Abstract
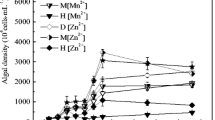
The objective of this study is to select and characterize the candidate for synchronous water purification and lipid production from eight freshwater microalgae strains (Chlorella sp. HQ, C. emersonii, C. pyrenoidosa, C. vulgaris, Scenedesmus dimorphus, S. quadricauda, S. obiquus, Scenedesmus sp. LX1). The strains Chlorella sp. HQ, C. pyrenoidesa, and S. obliquus showed superiority in biomass accumulation, while the top biomass producers did not correspond to the top lipid producers. S. quadricauda achieved higher lipid content (66.1%), and Chlorella sp. HQ and S. dimorphus ranked down in sequence, with lipid content above 30%. Considering nutrient removal ability (total nitrogen (TN): 52.97%; total phosphorus (TP): 84.81%), the newly isolated microalga Chlorella sp. HQ was the possible candidate for water purification coupled with lipid production. To further investigate the lipid producing and nutrient removal mechanism of candidate microalga, the ultra structural changes especially the lipid droplets under different water qualities (different TN and TP concentrations) were characterized. The results elucidate the nutrient-deficiency (TN: 3.0 mg·L–1; TP: 0.3 mg·L–1) condition was in favor of forming lipid bodies in Chlorella sp. HQ at the subcellular level, while the biomass production was inhibited due to the decrease in chloroplast number which could further suppress the nutrient removal effect. Finally, a twophase cultivation process (a nutrient replete phase to produce biomass followed by a nutrient deplete phase to enhance lipid content) was conducted in a photo-bioreactor for Chlorella sp. HQ to serve for algae-based synchronous biodiesel production and wastewater purification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou WG, Li Y C, Min M, Hu B, Zhang H, Ma X C, Li L, Cheng Y, Chen P, Ruan R. Growing wastewater-born microalga Auxenochlorella protothecoides UMN280 on concentrated municipal wastewater for simultaneous nutrient removal and energy feedstock production. Applied Energy, 2012, 98: 433–440
Zhu L D,Wang Z M, Takala J, Hiltumen E, Qin L, Xu Z B. Scale-up potential of cultivating Chlorella zofingiensis in piggerywastewater for biodiesel production. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 137: 318–325
Menger-Krug E, Niederste-Hollenberg J, Hillenbrand T, Hiessl H O, Niederste-Hollenberg J, Hillenbrand T, Hiessl H. Integration of microalgae systems at municipal wastewater treatment plants: implications for energy and emission balances. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(21): 11505–11514
Norainia M Y, Ong H C, Badrul M J, Chong W T. A review on potential enzymatic reaction for biofuel production from algae. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 39: 24–34
Chisti Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnology Advances, 2007, 25(3): 294–306
Tsukahara K, Sawayama S. Liquid fuel production using microalgae. Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 2005, 48(5): 251–259
Schenk P M, Thomas-Hall S R, Stephens E, Marx U C, Mussgnug J H, Posten C, Kruse O, Hankamer B. Second generation biofuels: high-efficiency microalgae for biodiesel production. BioEnergy Research, 2008, 1(1): 20–43
Río E D, Armendáriz A, García-Gómez E, García-González M, GuerreroMG. Continuous culture methodology for the screening of microalgae for oil. Journal of Biotechnology, 2015, 195: 103–107
Richmond A. Handbook of Microalgal Culture: Biotechnology and Applied Phycology. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, 2004
Li L, Cui J, Liu Q, Ding Y C, Liu J G. Screening and phylogenetic analysis of lipid-rich microalgae. Algal Research, 2015
Wu Y H, Hu H Y, Yu Y, Zhang T Y, Zhu S F, Zhuang L L, Zhang X, Lu Y. Microalgal species for sustainable biomass/lipid production using wastewater as resource: a review. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 33: 675–688
Yang J, Li X, Hu H Y, Zhang X, Yu Y, Chen Y S. Growth and lipid accumulation properties of a freshwater microalga, Chlorella ellipsoideas YJ1, in domestic secondary effluents. Applied Energy, 2011, 88(10): 3295–3299
Abreu A P, Fernandes B, Vicente A A, Teixeira J, Dragone G. Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris using industrial dairy waste as organic carbon source. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 118: 61–66
Ren H Y, Liu B F, Kong F, Zhao L, Xie G J, Ren N Q. Enhanced lipid accumulation of green microalga Scenedesmus sp. by metal ions and EDTA addition. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 169: 763–767
Zhang Q, Hong Y. Effects of stationary phase elongation and initial nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth and lipid-producing potential of Chlorella sp. HQ. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2014, 26(1): 141–149
State Environmental Protection Administration. Monitoring Method of Water and Wastewater. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002
Mata T M, Martins A A, Caetano N S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2010, 14(1): 217–232
Wu H Q, Miao X L. Biodiesel quality and biochemical changes of microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus in response to nitrate levels. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 170: 421–427
Zhu S N, Huang W, Xu J, Wang Z M, Xu J L, Yuan Z H. Metabolic changes of starch and lipid triggered by nitrogen starvation in the microalga Chlorella zofingiensis. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 152: 292–298
Zhang Q, Hong Y. Comparison of growth and lipid accumulation properties of two oleaginous microalgae under different nutrient conditions. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2014, 8(5): 703–709
Su Y A, Mennerich A, Urban B. Comparison of nutrient removal capacity and biomass settleability of four high-potential microalgal species. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 124: 157–162
Wang B, Li Y Q, Wu N, Lan C Q. CO2 bio-mitigation using microalgae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2008, 79(5): 707–718
Wijffels R H, Barbosa M J. An outlook on microalgal biofuels. Science, 2010, 329(5993): 796–799
Nascimento I A, Marques S S I, Cabanelas I T D, Pereira S A, Druzian J I, de Souza C O, Vich D V, de Carvalho G C, Nascimento M A. Screening microalgae strains for biodiesel production: lipid productivity and estimation of fuel quality based on fatty acids profiles as selective criteria. BioEnergy Research, 2013, 6(1): 1–13
Griffiths M J, Harrison S T L. Lipid productivity as a key characteristic for choosing algal species for biodiesel production. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2009, 21(5): 493–507
Williams P J B, Laurens L M L
Laurens LML. Microalgae as biodiesel and biomass feedstocks: review and analysis of the biochemistry, energetics and economics. Energy & Environmental Science, 2010, 3(5): 554–590
Zhao G L, Yu J Y, Jiang F F, Zhang X, Tan T W. The effect of different trophic modes on lipid accumulation of Scenedesmus quadricauda. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 114: 466–471
Heraud P, Wood B R, Tobin M J, Beardall J, McNaughton D. Mapping of nutrient-induced biochemical changes in living algalcells using synchrotron infrared microspectroscopy. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2005, 249(2): 219–225
Johnson D A. Ultrastructural and flow cytometric analyses of lipid accumulation in microalgae. Solar Energy Research Institute 1986
Hu Q, Sommerfeld M, Jarvis E, Ghirardi M, Posewitz M, Seibert M, Darzins A. Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances. Plant Journal, 2008, 54(4): 621–639
Sun X, Cao Y, Xu H, Liu Y, Sun J R, Qiao D R, Cao Y. Effect of nitrogen-starvation, light intensity and iron on triacylglyceride/ carbohydrate production and fatty acid profile of Neochloris oleoabundans HK-129 by a two-stage process. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 155: 204–212
Ho S H, Ye X T, Hasunuma T, Chang J S, Kondo A. Perspectives on engineering strategies for improving biofuel production from microalgae—A critical review. Biotechnology Advances, 2014, 32 (8): 1448–1459
Hernandez J P, de-Bashan L E, Bashan Y. Starvation enhances phosphorus removal from wastewater by the microalga Chlorella spp. co-immobilized with Azospirillum brasilense. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2006, 38(1–2): 190–198
Sydney E B, da Silva T E, Tokarski A, Novak A C, de Carvalho J C, Woiciecohwski A L, Larroche C, Soccol C R. Screening of microalgae with potential for biodiesel production and nutrient removal from treated domestic sewage. Applied Energy, 2011, 88 (10): 3291–3294
Li Y C, ZhouWG, Hu B, Min M, Chen P, Ruan R R. Integration of algae cultivation as biodiesel production feedstock with municipal wastewater treatment: strains screening and significance evaluation of environmental factors. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(23): 10861–10867
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, J., Zhang, Q., Qin, M. et al. Selection and characterization of eight freshwater green algae strains for synchronous water purification and lipid production. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 10, 548–558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-016-0831-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-016-0831-4