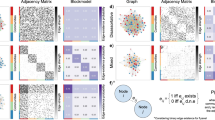
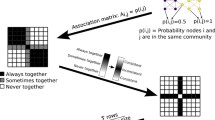
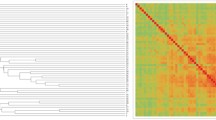
Abstract
The anatomical architecture of the mammalian brain can be modeled as the connectivity between functionally distinct areas of cortex and sub-cortex, which we refer to as the connectome. The community structure of the connectome describes how the network can be parsed into meaningful groups of nodes. This process, called community detection, is commonly carried out to find internally densely connected communities—a modular topology. However, other community structure patterns are possible. Here we employ the weighted stochastic block model (WSBM), which can identify a wide range of topologies, to the rat cerebral cortex connectome, to probe the network for evidence of modular, core, periphery, and disassortative organization. Despite its algorithmic flexibility, the WSBM identifies substantial modular and assortative topology throughout the rat cerebral cortex connectome, significantly aligning to the modular approach in some parts of the network. Significant deviations from modular partitions include the identification of communities that are highly enriched in core (rich club) areas. A comparison of the WSBM and modular models demonstrates that the former, when applied as a generative model, more closely captures several nodal network attributes. An analysis of variation across an ensemble of partitions reveals that certain parts of the network participate in multiple topological regimes. Overall, our findings demonstrate the potential benefits of adopting the WSBM, which can be applied to a single weighted and directed matrix such as the rat cerebral cortex connectome, to identify community structure with a broad definition that transcends the common modular approach.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aicher C, Jacobs AZ, Clauset A (2013) Adapting the stochastic block model to edge-weighted networks. arXiv:1305.5782
Aicher C, Jacobs AZ, Clauset A (2014) Learning latent block structure in weighted networks. J Complex Netw 3(2):221–248
Airoldi EM, Blei DM, Fienberg SE, Xing EP (2008) Mixed membership stochastic blockmodels. J Mach Learn Res 9:1981–2014
Akiki TJ, Abdallah CG (2019) Determining the hierarchical architecture of the human brain using subject-level clustering of functional networks. https://doi.org/10.1101/350462
Alexander-Bloch A, Lambiotte R, Roberts B, Giedd J, Gogtay N, Bullmore E (2012) The discovery of population differences in network community structure: new methods and applications to brain functional networks in schizophrenia. NeuroImage 59(4):3889–3900
Bassett DS, Sporns O (2017) Network neuroscience. Nat Neurosci 20(3):353–364
Bassett DS, Greenfield DL, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR, Moore SW, Bullmore ET (2010) Efficient physical embedding of topologically complex information processing networks in brains and computer circuits. PLoS Comput Biol 6(4):e1000748
Battiston F, Guillon J, Chavez M, Latora V, De Vico Fallani F (2018) Multiplex core–periphery organization of the human connectome. J R Soc Interface 15(146):20180514
Baum GL, Ciric R, Roalf DR, Betzel RF, Moore TM, Shinohara RT et al (2017) Modular segregation of structural brain networks supports the development of executive function in youth. Curr Biol 27(11):1561–1572
Betzel RF, Bassett DS (2017) Multi-scale brain networks. Neuroimage 160:73–83
Betzel RF, Avena-Koenigsberger A, Goni J, He Y, de Reus MA, Griffa A, Sporns O (2016) Generative models of the human connectome. Neuroimage 124(Pt A):1054–1064
Betzel RF, Medaglia JD, Papadopoulos L, Baum GL, Gur R, Gur R, Bassett DS (2017) The modular organization of human anatomical brain networks: accounting for the cost of wiring. Netw Neurosci 1(1):42–68
Betzel RF, Medaglia JD, Bassett DS (2018) Diversity of meso-scale architecture in human and non-human connectomes. Nat Commun 9(1):346
Betzel RF, Bertolero MA, Gordon EM, Gratton C, Dosenbach NUF, Bassett DS (2019) The community structure of functional brain networks exhibits scale-specific patterns of inter- and intra-subject variability. NeuroImage 202:115990
Blondel VD, Guillaume J-L, Lambiotte R, Lefebvre E (2008) Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J Stat Mech Theory Exp 10:P10008
Bota M, Swanson LW (2007) Online workbenches for neural network connections. J Comp Neurol 500(5):807–814
Bota M, Sporns O, Swanson LW (2015) Architecture of the cerebral cortical association connectome underlying cognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(16):E2093–E2101
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2012) The economy of brain network organization. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(5):336–349
Chen M, Nguyen T, Szymanski BK (2013) On measuring the quality of a network community structure. In: 2013 international conference on social computing. IEEE, pp 122–127
Contreras JA, Avena-Koenigsberger A, Risacher SL, West JD, Tallman E, McDonald BC et al (2019) Resting state network modularity along the prodromal late onset Alzheimer’s disease continuum. NeuroImage 22:101687
Crossley NA, Mechelli A, Vértes PE, Winton-Brown TT, Patel AX, Ginestet CE, Bullmore ET (2013) Cognitive relevance of the community structure of the human brain functional coactivation network. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(28):11583–11588
Faskowitz J, Yan X, Zuo X-N, Sporns O (2018) Weighted stochastic block models of the human connectome across the life span. Sci Rep 8(1):12997
Fortunato S, Barthelemy M (2007) Resolution limit in community detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(1):36–41
Fortunato S, Hric D (2016) Community detection in networks: a user guide. Phys Rep-Rev Sect Phys Lett 659:1–44
Good BH, de Montjoye Y-A, Clauset A (2010) Performance of modularity maximization in practical contexts. Phys Rev E 81(4):046106
Harriger L, van den Heuvel MP, Sporns O (2012) Rich club organization of macaque cerebral cortex and its role in network communication. PLoS One 7(9):e46497
He Y, Lim S, Fortunato S, Sporns O, Zhang L, Qiu J, Zuo XN (2018) Reconfiguration of cortical networks in MDD uncovered by multiscale community detection with fMRI. Cereb Cortex 28(4):1383–1395
Holland PW, Laskey KB, Leinhardt S (1983) Stochastic blockmodels: first steps. Soc Netw 5(2):109–137
Hric D, Peixoto TP, Fortunato S (2016) Network structure, metadata, and the prediction of missing nodes and annotations. Phys Rev X 6(3):031038
Jeub LG, Sporns O, Fortunato S (2018) Multiresolution consensus clustering in networks. Sci Rep 8(1):3259
Karrer B, Newman ME (2011) Stochastic blockmodels and community structure in networks. Phys Rev E 83(1 Pt 2):016107
Kurmukov A, Ananyeva M, Dodonova Y, Gutman B, Faskowitz J, Jahanshad N, Zhukov L (2017) Classifying phenotypes based on the community structure of human brain networks. In: Graphs in biomedical image analysis, computational anatomy and imaging genetics. Springer, Cham, pp 3–11
Kurmukov A, Musabaeva A, Denisova Y, Moyer D, Gutman B (2018) Connectivity-driven brain parcellation via consensus clustering. In: Connectomics in neuroimaging. Springer, Cham, pp 117–126
Kwak H, Choi Y, Eom Y-H, Jeong H, Moon S (2009) Mining communities in networks: a solution for consistency and its evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGCOMM conference on Internet measurement conference. ACM, pp 301–314
Lancichinetti A, Fortunato S (2012) Consensus clustering in complex networks. Sci Rep 2:336
Meilă M (2007) Comparing clusterings—an information based distance. J Multivar Anal 98(5):873–895
Meunier D, Achard S, Morcom A, Bullmore E (2009) Age-related changes in modular organization of human brain functional networks. Neuroimage 44(3):715–723
Moyer D, Gutman B, Prasad G, Faskowitz J, Ver Steeg G, Thompson P (2015a) Blockmodels for connectome analysis. 11th International Symposium on Medical Information Processing and Analysis (SIPAIM 2015): 96810A-96810A-96819
Moyer D, Gutman B, Prasad G, Ver Steeg G, Thompson P (2015b) Mixed membership stochastic blockmodels for the human connectome. In: MICCAI–workshop on bayesian and graphical models for biomedical imaging
Munkres J (1957) Algorithms for the assignment and transportation problems. J Soc Ind Appl Math 5(1):32–38
Najafi M, McMenamin BW, Simon JZ, Pessoa L (2016) Overlapping communities reveal rich structure in large-scale brain networks during rest and task conditions. NeuroImage 135:92–106
Newman ME (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(23):8577–8582
Noori HR, Schöttler J, Ercsey-Ravasz M, Cosa-Linan A, Varga M, Toroczkai Z, Spanagel R (2017) A multiscale cerebral neurochemical connectome of the rat brain. PLoS Biol 15(7):e2002612
Park H-J, Friston K (2013) Structural and functional brain networks: from connections to cognition. Science 342(6158):1238411
Pavlovic DM, Vertes PE, Bullmore ET, Schafer WR, Nichols TE (2014) Stochastic blockmodeling of the modules and core of the Caenorhabditis elegans connectome. PLoS One 9(7):e97584
Peel L, Larremore DB, Clauset A (2017) The ground truth about metadata and community detection in networks. Sci Adv 3(5):e1602548
Peixoto TP (2018) Nonparametric weighted stochastic block models. Phys Rev E 97(1–1):012306
Rubinov M, Sporns O (2010) Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 52(3):1059–1069
Rubinov M, Ypma RJ, Watson C, Bullmore ET (2015) Wiring cost and topological participation of the mouse brain connectome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(32):10032–10037
Schaub MT, Delvenne J-C, Rosvall M, Lambiotte R (2017) The many facets of community detection in complex networks. Appl Netw Sci 2(1):4
Schmitt O, Eipert P (2012) neuroVIISAS: approaching multiscale simulation of the rat connectome. Neuroinformatics 10(3):243–267
Shih C-T, Sporns O, Yuan S-L, Su T-S, Lin Y-J, Chuang C-C, Chiang A-S (2015) Connectomics-based analysis of information flow in the drosophila brain. Curr Biol 25(10):1249–1258
Shinn M, Romero-Garcia R, Seidlitz J, Váša F, Vértes PE, Bullmore E (2017) Versatility of nodal affiliation to communities. Sci Rep 7(1):4273
Sohn Y, Choi MK, Ahn YY, Lee J, Jeong J (2011) Topological cluster analysis reveals the systemic organization of the Caenorhabditis elegans connectome. PLoS Comput Biol 7(5):e1001139
Sporns O (2011) The human connectome: a complex network. Ann NY Acad Sci 1224(1):109–125
Sporns O (2013) Making sense of brain network data. Nat Methods 10(6):491–493
Sporns O, Betzel RF (2016) Modular Brain Networks. Annu Rev Psychol 67:613–640
Sporns O, Tononi G, Kötter R (2005) The human connectome: a structural description of the human brain. PLoS Comput Biol 1(4):e42
Swanson LW, Sporns O, Hahn JD (2016) Network architecture of the cerebral nuclei (basal ganglia) association and commissural connectome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(40):E5972–E5981
Swanson LW, Hahn JD, Sporns O (2017) Organizing principles for the cerebral cortex network of commissural and association connections. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(45):E9692–E9701
Swanson LW, Hahn JD, Jeub LGS, Fortunato S, Sporns O (2018) Subsystem organization of axonal connections within and between the right and left cerebral cortex and cerebral nuclei (endbrain). Proc Natl Acad Sci 115(29):E6910–E6919
Swanson LW, Sporns O, Hahn JD (2019) The network organization of rat intrathalamic macroconnections and a comparison with other forebrain divisions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(27):13661–13669
Tunç B, Verma R (2015) Unifying inference of meso-scale structures in networks. PLoS One 10(11):e0143133
van den Heuvel MP, Scholtens LH, de Reus MA (2016) Topological organization of connectivity strength in the rat connectome. Brain Struct Funct 221(3):1719–1736
Xiaoran Y, Cosma S, Jacob EJ, Florent K, Cristopher M, Lenka Z, Yaojia Z (2014) Model selection for degree-corrected block models. J Stat Mech 2014(5):P05007
Yeh F-C, Panesar S, Fernandes D, Meola A, Yoshino M, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Verstynen T (2018) Population-averaged atlas of the macroscale human structural connectome and its network topology. NeuroImage 178:57–68
Zhao T, Cao M, Niu H, Zuo X-N, Evans A, He Y, Shu N (2015) Age-related changes in the topological organization of the white matter structural connectome across the human lifespan. Hum Brain Mapp 36(10):3777–3792
Zingg B, Hintiryan H, Gou L, Song MY, Bay M, Bienkowski MS, Toga AW (2014) Neural networks of the mouse neocortex. Cell 156(5):1096–1111
Acknowledgements
O.S. acknowledges funding support by the National Institutes of Health (R01 AT009036-01 and R01 MH122957-01). This material is based on the work supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship under Grant No. 1342962 (J.F.). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. Supercomputing was supported in part by Lilly Endowment, Inc., through its support for the Indiana University Pervasive Technology Institute, and in part by the Indiana METACyt Initiative. The Indiana METACyt Initiative at IU was also supported in part by Lilly Endowment, Inc. We would like to thank Christopher Aicher and Aaron Clauset for implementing and hosting the WSBM code package.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faskowitz, J., Sporns, O. Mapping the community structure of the rat cerebral cortex with weighted stochastic block modeling. Brain Struct Funct 225, 71–84 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01984-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01984-9