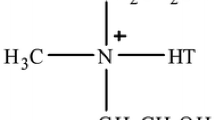Abstract
Polymeric nanocomposites, which are hybrids of polymers and modified inorganic clay with organic surfactants, are extremely attractive in both science and industry. These materials present improvements in such polymer properties as modulus, heat capacity, thermal stability, flame resistance, and so on. Research has been conducted in recent decades to obtain high-quality materials that can be used in applications like food packing, car components, and combustible cells. Polymeric nanocomposites present many advantages in relation to composites due to the quantity of filler added to the polymer and also to the improved properties. In a composite, the quantity of filler must be as high as possible (i.e., over 30%). In the polymeric nanocomposite the quantity of filler varies from 1% to 5% because of the nanosize of the particles. These nanoparticles often have a large surface area that results in improved polymer-matrix properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.C. Rodrigues, M.I.B. Tavares, and V.J.R.R. Pita, Macromol. Symp., 245 (2007), p. 166.
D. Bikiaris et al., Pol. Deg. and Stab., 59 (1998), p. 287.
M.Z. Rong et al., J. Mater. Sci. Lett, 19 (2000), p. 1159.
M.Z. Rong et al., Polym. Commun., 42 (2001), p. 3301.
M.Z. Rong et al., Polymer, 42 (2001), p. 167.
H. Qin et al., Polymer Degradation and Stability, 81 (2003), p. 497.
J.M. Garces et al., Advanced Mater., 12 (2000), p. 1835.
Y. Kurokawa et al., J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 16 (1997), p. 1670.
Y. Kurokawa, H. Yasuda, and A. Oya, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 15 (1996), p. 1481.
F.A. Bovey and P.A. Mirau, NMR of Polymers (New York: Academic Press, 1996), pp. 11–19.
R.A. Komoroski, High Resolution NMR Spectroscopy of Synthetic Polymers in Bulk (Deerfield Beach, FL: VCH Publishers, 1986), pp. 118–136.
J.K.M. Sandres and B.K. Hunter, Modern NMR Spectroscopy, A Guide of Chemists, 2nd edition (Oxford, U.K.: Oxford University Press, 1996), pp. 21–23.
P.T. Callaghan, Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy (New York: Oxford University Press, Inc., 1991), pp. 135–140.
D.L. Vanderhart, A. Asano, and J.W. Gilman, Chemistry of Materials, 13 (2001), pp. 3796–3809.
S. Hotta and D.R. Paul, Polymer, 45 (2004), p. 7639.
M.A. Osman, J.E.R. Rupp, and U.W. Suter, Polymer, 46 (2005), p. 8202.
M. Alexandre and P. Dubois, Materials Science and Engineering, 28 (2000), pp. 1–63.
P.C. Le Baron, Z. Wang, and T.J. Pinnavaia, Applied Clay Science, 15 (1999), pp. 11–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, T.C., Tavares, M.I.B., Soares, I.L. et al. The characterization of high-density polyethylene/organoclay nanocomposites. JOM 61, 38–41 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-009-0006-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-009-0006-x