils and the wheat corp. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:424–430
Mohawesh O, Mahmoud M, Janssen M, Lennartz B (2014) Effect of irrigation with olive mill wastewater on soil hydraulic and solute transport properties. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:927–934
Mahmoud M, Janssen M, Haboub N, Nassour A, Lennartz B (2010) The impact of olive mill wastewater application on flow and transport properties in soils. Soil Till Res 107:36–41
Manning DAC, Lopez-Capel E, Barker S (2005) Seeing soil carbon: use of thermal analysis in the characterization of soil C reservoirs of differing stability. Mineral Mag 69:425–435
Mekki A, Dhouib A, Aloui F, Sayadi S (2006a) Olive wastewater as an ecological fertiliser. Agron Sustain Dev 26:61–67
Mekki A, Dhouib A, Sayadi S (2006b) Changes in microbial and soil properties following amendment with treated and untreated olive mill wastewater. Microbiol Res 161:93–101
Mulinacci N, Romani A, Galardi C, Pinelli P, Giaccherini C, Vincieri FF (2001) Polyphenolic content in olive oil waste waters and related olive samples. J Agric Food Chem 49:3509–3514. doi:10.1021/jf000972q
Paredes C, Cegarra J, Roig A, Sánchez-Monedero MA, Bernal MP (1999) Characterization of olive mill wastewater (alpechin) and its sludge for agricultural purposes. Bioresour Technol 67:111–115
Peikert B, Schaumann GE, Keren Y, Bukhanovsky N, Borisover M, Garfha MA, Shoqeric JH, Dag A (2015) Characterization of topsoils subjected to poorly controlled olive oil mill wastewater pollution in West Bank and Israel. Agric Ecosyst Environ 199:176–189
Peltre C, Fernandez JM, Craine JM, Plante AF (2013) Relationships between biological and thermal indices of soil organic matter stability differ with soil organic carbon level. Soil Sci Soc Am J 77:2020–2028
Piotrowska A, Iamarino G, Rao MA, Gianfreda L (2006) Short-term effects of olive mill waste water (OMW) on chemical and biochemical properties of a semiarid Mediterranean soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:600–610
Piotrowska A, Rao MA, Scotti R, Gianfreda L (2011) Changes in soil chemical and biochemical properties following amendment with crude and dephenolized olive mill waste water (OMW). Geoderma 161:8–17
Plante AF, Fernández JM, Leifeld J (2009) Application of thermal analysis techniques in soil science. Geoderma 153:1–10
Plante AF, Fernandez JM, Haddix ML, Steinweg JM, Conant RT (2011) Biological, chemical and thermal indices of soil organic matter stability in four grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1051–1058
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org
Rovira P, Vallejo VR (2000) Examination of thermal and acid hydrolysis procedures in characterization of soil organic matter. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:81–100
Rozzi A, Malpei F (1996) Treatment and disposal of olive mill effluents. Int Biodeter Biodeg 38:135–144
Saadi I, Raviv M, Berkovich S, Hanan A, Aviani I, Laor Y (2013) Fate of soil-applied olive mill wastewater and potential phytotoxicity assessed by two bioassay methods. J Environ Qual 42:1791–1801
Schaumann GE, Borisover M, Nasser A, Bukhanovsky N, Hasan J, Marei Sawalha A (2010) Potential effects of olive oil production waste water on soil quality. Acta Hortic 888:337–344
Schnitzer MIH (1967) Thermogravimetric analysis of the salts and metal complexes of a soil fulvic acid. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 31:7–15
Sierra J, Marti E, Garau MA, Cruanas R (2007) Effects of the agronomic use of olive oil mill wastewater: field experiment. Sci Total Environ 378:90–94
Siewert C (2004) Rapid screening of soil properties using thermogravimetry. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:1656–1661
Simpson MJ, Hatcher PG (2004) Overestimates of black carbon in soils and sediments. Naturwissenschaften 91:436–440
Steinmetz Z, Kurtz MP, Dag A, Zipori I, Schaumann GE (2015) The seasonal influence of olive mill wastewater applications on an orchard soil under semi-arid conditions. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:641–648
Tamimi N, Diehl D, Njoum M, Marei Sawalha A, Schaumann GE (2016) Effects of olive mill wastewater disposal on soil: interaction mechanisms during different seasons. J Hydrol Hydromechan 64:176–195
Trif-Tordai G, Ionel I (2011) Waste biomass as alternative bio-fuel—co-firing versus direct combustion. In: Manzanera M (ed) Alternative fuel. InTech. doi:10.5772/25030
Wang H, Boutton TW, Xu W, Hu G, Jiang P, Bai E (2015) Quality of fresh organic matter affects priming of soil organic matter and substrate utilization patterns of microbes. Scientific Reports 5:10102
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge that this research was conducted within the trilateral project “OLIVEOIL SCHA849/13” funded by German Research Foundation Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zucong Cai
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamimi, N., Schaumann, G.E. & Diehl, D. The fate of organic matter brought into soil by olive mill wastewater application at different seasons. J Soils Sediments 17, 901–916 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1584-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1584-1